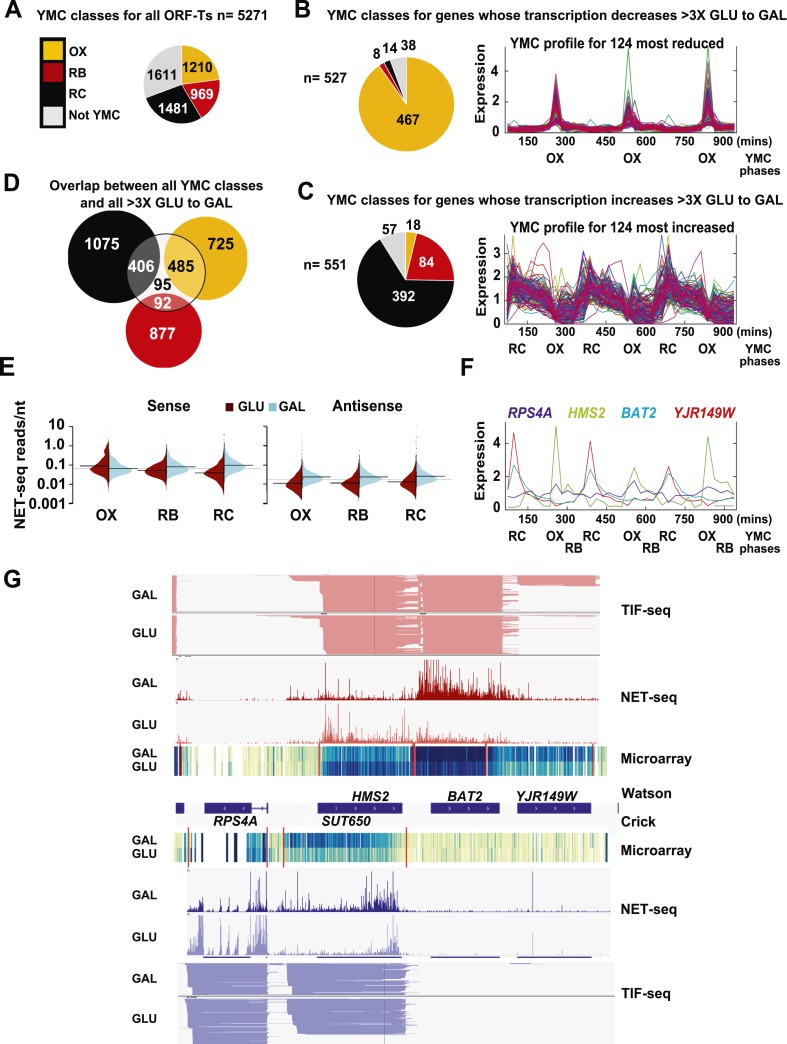
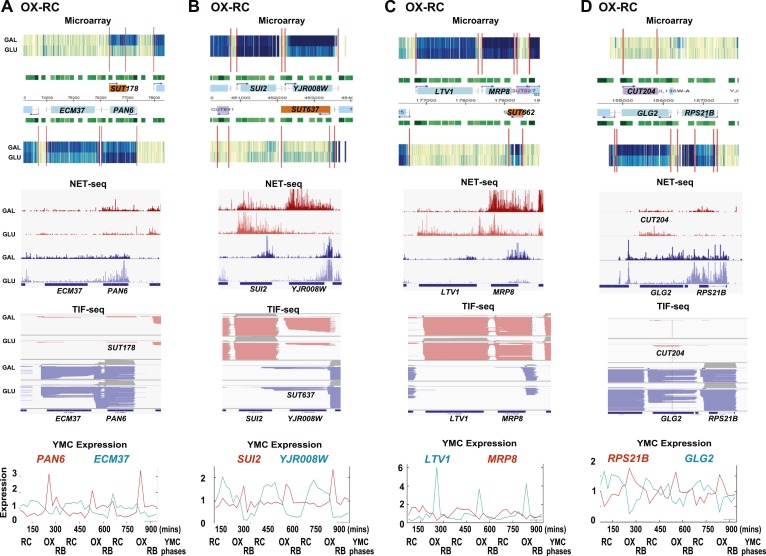
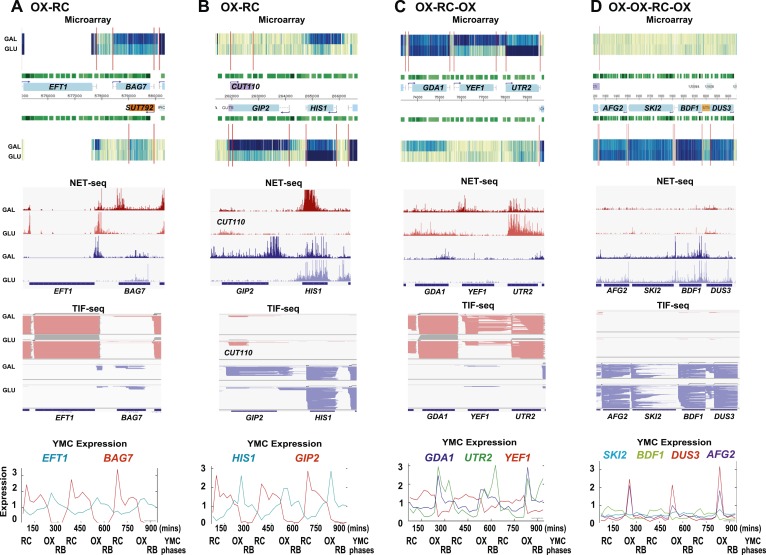
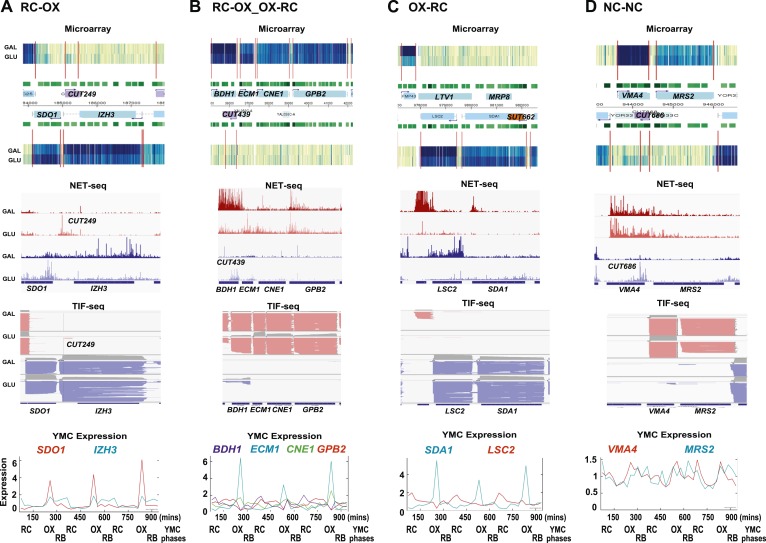
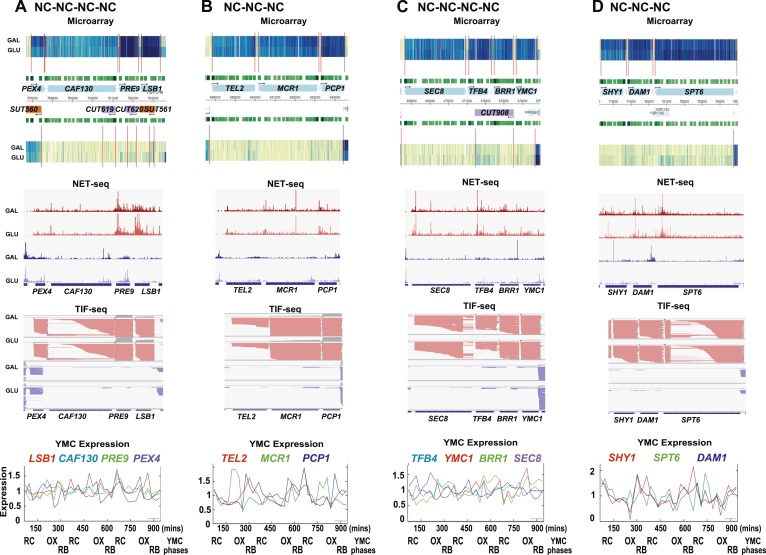
Figure 1. Reciprocal switching of expression by carbon source reveals links to the YMC.
(A) The distribution of all ORF-Ts into different YMC phases. OX, oxidative phase; RB, reductive building phase; RC, reductive charging phase of the YMC. (B, C, F) YMC profiles (SCEPTRANS; http://moment.utmb.edu/cgi-bin/main_cc.cgi) (Kudlicki et al., 2007) showing cycling expression at 124 genes with the (B) most reduced and (C) most increased transcription (NET-seq) after a switch from glucose (GLU) to galactose (GAL) for 3 h and (F) at the HMS2:BAT2 locus. (D) Overlap between all YMC classes and all ORF-Ts showing >threefold change in transcription on the GLU to GAL shift. (E) NET-seq reads on sense or antisense strands genome-wide in GLU (red) or GAL (blue) for ORF-Ts with peak expression in phases of the YMC indicated. (G) Strand-specific TIF-seq (Pelechano et al., 2013), microarray and NET-seq data at the HMS2:BAT2 locus. Profiles from cells cultured in GLU or GAL on the Watson strand (top) or Crick strand (bottom) are shown. The TIF-seq data indicate each different transcript isoform, microarray data indicate levels of steady-state poly(A)+ RNA (blue—darker colour for more RNA) and the NET-seq data (normalized, unique, and clipped to 3′OH) display transcript reads (scale 0–30) associated with elongating RNAPII. Screen shots are displayed using IGV (Robinson et al., 2011; Thorvaldsdottir et al., 2013).