Abstract
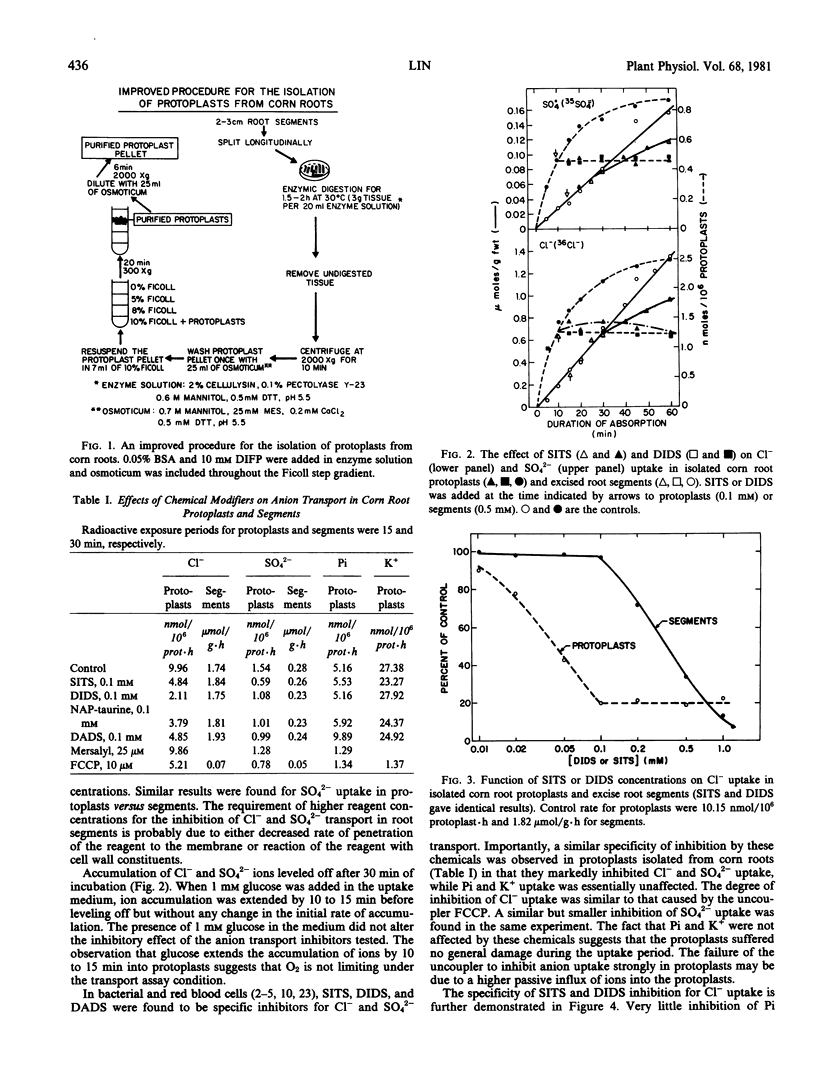
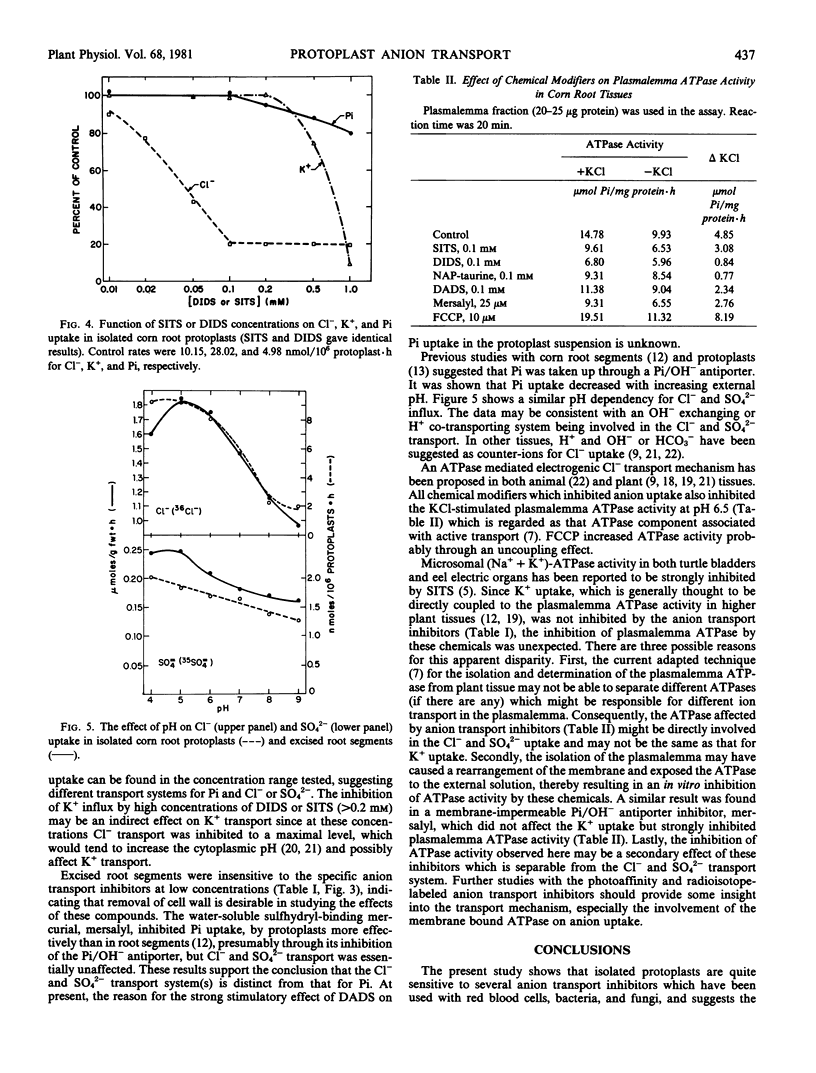
The effects of several amino-reactive disulfonic stilbene derivatives and N-(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)-2-aminoethylsulfonate on Cl−, SO42−, and inorganic phosphate (Pi) uptake in protoplasts isolated from corn root tissue were studied. 4-Acetamido-4′-isothiocyano-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid, 4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid, 4,4′-diamino-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid, and NAP-taurine inhibited Cl− and SO42− but not Pi and K+ uptake in corn root protoplasts; whereas mersalyl inhibited Pi but not Cl− or SO42− uptake. The rate of uptake of all anions decreased with increasing external pH. In addition, these reagents markedly inhibited plasmalemma ATPase activity isolated from corn root tissue. Excised root segments were less sensitive to Cl− and SO42− transport inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boos W. Bacterial transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):123–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. I. Localization of disulfonic stilbene binding sites in proteins involved in permeation. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):207–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. II. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on disulfonic stilbene sites of surface proteins. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):227–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01870089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives. J Membr Biol. 1972 Dec 29;10(3):311–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01867863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenspeck G., Brodsky W. A. Effects of 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyano-2,2-disulfonic stilbene on ion transport in turtle bladders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):555–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerin M., Napias C. Phosphate transport in yeast mitochondria: purification and characterization of a mitoribosomal synthesis dependent proteolipid showing a high affinity for phosphate. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2510–2516. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T. Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:392–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L., Passow H. Anion transport across the erythrocyte membrane, in situ proteolysis of band 3 protein, and cross-linking of proteolytic fragments by 4,4'-diisothiocyano dihydrostilbene-2,2'-disulfonate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):498–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepke S., Fasold H., Pring M., Passow H. A study of the relationship between inhibition of anion exchange and binding to the red blood cell membrane of 4,4'-diisothiocyano stilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid (DIDS) and its dihydro derivative (H2DIDS). J Membr Biol. 1976 Oct 20;29(1-2):147–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01868957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. Corn Root Protoplasts: ISOLATION AND GENERAL CHARACTERIZATION OF ION TRANSPORT . Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):550–554. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Hanson J. B. Phosphate absorption rates and adenosine 5'-triphosphate concentrations in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):250–256. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. Potassium and Phosphate Uptake in Corn Roots: Further Evidence for an Electrogenic H/K Exchanger and an OH/Pi Antiporter. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):952–955. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Wittenbach V. A. Subcellular localization of proteases in wheat and corn mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):969–972. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passow H., Fasold H., Lepke S., Pring M., Schuhmann B. Chemical and enzymatic modification of membrane proteins and anion transport in human red blood cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;84:353–379. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3279-4_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petraglia T., Poole R. J. ATP Levels and their Effects on Plasmalemma Influxes of Potassium Chloride in Red Beet. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):969–972. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae A. S., Strickland K. P., Medveczky N., Rosenberg H. Studies of phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. I. Reexamination of the effect of osmotic and cold shock on phosphate uptake and some attempts to restore uptake with phosphate binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. M., Boron W. F. Role of choloride transport in regulation of intracellular pH. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):73–74. doi: 10.1038/264073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Richards F. M. Photochemical labeling of the surface proteins of human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 18;13(13):2720–2726. doi: 10.1021/bi00710a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


