Abstract
Objectives
To identify barriers that are common and unique to six selected vulnerable groups: low socioeconomic status; Indigenous; mental illness and substance abuse; homeless; prisoners; and at-risk youth.
Design
A systematic review was carried out to identify the perceived barriers to smoking cessation within six vulnerable groups.
Data sources
MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL and PsycInfo were searched using keywords and MeSH terms from each database's inception published prior to March 2014.
Study selection
Studies that provided either qualitative or quantitative (ie, longitudinal, cross-sectional or cohort surveys) descriptions of self-reported perceived barriers to quitting smoking in one of the six aforementioned vulnerable groups were included.
Data extraction
Two authors independently assessed studies for inclusion and extracted data.
Results
65 eligible papers were identified: 24 with low socioeconomic groups, 16 with Indigenous groups, 18 involving people with a mental illness, 3 with homeless groups, 2 involving prisoners and 1 involving at-risk youth. One study identified was carried out with participants who were homeless and addicted to alcohol and/or other drugs. Barriers common to all vulnerable groups included: smoking for stress management, lack of support from health and other service providers, and the high prevalence and acceptability of smoking in vulnerable communities. Unique barriers were identified for people with a mental illness (eg, maintenance of mental health), Indigenous groups (eg, cultural and historical norms), prisoners (eg, living conditions), people who are homeless (eg, competing priorities) and at-risk youth (eg, high accessibility of tobacco).
Conclusions
Vulnerable groups experience common barriers to smoking cessation, in addition to barriers that are unique to specific vulnerable groups. Individual-level, community-level and social network-level interventions are priority areas for future smoking cessation interventions within vulnerable groups.
Trial registration number:
A protocol for this review has been registered with PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (Identifier: CRD42013005761).
Keywords: barriers, vulnerable populations, review, smoking cessation, disadvantage
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This study provides a valuable synthesis of the literature examining the perceived barriers to smoking cessation common and unique across six vulnerable groups.
The comparison between vulnerable groups allowed for the identification of common barriers shared across vulnerable groups that are modifiable through short term public health behaviour change strategies.
While the overall quality of the studies included in this review was acceptable, most studies failed to provide information regarding the trustworthiness (qualitative studies) or reliability and validity (quantitative studies) of the research.
Introduction
Tobacco use is the leading global cause of avoidable death worldwide1 and a key modifiable risk factor for the development of a range of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and some cancers.1
The prevalence of tobacco smoking is inversely related to socioeconomic position (SEP) in high-income countries.1 For example, in 2010 in Australia, the prevalence of smoking was 24.6% in the lowest socioeconomic areas compared with 12.5% in the highest socioeconomic areas.2 The highest rates of smoking are evident among those who, in addition to low socioeconomic status, have other characteristics that distinguish them from the general population such as Indigenous groups (31–51.8%);3–5 people with a mental illness (31.7–32.4%),6 those with substance abuse disorders (77%);7 the homeless (73%);8 and prisoners (78–84%).9 10 These groups were selected because they represent a large proportion of those classified as vulnerable to socioeconomic disadvantage.11 It should be noted that although members of vulnerable groups are more likely to be socioeconomically disadvantaged, not all members are. For the purposes of this review, vulnerable groups are defined as groups that are more likely to experience social and material disadvantage due to lower income, cultural differences and social exclusion.12
Conflicting evidence exists regarding whether the rates of quit attempts in low SEPs are similar to13 14 or lower15–18 than the rates made by smokers in higher SEPs. However, the success rate of quit attempts for lower SEP individuals is much lower than the success rate in their higher SEP counterparts.14 19
There are many reasons quit success may be lower in vulnerable groups.20 21 Within the health behaviour literature, factors that prevent an individual from undertaking health behaviour change have been referred to as barriers. Barriers are often conceptualised as either structural or individual psychosocial factors.22 Structural barriers include systems, organisations and the relationship between systems and individuals, for example, lack of accessible smoking cessation programmes. Individual barriers refer to the subjective experience of the individual, for example, physical addiction to nicotine.
This definition of barriers is congruent with the social determinants of health framework (SDHF).23 The SDHF holds that an individual's health is influenced by factors across many levels, from individual genetic and physical characteristics, social and community networks, to broader influences of culture, socioeconomic determinants and the environment. This framework has been used to examine the determinants of health inequities.24 Because the SDHF classifies determinants of health as individual, social, and broader cultural and environmental factors, it also allows the identification of distinct levels of intervention for health policies.
Within the general population, cross-sectional studies have found variation in the most commonly reported barriers to cessation. Enjoyment (79%);25 cravings (75%);25 and stress management (36–63%)25 26 are the most frequently reported barriers. Irritability (39–42%);27 habit (39%);26 withdrawal symptoms (28–48%);25 26 fear of failure (17–32%);25 26 and concern about weight gain (27–34%)25–27 are also identified as barriers to cessation.
The effect of SEP on perceived barriers to quitting was examined in a representative sample (n=2133) in the UK.28 Enjoyment (51%) and stress relief (47%) were the most frequently endorsed motives for continuing to smoke across the sample; however, as SEP decreased, the likelihood of reporting stress management and avoiding boredom as motives to continue to smoke increased. This suggests that smokers from vulnerable groups may experience barriers to smoking cessation differently than those in the general population.28
Smoking in vulnerable groups is known to be influenced and perpetuated by a complex range of social, cultural and environmental factors,29 including high acceptability of smoking30 and more tobacco retail outlets in low socioeconomic areas.31 Two previous studies have reviewed the literature to examine barriers to quitting smoking among vulnerable groups. One focused on Aboriginal pregnant women,32 and one focused on the barriers to smoking cessation service utilisation among low-income smokers.33 Both reviews found that pro-smoking social norms, inadequate knowledge regarding smoking-related risks and lack of access to appropriate cessation services inhibited participants’ ability to quit.
As the term ‘vulnerable’ applies to multiple discrete groups, it is important to understand which barriers (if any) are unique, for example, cultural factors that inhibit smoking cessation may be unique to some Indigenous groups.32 A systematic examination of potential unique barriers would be valuable in order to develop and deliver appropriate suites of intervention techniques for specific vulnerable groups.
Understanding the perceived barriers to quitting is important in order to better understand smoking, relapse and quitting-related behaviours, to inform appropriate policy, and to facilitate the development of effective tailored smoking cessation interventions. Given the exceptionally high smoking rates and low quit success among vulnerable groups, there is a critical need for a systematic and comprehensive review of the literature of the perceived barriers to quitting smoking among vulnerable smokers.
Aims
This systematic review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of the self-reported barriers to quitting smoking within six vulnerable groups by reviewing the qualitative and quantitative literature. The review will focus on the perceived, self-reported barriers to smoking cessation in six selected vulnerable groups: low socioeconomic status (low SES); Indigenous; mental illness and substance abuse; homeless; prisoners; and at-risk youth. These groups were selected because they represent a large proportion of those classified as vulnerable to socioeconomic disadvantage;11 who exhibit smoking rates higher than those of the general population;2–10 and who are identified as priority groups targeted for smoking cessation programmes and policies by peak health authorities.34–36 Specifically, the review aims to:
Identify barriers that are common across all vulnerable groups included in the review; and
Identify barriers that may be unique to specific groups.
The results of the review will be used to develop a practical model to help understand the barriers to quitting among vulnerable groups and to aid smoking cessation intervention development.
Method
Study design
Guidelines for the reporting of systematic reviews (PRISMA)37 and qualitative synthesis (ENTREQ)38 were followed. A protocol for this review was registered with PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (Identifier: CRD42013005761).
Databases and search
MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL and PsycInfo were searched using keywords and MeSH terms from each database's inception published prior to March 2014. The reference lists of key articles and reviews were also manually searched in order to identify any other relevant articles. An extensive list of search terms was used in order to ensure that as many relevant articles as possible were captured (see table 1).
Table 1.
Search strategy
| 1 | Tobacco/ |
| 2 | Tobacco use/ |
| 3 | Tobacco use cessation/ |
| 4 | Tobacco smoking/ |
| 5 | Smoking/ |
| 6 | Smoking Cessation/ |
| 7 | Tobacco use cessation/ |
| 8 | Tobacco dependence/ |
| 9 | Cigarette smoking/ |
| 10 | Or/1–9 |
| 11 | Homeless youth/ |
| 12 | Homeless persons/ |
| 13 | Housing/ |
| 14 | Homeless mentally ill/ |
| 15 | Homelessness or homeless/ |
| 16 | Community programs/ |
| 17 | Or/11–16 |
| 18 | Prisoner or Prisons/ |
| 19 | Correctional Health Services/ |
| 20 | Correctional facilities/ |
| 21 | Jail/ |
| 22 | Or/18–21 |
| 23 | Anxiety/ |
| 24 | Depression/ |
| 25 | Schizophrenia/ |
| 26 | Mentally Ill persons/ |
| 27 | Mental health/ |
| 28 | Mental illness/ |
| 29 | Mental disorder/ |
| 30 | Mental disease/ |
| 31 | Mental patient/ |
| 32 | Mental health services/ |
| 33 | Substance-related disorders/ |
| 34 | Drug use/ |
| 35 | Drug abuse/ |
| 36 | Alcohol-related disorders/ |
| 37 | Or/23–36 |
| 38 | Adolescent behaviour/ |
| 39 | Juvenile delinquency/ |
| 40 | Juvenile offenders/ |
| 41 | Disruptive Behaviors or disruptive behaviours/ |
| 42 | At-risk youth/ |
| 43 | At-risk young people/ |
| 44 | Or/38–43 |
| 45 | Indigenous/ |
| 46 | Indigenous health/ |
| 47 | Indigenous peoples/ |
| 48 | Indigenous populations/ |
| 49 | Aboriginal/ |
| 50 | Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders/ |
| 51 | Inuits/ |
| 52 | Eskimo/ |
| 53 | Alaska Native/ |
| 54 | Indians/ |
| 55 | Native American/ |
| 56 | Native Hawaiian/ |
| 57 | American Indian/ |
| 58 | Indians, North American/ |
| 59 | Indians, South American/ |
| 60 | Indians, Central American/ |
| 61 | First Nations/ |
| 62 | Pacific Islander/ |
| 63 | Maori/ |
| 64 | Oceanic ancestry group/ |
| 65 | American Native Continental Ancestry Group/ |
| 66 | Or/45–65 |
| 67 | Poverty |
| 68 | Social status |
| 69 | Social class |
| 70 | Low income population |
| 71 | Inequalities |
| 72 | Socioeconomic status |
| 73 | Socioeconomic factors |
| 74 | Disadvantaged |
| 75 | Underserved |
| 76 | Or/67–75 |
| 77 | Related to smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 78 | Correlated with smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 79 | Associated with smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 80 | That affect smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 81 | That inhibit smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 82 | That prevent smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 83 | Barriers to smoking cessation/quitting smoking |
| 84 | Factor$ or Determinant$ or Variable$ or Covariable$ or Predictor$ or Barrier$ |
| 85 | Or/77–84 |
| 86 | 10 AND 85 AND 17 |
| 87 | 10 AND 85 AND 22 |
| 88 | 10 AND 85 AND 37 |
| 89 | 10 AND 85 AND 44 |
| 90 | 10 AND 85 AND 66 |
| 91 | 10 AND 85 AND 76 |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies that provided either qualitative or quantitative (ie, longitudinal, cross-sectional or cohort surveys) descriptions of perceived self-reported barriers to quitting smoking in low SES groups, Indigenous groups, people with a mental illness or substance abuse problems, people who are homeless, prisoners or at-risk youth were included. See table 2 for definitions used as inclusion criteria for each vulnerable group. Only studies carried out in high-income countries were included as middle-income and low-income countries may present different contextual, political and economic barriers that require separate consideration. Only studies published in English were included as resources required to translate articles were beyond the scope of this review. Intervention studies were excluded, as barriers discussed within these studies related to use of the intervention being tested and not barriers to smoking cessation per se. Studies examining factors associated with quit attempts or success were excluded unless they included results on the perceived barriers self-reported by participants from vulnerable groups. Studies describing provider reports of the barriers to the provision of smoking cessation support or treatment, and unpublished grey literature, were also excluded. There were no cut-offs for sample size.
Table 2.
Inclusion criteria definitions of each group
| Group | Definition |
|---|---|
| Low SES | Because definitions of low SES vary across high-income countries this study used an inclusive definition of low SES. Studies were included if they described participants as being low SES and gave at least one measure of SES. This measure could be income (above/below poverty level); address in deprived neighbourhood, etc |
| Indigenous groups | The following definition was used to define potential Indigenous studies in accordance with previous studies:39 “the experiences shared by a group of people who have inhabited a country for thousands of years, which often contrast with those of other groups residing in the same country for a few hundred years”40 |
| Mental illness | People with a mental illness were defined as individuals who had been diagnosed with a mental illness, severe mental illness or were described as inpatients or outpatients in a mental health rehabilitation facility. Substance use disorders were also included. All mental illnesses were included |
| At-risk youth | At-risk youth were defined as individuals under the age of 21 who have experienced or are experiencing: problems at school; physical, sexual or psychological abuse; mental or physical health problems; economic disadvantage; or who have committed a violent or delinquent act (USA Code36) |
| Prisoners | Prisoners included those currently incarcerated and also ex-prisoners living in the community |
| Homeless | Homeless individuals were defined as those individuals described as meeting national criteria for homelessness or those individuals accessing services provided to homeless persons |
| Smoker | Smokers were defined as self-reported daily or occasional cigarette smokers. Studies that also assessed ex-smokers were only included if the majority of participants were current smokers, or if the results were reported by smoking status. Studies were excluded if they focused solely on ex-smokers or non-smokers |
SES, socioeconomic status.
Data extraction
The titles and abstracts of retrieved publications were assessed by one reviewer (LT) against eligibility criteria and excluded if they did not meet inclusion criteria. A second reviewer (a research assistant) independently assessed 20% of the returned abstracts for inclusion with 100% agreement between reviewers. Data from included journal articles were extracted into summary tables independently by one reviewer (LT) and a random 20% checked by a second (research assistant). Agreement was again high (97%). Discrepancies were settled by discussion between the reviewers. Data extracted from the articles included: study aims, setting, sample characteristics, response rates, study methodology, data analysis and the barriers identified. Barriers were defined as factors that prevented smoking cessation and/or quit attempts or were reported as primary reasons for continuing to smoke.
Risk of bias in individual studies
Quality assessment was performed independently by all authors, with two reviewers per manuscript. The methodological quality of qualitative studies was assessed using the McMaster Qualitative Criteria Form.41 Quantitative studies were assessed using a tool adapted from the STROBE statement.42 As there is a lack of an agreed, valid and reliable measure to assess the quality of mixed methods studies,43 the McMaster guidelines as well as the adapted quantitative framework were applied to the corresponding qualitative and quantitative components of any mixed methods studies identified.
Synthesis of results
Results were synthesised by vulnerable group using narrative synthesis and inductive data analysis techniques. Narrative synthesis allows the examination of studies that are highly heterogeneous in their research questions, samples and methods.44 45 In order to avoid potential biases, care was taken to also identify points of difference between studies.46 Where a barrier was reported in more than one study, this was recorded. In quantitative studies, the proportion of respondents reporting each barrier was calculated. Barriers were combined into categories and then classified using the SDHF.23 For the purposes of this review, individual factors were defined as physical or psychological barriers to quitting smoking: for example, the individual's level of nicotine dependence or motivation to quit. Lifestyle factors were defined as health behaviours (including alcohol and other drug use) that impeded an individual's ability to quit. Social and community networks were defined as the impact of an individual's family and friend networks, and the wider community. Living and working conditions encompassed factors including housing, healthcare, education and employment. The final domain was the broader socioeconomic, cultural and environmental background perceived to influence smoking cessation.
Results
Search results
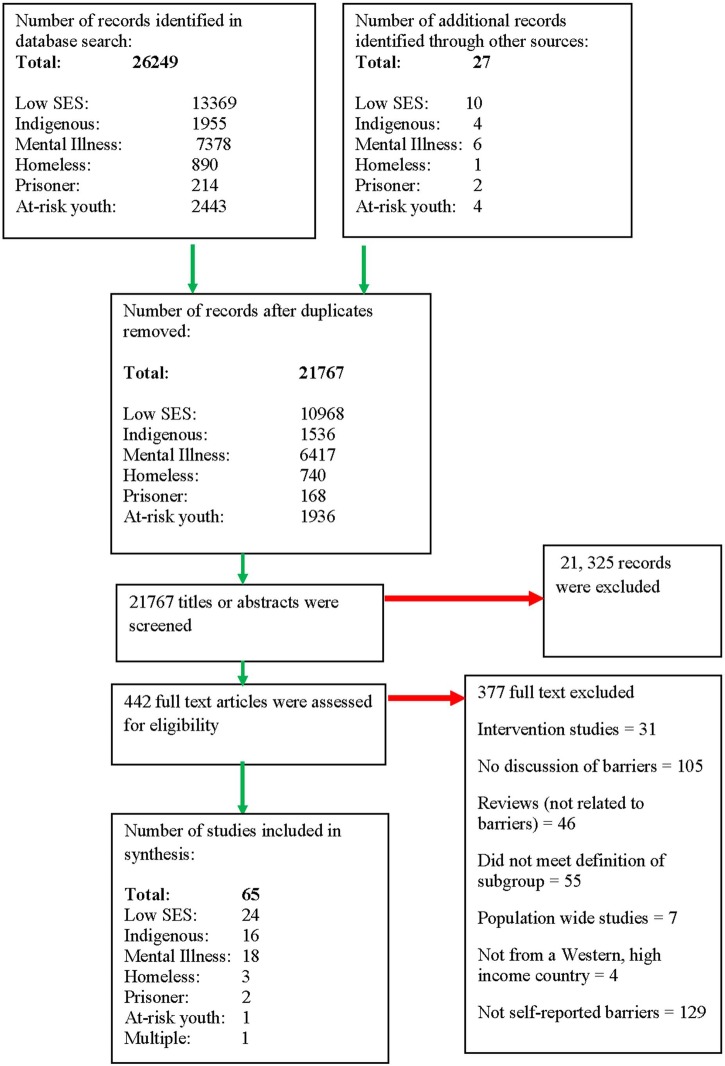
After duplicates were removed, 21 767 studies were identified from electronic searches and a further 27 from manual searches. Of those, 65 studies met inclusion criteria and were included in the review (see figure 1). Online supplementary file 1 contains a list of full text articles that were retrieved, reviewed and excluded as per the inclusion criteria. Two systematic reviews concerning Indigenous Australian pregnant women32 and pregnant women,47 and two critical reviews providing summaries of the barriers to quitting,33 48 were also identified from hand searches.
Figure 1.
Database search results (SES, socioeconomic status).
Study characteristics
The majority of studies (n=24) identified barriers to smoking cessation in low SES groups,30 49–71 Indigenous groups (n=16)72–87 and people with a mental illness (n=18)88–105 including two concerning those with substance use disorders.101 104 Three studies reported barriers to quitting within the homeless106–108 and two reported barriers within prisoner groups.109 110 One study with at-risk youth was identified.111 Two other studies concerning Alaska Native participants (age range from 11 to 18)86 and people with a mental illness (age range from 16 to 23)103 included younger people as participants. One study was identified that was carried out with participants who were homeless as well as addicted to drugs and/or alcohol.112 Since the study comprised participants who met criteria for inclusion in two of the vulnerable groups included in this review (the homeless and mental illness/substance use groups), this study was included in a seventh category containing ‘multiple’ participant groups. Online supplementary files 2–4 summarise the included quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods studies, respectively. An overview of the characteristics of included studies can be found in online supplementary file 5.
Quality assessment of qualitative studies
The results of the quality assessment of qualitative studies are presented in supplementary file 6. Overall, the quality of studies varied widely. The majority of studies did not explicitly state their study design (n=38); of those that did, most used Grounded Theory.57 59 61 93 98 99 Most studies provided adequate descriptions of the study sites; participants; data collection methods and analysis techniques. Studies generally performed poorly when assessed on four components of trustworthiness, with only 17 studies meeting all four criteria (credibility; transferability; dependability and confirmability).49 52 56 58 65 67 71 73 74 77 78 70 82 83 85 86 93 It should be noted that none of the mixed methods studies explicitly described their methodology as mixed methods nor did they report integrating the qualitative and quantitative findings in a systematic way.
Quality assessment of quantitative studies
The results of the quality assessment of quantitative studies are presented in online supplementary file 7. Sample sizes in the quantitative studies ranged from 36 to 500 participants. Response rates ranged from 42% to over 97% (three studies did not provide response rates).100 104 106 All but one study104 clearly stated eligibility criteria. All studies stated their outcome a priori and no conflicts of interest were identified. The validity and reliability of survey measures used to assess barriers to cessation were reported in one study.60 Three studies employed techniques such as pilot testing and input from key stakeholders in developing the tools used.70 104 109
Perceived barriers to smoking cessation
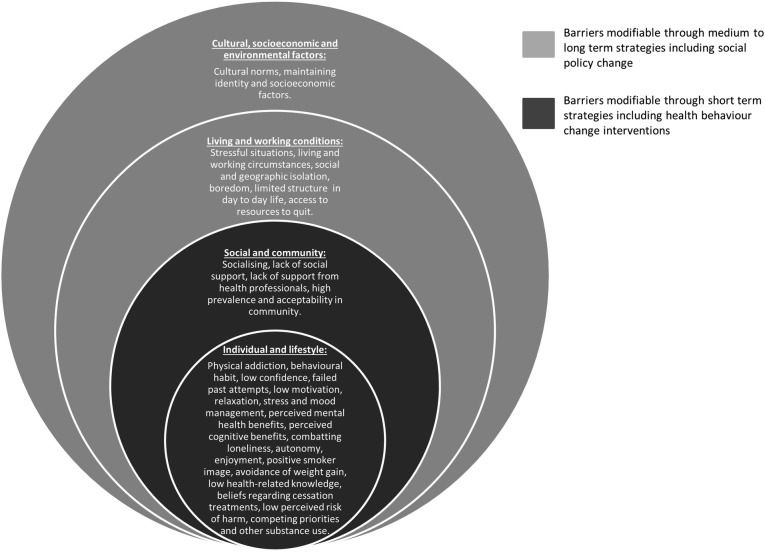
The barriers to quitting smoking endorsed over multiple studies included: smoking for stress management; enjoyment of smoking; addiction to nicotine; habit; social acceptability of smoking; lack of support to quit and access to quit resources; boredom; stressful life factors; pro-smoking living environments; smoking cultural norms; and socioeconomic disadvantage. Figure 2 demonstrates the barriers reported in this review categorised by the SDHF. For brevity, the current results section will focus on those barriers that were common across all groups and unique to certain vulnerable groups. Online supplementary file 8 provides a detailed description of all the barriers identified in this review. Table 3 provides a summary of the barriers extracted from the qualitative studies. References of studies that report one or more barriers at a given level of the SDHF are included in table 3. Table 4 provides a summary of the results of quantitative studies including the proportion of participants endorsing the barrier and the study reference.
Figure 2.
Model of the barriers to smoking cessation.
Table 3.
A summary of the self-reported barriers to smoking cessation—qualitative and mixed methods studies by vulnerable group
| Barrier | Low SES groups (n=22) | Indigenous groups (n=16) | People with a mental illness(n=13) | Homeless groups (n=3) | Prisoner groups (n=2) | At-risk youth (n=1) | Multiple groups (n=1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual and lifestyle factors | |||||||
| Stress management | 50–59 61–63 65–69 | 72 74 75 79 81 83 84 86 87 | 89 90 92 93 95–98 105 | 108 | 110 | 111 | 112 |
| Enjoyment | 50 54–56 59 62 63 65 67 | 79 81–83 | 89 90 92–94 97 98 105 | 111 | |||
| Addiction | 49 50 54 57 59 67–69 | 72 74 75 81 83 84 86 | 90–92 98 | ||||
| Habit | 50 57 65 68 | 75 79 83 84 | 92 105 | ||||
| Mental health benefits | 58 67 | 74 | 89 91–99 | ||||
| Weight gain | 30 49 52–54 64 67 | 72 74 84 | 91 98 | ||||
| Competing priorities | 56 63 | 74 75 87 | 89 91 98 99 | 108 | |||
| Rationalisations | 54–56 58 61 67 | 74 78 82 87 | 89 97 | ||||
| Other substance use | 49 56 59 62 | 74 76 81 84 | 89 | 112 | |||
| Autonomy | 56 58 68 | 83 | 93 97–99 | ||||
| Low confidence | 52 53 56 63 67 69 | 73 84 | 92 96 98 | 112 | |||
| Cognitive benefits | 51 | 83 | 93–95 | ||||
| Loneliness | 52 59 65 | 93 97 98 | |||||
| Low risk of harm | 58 | 87 | 95 97 | ||||
| Low motivation | 92 94 97 98 | ||||||
| Past failed attempts | 61 | 74 | |||||
| Positive smoker image | 30 57 | 97 | |||||
| Social and community networks | |||||||
| Prevalence and acceptability | 30 51–54 56 62 66 68 69 | 72 74 76 79 83 85–87 | 90 91 93 95 96 105 | 108 | 110 | 111 | 112 |
| Lack of social support | 30 49 54–56 58 64 67–69 | 74 75 77 79 83 84 | 91 94 98 | 108 | |||
| Social activity | 30 49 53 57 62 | 73–75 79 85 87 | 89 90 92 93 95 97 98 | ||||
| Lack of health and other professional support | 52 54–56 58 | 74 77 79 83 86 | 91–93 95 96 | 108 | 110 | 111 | 112 |
| Living and working conditions | |||||||
| Access to quit resources | 52 55 56 61–64 | 72–74 78 81 85 86 | 93 96 98 | 108 | 110 | ||
| Boredom | 50–52 54–56 59 65 | 75 86 | 90 94 95 97 99 | 108 | 110 | ||
| Concerns regarding treatment | 50 52 56 58 61–63 69 | 72–74 77 78 81 86 | 91 93 96 105 | 108 | |||
| Stressful factors | 56 58 59 62 63 65 68 | 74 75 85 | 110 | ||||
| Living and working circumstances | 30 54 58 | 74 | 96 | ||||
| Cultural, socioeconomic and environmental factors | |||||||
| Cultural norms | 56 62 | 72–75 78 81–83 85–87 | 93 94 98 | 110 | |||
| Socioeconomic factors | 65 | 97 | |||||
SES, socioeconomic status.
Table 4.
A summary of the barriers to smoking cessation—reported prevalence of each barrier by vulnerable group for studies using quantitative and mixed methods*,†
| Reported prevalence of each barrier N/total N (%) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier | Low SES groups (n=2) | Indigenous groups (n=1) | People with a mental illness (n=5) | Homeless groups (n=2) | Prisoner groups (n=1) |
| Individual and lifestyle factors | |||||
| Stress management | 63/130 (48)79 | 30/78 (39)104 | 82/186 (44)107 | ||
| Relaxation | 261/500 (52) (60) | 22/130 (17)79 | 13/30 (42) 100 7/72 (10)88 |
||
| Enjoyment | 33/130 (25)79 | 34/72 (47)88 21/105 (20)90 30/78 (39)104 |
|||
| Addiction | 431/500 (86)60 | 51/130 (39)79 | 56 (53)90 10/30 (33)100 |
93/186 (50)107 | |
| Cravings | 53/78 (68)104 47/96 (48)101 |
||||
| Withdrawal symptoms | 85/96 (87)101 | ||||
| Habit | 411/500 (82)60 | 95/130 (73)79 | 26/72 (36)88 20/105 (19)90 17/30 (58)100 |
||
| Perceived mental health benefits | 6–30/130 (5–23)79 | 21/105 (20)90 7–8/72 (10–11)88 41/78 (53)104 41–76/96 (42–78)101 |
|||
| Concentration | 27–56/96 (28–55)101 | ||||
| Low levels of motivation | 131/350 (38)70 | 46/96 (47)101 | |||
| Weight gain | 69/350 (20)70 | 6/130 (5)79 | 3/72 (4)88 39/96 (40)101 |
38/186 (20)107 | |
| Other substance use | 3/72 (4)88 2–8/78 (3–10)104 13–40/96 (13–41)101 |
||||
| Problems getting to sleep | 23/96 (23)101 | ||||
| Low confidence and perceived difficulty | 87–202/350 (25–58)70 | 22/78 (24)104 | 25/34 (74)109 | ||
| Social and community networks | |||||
| High prevalence and acceptability in the community | 332/500 (66)60 116/350 (33)70 |
5/130 (12)79 | 13/105 (13)90 5/72 (7)88 34/78 (43)104 |
78/186 (42)107 | 27/34 (79)109 |
| Lack of social support | 90/350 (26)70 | 48/186 (26)107 70–79/98 (71–79)106 |
10/34 (29)109 | ||
| Lack of health and other professional support | 3/72 (4)88 | 19/34 (56)109 | |||
| Social activity | 44/130 (34)79 | 17/30 (58)100 2/72 (3)88 |
|||
| Availability of cigarettes | 5/130 (4)79 | 8/105 (8)90 5/72 (7)88 |
|||
| Living and working conditions | |||||
| Access to quit resources | 108/350 (31)70 | 9/34 (27)109 | |||
| Boredom | 242/500 (48)60 | 38/130 (29)79 | 9/72 (13)88 13/105 (13)90 |
||
| Stressful factors | 4/72 (6)88 | ||||
| Living environments | 20 (59)109 | ||||
*Decimals rounded to nearest whole number where appropriate.
†Numerators/denominators are presented first, followed by proportion (in parentheses), followed by reference.
SES, socioeconomic status.
Barriers common across all groups
Three barriers were present in all six vulnerable groups included in this review: (1) stress management, (2) lack of support to quit from health professionals and other service providers, and (3) high prevalence and acceptability of smoking within vulnerable communities.
Within the SDHF, stress management was categorised as an individual level barrier. Forty qualitative studies identified stress management as a significant barrier to smoking cessation.50–56 58 59 61–63 65 67–69 72 74 75 80 81 83 84 86 87 89 90 92 93 95–97 99 100 103 105 108 110–112 Smoking was used as a coping mechanism52 58 62–65 69 74 89 90 92 97 99 in reaction to daily stressors as well as the stress inherent in vulnerable lives. Three quantitative studies reported stress management as a barrier to quitting with Maori participants (48%),79 participants with substance use disorders (39%)104 and homeless participants (44%).107 Of note, participants in two studies reported that smoking also directly contributed to the stress experienced by participants.51 111 Participants also reported using smoking to manage their emotions and mood.58 65 72 83 84 90 93 98 103 Twenty-three per cent of participants from a Maori sample indicated managing emotions was a barrier to quitting,79 42% of these individuals had a substance use disorder.101
High prevalence and acceptability of smoking within vulnerable communities was categorised as a community and social network level barrier. Eight qualitative53 54 69 75 79 80 98 111 and four quantitative60 101 107 109 studies found that being around other smokers was a barrier to quitting. This finding is reinforced by participants describing the high prevalence of smoking among family and friends in 22 studies30 51 52 56 62 68 69 72 74 76 81 83 85–87 90 93 95 96 103 111 112 and in the wider community in 18 studies.30 51 52 56 62 66 69 72 74 76 81 83 85–87 93 96 112 Tobacco was readily available and easily accessible within vulnerable communities51 62 66 76 83 90 91 111 and smoking was considered to be highly acceptable30 79 81–83 85–87 and normalised behaviour.52 56 62 66 69 79 81–83 85 87
Lack of support to quit from health and other service providers was also categorised as a social and community network barrier. Other service providers include management and staff in prisons, homeless shelters and organisations, and members of the community. Thirteen qualitative studies52 55 56 58 74 77 83 86 91 92 95 108 112 and one quantitative study109 reported a perceived lack of support from health professionals regarding smoking cessation. Cases of family members and health professionals actively discouraging quit attempts and encouraging maintenance of smoking due to concerns about the individual's mental health92 93 95 96 112 or because smoking was perceived to be the individual's only source of enjoyment54 77 79 83 were reported. Three studies identified tobacco use by health professionals and others involved in the participants’ care as a barrier to cessation.77 95 109 Over half (55.9%) of prisoners surveyed reported observing members of staff smoking as a barrier to quitting.109 Studies involving people with a mental illness and prisoners identified use of cigarettes in order to reward or punish behaviour by health professionals and other service providers93 95 96 110 as a barrier to quitting. Twenty-nine per cent of prisoners also indicated that not receiving cessation support from prison staff prevented them from quitting smoking.109 Twenty-six per cent of substance abusing individuals reported they did not have enough support to quit. One study involving at risk youth identified smoking being unaddressed by teachers and members of the police force as a barrier to smoking cessation.111
Barriers unique to certain vulnerable groups
Indigenous, prisoner, mentally ill, homeless and at-risk youth reported unique barriers to smoking cessation. Racism, historical factors,74 75 85 ceremonial use of tobacco,72 73 82 85 86 cultural values that promote sharing, kinship and reciprocity,83 cultural values of pride, independence and self-reliance that affect help-seeking behaviour,81 82 cultural values concerning health and privacy,84 and maintenance of cultural identity73–75 82 83 85 were identified as barriers within Indigenous groups. Smoking cessation could therefore exclude an individual from fully participating in their culture or potentially challenge their family, personal or community relationships.
Living environments and the stressful context of prison presented unique barriers for prisoners, including social isolation, anxiety regarding legal matters, transfers to other prisons, use of cigarettes as currency, use of cigarettes as a way to reward or punish behaviour, bullying, missing family and restricted movement throughout the day.110
Low levels of motivation,92 94 97 98 concerns about ability of cessation services to handle mental health issues,91 93 96 identity and belonging,93 94 98 and symptom management88–98 were barriers for people with mental illness.
Competing needs and prioritising the need to find shelter/place to live were unique barriers for individuals who were homeless.108 Very high levels of accessibility of cigarettes and the regular practice of selling cigarettes to those under 18 years of age were identified by one study with at-risk youth as a unique barrier.111
Discussion
This is the first systematic review reporting perceived barriers to smoking cessation across a range of vulnerable groups. The findings from 54 qualitative, 8 quantitative and 3 mixed methods studies demonstrate that barriers to quitting smoking operate at multiple levels, including individual and lifestyle factors; social and community networks; living conditions; and cultural and socioeconomic factors. These include: smoking for stress management; enjoyment of smoking; addiction to nicotine; habit; social acceptability of smoking; lack of support to quit and access to quit resources; boredom; stressful life factors; pro-smoking living environments; cultural norms; and socioeconomic disadvantage. Stress management, lack of support from health professionals and other service providers, and the high prevalence and acceptability of smoking in communities were the three barriers common across all six vulnerable groups included in this review. The identification of perceived barriers common across vulnerable groups is an extension of the previous literature.
The identified barriers broadly reflect those reported in two systematic reviews limited to pregnant smokers47 and Indigenous Australian pregnant smokers,32 and two critical reviews providing summaries of the challenges to cessation among low-income smokers33 and low income, rural, homeless, hard core, immigrant and HIV-positive smokers.48 Addiction to nicotine, habit, stress management, enjoyment and weight gain are typically reported barriers to smoking cessation within the general population.26–28 114 No studies were found that directly compared barriers experienced by vulnerable groups and smokers in the general population. To the authors’ knowledge, only one study has assessed the effect of SEP on barriers to quitting smoking, and identified that decreasing SEP was associated with higher likelihood of reporting stress management and boredom as barriers.28 This review did not aim to provide direct comparisons between vulnerable groups and the general population due to the heterogeneity of studies. Additionally, comparisons by gender were beyond the scope of this review, but should be considered for further research, as socioeconomic disadvantage has differential effects on males and females,20 and preliminary evidence suggests barriers to cessation may differ by gender.28 70
Nevertheless, the novel results of this review indicate that vulnerable smokers report a number of additional barriers to cessation that operate within their social and community networks, living conditions, and wider cultural and socioeconomic contexts. Social and community barriers include: lack of support to quit from peers as well as health and other professionals; high prevalence and acceptability of smoking within vulnerable communities; and smoking as a social activity. Living conditions include: stressful factors; pro-smoking living and working circumstances; lack of access to quit resources; social and geographical isolation; and boredom. Cultural norms and socioeconomic disadvantage also presented barriers to quitting.
Main barriers identified across all vulnerable groups
Stress management
Stress management was a frequently reported individual-level barrier. Smokers typically demonstrate higher levels of stress and low mood than non-smokers and ex-smokers.115–117 Smoking may provide a coping mechanism for individuals who are prone to higher levels of stress118–120 or smoking may act as a stressor due to neurobiological processes or through the experience of withdrawal symptoms.120 Stressors associated with vulnerable groups (eg, unemployment, financial stress and poverty) may compound stress levels within vulnerable groups. Given that vulnerable smokers may be more likely to report smoking in order to relieve stress,28 incorporating stress management techniques into interventions targeted at vulnerable groups may help to increase cessation.
Lack of support to quit from health professionals and other service providers
At the social and community level, a lack of support to quit from health professionals and other service providers was identified. This reflects research that suggests smokers from low SEPs are less likely to receive advice to quit from a healthcare provider than their more higher SEP counterparts,121 despite evidence demonstrating brief advice can increase the likelihood of successful quitting.122 123 Organisational and individual factors both affect the provision of quit advice by health and other service providers. These include lack of time, confidence, knowledge and counselling skills.124 Efforts should be focused on improving health professionals’ ability to offer quit advice, and may benefit from examining how best to ensure compliance to existing guidelines that provide clear recommendations on identifying individuals who are at higher risk of smoking and addressing the unique issues that these individuals face.
Tailoring interventions to the specific needs of vulnerable groups may be effective. Tailored interventions for behaviour change have been found to be effective compared with no intervention or dissemination of guidelines or educational materials alone.125 Given that this review identified three common barriers across the six vulnerable groups included in this review, we argue that subsequent smoking cessation interventions in vulnerable groups should seek to address these factors. Programmes should include specific modules on stress management techniques and how best to combat stress in vulnerable groups, as well as educating smokers about how stress relief and relief from nicotine withdrawal symptoms can be confounded.
Smoking cessation interventions should be designed to maximise participation by vulnerable groups, addressing the key barriers around acceptability and access to interventions. Utilising existing services and organisations that are highly accessed by vulnerable groups and are a trusted source of help for vulnerable groups is also necessary. There is accumulating evidence that social and community service organisations are well placed to provide brief smoking cessation advice to highly vulnerable clients.126 127
High prevalence and acceptability of smoking
The high prevalence and social acceptability of smoking within vulnerable communities was frequently reported. Considerable measures have been taken to address the denormalisation of smoking in the general population through regulation and legislative changes such as restrictions in advertising, smoke-free environment policies and point-of-sale restriction.1 128 129 Participants who were homeless, experiencing mental illness and prisoners cited a lack of restrictions on smoking within their living environments (or lack of enforcement of existing policies) as a factor that reinforced their smoking. While there are challenges associated with their implementation, smoke-free areas can be successfully implemented within mental health treatment centres and prisons,130–132 and there is potential to extend these restrictions to homeless shelters and public housing developments.
Efforts to encourage the denormalisation of smoking in the environments of vulnerable communities require further exploration. Providing access to acceptable and effective behavioural and pharmacological supports should ensure that denormalisation does not result in compounding stigma and further isolating vulnerable groups.128 133
Barriers specific to certain groups
Indigenous groups
Indigenous groups identified unique stressors linked to smoking including racism and historical factors; cultural practices including ceremonial use of tobacco and cultural values that promote sharing, kinship and reciprocity, and the importance of smoking as a way to maintain cultural identity. Cultural values also had effects on the willingness of Indigenous participants to access smoking support services. Certain Indigenous groups may be less likely to receive advice to quit or engage with services designed to aid in cessation.134 However, it is important to note that smoking cessation programmes have been shown to be effective within Indigenous groups.113 135 Culturally appropriate interventions tailored to the needs of Indigenous smokers should continue to be developed, implemented and evaluated. These programmes should acknowledge the cultural significance of tobacco use, and the important historical and social factors associated with Indigenous groups and smoking.136
Prisoners
Prisoners identified unique stressors within their living conditions that contributed to their smoking including social isolation, anxiety regarding legal matters and transfers to other prisons. A recent multicomponent randomised controlled trial that included improving stress management skills in prisoners found similar point prevalence abstinence rates as another trial conducted with prisoners9 137 138 and other community-based studies. Thus, smoking cessation programmes can be effective even in prison environments that are highly conducive to smoking and should form a part of routine care within prison systems.
People with a mental illness
Low motivation to quit smoking was only reported in studies involving smokers with a mental illness. This contradicts research showing no difference in motivation to quit between those with severe mental illness and the general population.139 A recent review concluded there is some evidence to suggest that individuals diagnosed with a psychotic disorder are slightly less motivated to quit than those diagnosed with depression.139 Possible reasons for this include the symptoms associated with schizophrenia (including amotivation), management of side effects of medications (including parkinsonism), limited support systems, low perceived vulnerability to smoking-related disease, lack of alternate coping mechanisms and poverty.139 140 Information on the diagnoses of participants was only reported in one of the studies reporting motivation as a barrier in this review,92 where the majority of participants were diagnosed with a psychotic disorder. However, other studies did not provide information on participants’ diagnoses and further exploration is beyond the scope of this review.
Symptom management also presented a significant barrier within studies concerning people with a mental illness. There is evidence to suggest that biochemical processes between nicotine and other substances in tobacco improve some symptoms of mental illness.140 Additionally, smokers with a mental illness may be more likely to misattribute their withdrawal symptoms as recurring mental illness symptoms. Further investigation and education regarding cessation and symptom management with people with a mental illness is warranted. Integrating smoking cessation care with mental health and addiction treatments can be effective at promoting cessation rates in groups with mental illness.131 132 However, future studies need to investigate ways to maintain long-term smoking cessation as well as systems-level changes that may support smoking cessation in people with mental illness.141
Barriers to smoking cessation in vulnerable groups: a model
Figure 2 visually demonstrates the broad range of barriers to cessation reported by vulnerable groups, many of which exist outside the realm of the individual. This model demonstrates the interconnectedness of individual and lifestyle factors with the wider social and community factors, living conditions and cultural, socioeconomic and environmental factors. The two darker spheres holding social and community networks, and individual and lifestyle factors, identify those factors that are potentially modifiable through short-term health behaviour change interventions. This model does not provide an exhaustive list of all the factors that prevent vulnerable individuals from smoking cessation. It does provide a framework for understanding the perceived self-reported barriers to quitting smoking identified in this review.
Strengths and limitations
This synthesis of the literature provides evidence of the perceived barriers to smoking cessation by examining the methodological quality of studies, and comparing between and within selected vulnerable groups. However, this review has some limitations. While the overall quality of the studies included in this review was acceptable, most qualitative studies failed to provide information regarding the trustworthiness of the research, and most quantitative studies failed to provide information on the validity and reliability of the survey measures used to assess barriers. Strategies for enhancing the trustworthiness of qualitative research have been concisely summarised142 and future qualitative studies should seek to employ these strategies where possible. Future quantitative studies should seek to report at least brief psychometric properties of survey measures used to assess barriers to smoking cessation, including reliability and validity.
Of the quantitative studies included, the majority used convenience samples. It is not generally feasible to target vulnerable and hard to reach populations using random population sampling procedures. This limits the generalisability and transferability of the included studies to wider vulnerable populations. Nevertheless, the agreement in findings between qualitative studies does suggest that these results are robust.
The nature of the studies included in this review means that no weight is given to the different barriers and the authors cannot provide comment on which, if any, barriers should be made a priority to target in smoking cessation interventions with vulnerable groups. Given limited resources and funds, addressing all barriers is rarely possible. Future research is needed to identify those barriers that are most important to address first, and to prioritise resourcing and intervention development.
The results of this review were broadly categorised according to the SDHF, however, these categories are not mutually exclusive and certain barriers were able to be included in multiple categories (eg, stress and stressful factors could be categorised as either individual-level barriers or barriers within the living conditions level). The reviewed studies do not directly clarify whether the nature of stress experienced in vulnerable groups is personal or contextual. Constructs such as coping and resilience143 143a have been hypothesised as mediators between stress and smoking in low socioeconomic groups.144
Similarly, as this review sought to provide a summary of vulnerable smokers’ perceived self-reported barriers to cessation, other barriers that may be important determinants of quit attempts and success were not considered. Barriers such as the knowledge and attitudes of staff and health professionals, and the capacity of services to offer smoking cessation programmes, which have been identified within the literature,124 should also be considered when examining the challenges facing vulnerable groups.
This review was only able to identify five studies that examined the barriers to quitting smoking within prisoner (n=2 studies) and homeless (n=3) groups, and one study focusing on at-risk youth. These results indicate more research is required with these groups to examine the barriers to smoking cessation. More studies investigating the barriers to cessation within these groups may lead to identification of additional common and unique barriers across vulnerable groups. Additionally, this review was limited to studies conducted within one of six vulnerable groups. Other groups that show high rates of smoking include lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender groups;145 culturally and linguistically diverse groups;146 and rural and remote communities.147 The authors acknowledge the disparity in smoking prevalence in these groups, however, their inclusion would have increased the breadth of the review to a level that would be too broad and complex to be useful. These groups may experience barriers to cessation different to those experienced by the groups included in this review. It should also be noted that individuals within the included groups often experience multiple forms of disadvantage, for example, people who are homeless are more likely to experience a mental illness148 and Indigenous communities are more likely to be over-represented in lower SEPs.3
Conclusions
These results support findings that vulnerable groups experience common barriers to smoking cessation, and also barriers which are unique to specific vulnerable groups. Stress management, high prevalence and acceptability of smoking, and lack of support to quit were identified as priority areas for cessation research, programme implementation and policy change. Many of the barriers identified within this review are modifiable through short-term health behaviour change strategies. For heterogeneous groups of vulnerable individuals, intervention development should seek to address those barriers common to all vulnerable groups identified in this review. For relatively homogeneous groups of vulnerable individuals, interventions should seek to address the unique barriers faced by those groups in addition to those barriers identified as common to all vulnerable groups.
These findings, coupled with lower success rates in quitting within vulnerable groups relative to the success rates in more advantaged groups,14 19 suggest that interventions with vulnerable groups need to address wider social, community and cultural factors as well as individualised cessation support. Addressing the predictors of cessation found within the general population, such as nicotine dependence and enjoyment, remain important for vulnerable groups.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Research Assistant Ms Madeleine Randell and to Dr Michelle Anderson for providing valuable comment on draft manuscripts.
Footnotes
Contributors: All authors conceived the initial scope and subject of the review. LT carried out all searches, wrote up drafts and performed quality assessment. BB, CP and JB provided extensive feedback and contributions to drafts of the paper. All authors completed quality assessment of the included papers. BB and LT completed narrative synthesis. All authors have read and met the ICMJE criteria for authorship.
Funding: BB is supported by a Cancer Institute NSW Career Development Fellowship and a University of Newcastle Faculty of Health and Medicine Q5 Gladys M Brawn Career Development Fellowship. JB is supported by an Australian Research Council Post-Doctoral Industry Fellowship and Newcastle Cancer Control Collaborative funding. CP is supported by an NHMRC Career Development Fellowship. LT is supported by a 50:50 scholarship from the University of Newcastle Faculty of Health and Medicine, and the Cancer Institute NSW.
Competing interests: None.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1.World Health Organization (WHO). WHO report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic Geneva, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). 2010 National Drug Strategy Household Survey: detailed findings. Canberra, 2010. Contract No.: Cat. no. PHE145. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. The health and welfare of Australia's Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people, an overview 2011. Canberra, 2011. Contract No.: Cat. no. IHW 42. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDCP). Current cigarette smoking among adults—United States, 2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2012;61:889–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Statistics Canada. Canadian Community Health Survey 2000/01. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lawrence D, Mitrou F, Zubrick SR. Smoking and mental illness: results from population surveys in Australia and the United States. BMC Public Health 2009;9:285 10.1186/1471-2458-9-285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kelly P, Baker AL, Deane FP et al. . Prevalence of smoking and other health risk factors in people attending residential substance abuse treatment. Drug Alcohol Rev 2012;31:638–44. 10.1111/j.1465-3362.2012.00465.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baggett TP, Rigotti NA. Cigarette smoking and advice to quit in a national sample of homeless adults. Am J Prev Med 2010;39:164–72. 10.1016/j.amepre.2010.03.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cropsey K, Eldridge G, Weaver M et al. . Smoking cessation intervention for female prisoners: addressing an urgent public health need. Am J Public Health 2008;98:1894–901. 10.2105/AJPH.2007.128207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Indig D, Topp L, Ross B et al. . 2009 NSW Inmate Health Survey: Key Findings Report Sydney: Justice Health 2010.
- 11.Wiebel WW. Identifying and gaining access to hidden populations. NIDA Res Monogr 1990;98:4–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McLachlan R, Gilfillan G, Gordon J. Deep and Persistent Disadvantage in Australia. Canberra: Productivity Commission; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hyland A, Borland R, Li Q et al. . Individual-level predictors of cessation behaviours among participants in the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Four Country Survey. Tob Control 2006;15(Suppl 3):iii83–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kotz D, West R. Explaining the social gradient in smoking cessation: it's not in the trying, but in the succeeding. Tob Control 2009;18:43–6. 10.1136/tc.2008.025981 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gilman SE, Martin LT, Abrams DB et al. . Educational attainment and cigarette smoking: a causal association? Int J Epidemiol 2008;37:615–24. 10.1093/ije/dym250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hatziandreu EJ, Pierce JP, Lefkopoulou M et al. . Quitting smoking in the United States in 1986. J Natl Cancer Inst 1990;82:1402–6. 10.1093/jnci/82.17.1402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Levy DT, Romano E, Mumford E. The relationship of smoking cessation to sociodemographic characteristics, smoking intensity, and tobacco control policies. Nicotine Tob Res 2005;7:387–96. 10.1080/14622200500125443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Reid JL, Hammond D, Boudreau C et al. . Socioeconomic disparities in quit intentions, quit attempts, and smoking abstinence among smokers in four western countries: findings from the International Tobacco Control Four Country Survey. Nicotine Tob Res 2010;12(Suppl):S20–33. 10.1093/ntr/ntq051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Giskes K, van Lenthe FJ, Turrell G et al. . Smokers living in deprived areas are less likely to quit: a longitudinal follow-up. Tob Control 2006;15:485–8. 10.1136/tc.2006.015750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Graham H, Inskip HM, Francis B et al. . Pathways of disadvantage and smoking careers: evidence and policy implications. J Epidemiol Community Health 2006;60(Suppl 2):7–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hiscock R, Bauld L, Amos A et al. . Socioeconomic status and smoking: a review. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2012;1248:107–23. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06202.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Melnyk KA. Barriers: a critical review of recent literature. Nurs Res 1988;37:196–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dahlgren G, Whitehead M. Policies and strategies to promote equity in health. Copenhagen, Institute for Futures Studies; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Marmot M. Social determinants of health inequalities. Lancet 2005;365:1099–104. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)71146-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Theobald W, Smith SS, Fiore M. Insights: Smoking in Wisconsin University of Wisconsin Medical School: UW Center for Tobacco Research and Intervention, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guirguis AB, Ray SM, Zingone MM et al. . Smoking cessation: barriers to success and readiness to change. Tenn Med 2010;103:45–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Orleans CT, Jepson C, Resch N et al. . Quitting motives and barriers among older smokers. The 1986 Adult Use of Tobacco Survey revisited. Cancer 1994;74(7 Suppl):2055–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fidler JA, West R. Self-perceived smoking motives and their correlates in a general population sample. Nicotine Tob Res 2009;11:1182–8. 10.1093/ntr/ntp120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Poland B, Frohlich K, Haines RJ et al. . The social context of smoking: the next frontier in tobacco control? Tob Control 2006;15:59–63. 10.1136/tc.2004.009886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Paul CL, Ross S, Bryant J et al. . The social context of smoking: a qualitative study comparing smokers of high versus low socioeconomic position. BMC Public Health 2010;10:211 10.1186/1471-2458-10-211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rodriguez D, Carlos HA, Adachi-Mejia AM et al. . Predictors of tobacco outlet density nationwide: a geographic analysis. Tob Control 2013;22:349–55. 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2011-050120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gould GS, Munn J, Watters T et al. . Knowledge and views about maternal tobacco smoking and barriers for cessation in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders: a systematic review and meta-ethnography. Nicotine Tob Res 2013;15:863–74. 10.1093/ntr/nts211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gollust SE, Schroeder SA, Warner KE. Helping smokers quit: understanding the barriers to utilization of smoking cessation services. Milbank Q 2008;86:601–27. 10.1111/j.1468-0009.2008.00536.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Australian National Preventive Health Agency. A priority-driven research agenda for tobacco control in Australia. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 35.World Health Organisation. Report on the global tobacco epidemic 2013.
- 36.U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Ending the tobacco epidemic: a tobacco control strategic action plan for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Washington DC: Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al. . Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000097 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E et al. . Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med Res Methodol 2012;12:181 10.1186/1471-2288-12-181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carson KV, Brinn MP, Peters M et al. . Interventions for smoking cessation in Indigenous populations. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;1:CD009046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cunningham C, Stanley F. Indigenous by definition, experience, or world view. BMJ 2003;327:403–4. 10.1136/bmj.327.7412.403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Letts L, Wilkins S, Stewart D et al. . Critical review form—qualitative studies (version 2.0). McMaster University, 2007. http://www.fhs.mcmaster.ca/rehab/ebp/ [Google Scholar]
- 42.Barley EA, Murray J, Walters P et al. . Managing depression in primary care: A meta-synthesis of qualitative and quantitative research from the UK to identify barriers and facilitators. BMC Fam Pract 2011;12:47 10.1186/1471-2296-12-47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.O'Cathain A, Murphy E, Nicholl J. The quality of mixed methods studies in health services research. J Health Serv Res Policy 2008;13:92–8. 10.1258/jhsrp.2007.007074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, et al. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. A product from the ESRC Methods Programme. Lancaster: Institute of Health Research; 2006.
- 45.Rumrill PD Jr, Fitzgerald SM. Using narrative literature reviews to build a scientific knowledge base. Work 2001;16:165–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Denyer D, Tranfield D. Using qualitative research synthesis to build an actionable knowledge base. Manage Decis 2006;44:213–27. 10.1108/00251740610650201 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ingall G, Cropley M. Exploring the barriers of quitting smoking during pregnancy: a systematic review of qualitative studies. Women Birth 2010;23:45–52. 10.1016/j.wombi.2009.09.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Browning K, Baker CJ, McNally GA et al. . Nursing research in tobacco use and special populations. Annu Rev Nurs Res 2009;27:319–42. 10.1891/0739-6686.27.319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ahijevych K, Kuun P, Christman S et al. . Beliefs about tobacco among Appalachian current and former users. Appl Nurs Res 2003;16:93–102. 10.1016/S0897-1897(03)00009-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bancroft A, Wiltshire S, Parry O et al. . “It's like an addiction first thing...afterwards it's like a habit”: daily smoking behaviour among people living in areas of deprivation. Soc Sci Med 2003;56: 1261–7. 10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00124-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Beech BM, Scarinci IC. Smoking attitudes and practices among low-income African-Americans: qualitative assessment of contributing factors. Am J Health Promot 2003;17:240–8. 10.4278/0890-1171-17.4.240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bryant J, Bonevski B, Paul C et al. . Developing cessation interventions for the social and community service setting: a qualitative study of barriers to quitting among disadvantaged Australian smokers. BMC Public Health 2011;11:493 10.1186/1471-2458-11-493 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Copeland L. An exploration of the problems faced by young women living in disadvantaged circumstances if they want to give up smoking: can more be done at general practice level? Fam Pract 2003;20:393–400. 10.1093/fampra/cmg410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dunn CL, Pirie PL, Lando HA. Attitudes and perceptions related to smoking among pregnant and postpartum women in a low-income, multiethnic setting. Am J Health Promot 1998;12:267–74. 10.4278/0890-1171-12.4.267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Franco L, Welsby D, Eccleston P et al. . A qualitative study about smoking cessation with clients of community service organisations that work with disadvantaged families. Health Promot J Austr 2011;22:153–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lacey LP, Manfredi C, Balch G et al. . Social support in smoking cessation among black women in Chicago public housing. Public Health Rep 1993;108:387–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Moffatt J, Whip R, Moffatt J. The struggle to quit: barriers and incentives to smoking cessation. Health Educ J 2004;63:101–12. 10.1177/001789690406300202 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nichter M, Nichter M, Muramoto M et al. . Smoking among low-income pregnant women: an ethnographic analysis. Health Educ Behav 2007;34:748–64. 10.1177/1090198106290397 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Peretti-Watel P, Constance J. “It's all we got left”. Why poor smokers are less sensitive to cigarette price increases. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2009;6:608–21. 10.3390/ijerph6020608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Price JH, Everett SA. Perceptions of lung cancer and smoking in an economically disadvantaged population. J Community Health 1994;19:361–75. 10.1007/BF02260405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Roddy E, Antoniak M, Britton J et al. . Barriers and motivators to gaining access to smoking cessation services amongst deprived smokers––a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 2006;6:147 10.1186/1472-6963-6-147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stead M, MacAskill S, MacKintosh AM et al. . “It's as if you're locked in”: qualitative explanations for area effects on smoking in disadvantaged communities. Health Place 2001;7:333–43. 10.1016/S1353-8292(01)00025-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stewart MJ, Brosky G, Gillis A et al. . Disadvantaged women and smoking. Can J Public Health 1996;87:257–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Stewart MJ, Gillis A, Brosky G et al. . Smoking among disadvantaged women: causes and cessation. Can J Nurs Res 1996;28:41–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stewart MJ, Greaves L, Kushner KE et al. . Where there is smoke, there is stress: low-income women identify support needs and preferences for smoking reduction. Health Care Women Int 2011;32:359–83. 10.1080/07399332.2010.530724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Stillman FA, Bone L, Avila-Tang E et al. . Barriers to smoking cessation in inner-city African American young adults. Am J Public Health 2007;97:1405–8. 10.2105/AJPH.2006.101659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Tod AM. Barriers to smoking cessation in pregnancy: a qualitative study. Br J Community Nurs 2003;8:56–64. 10.12968/bjcn.2003.8.2.11088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tsourtos G, Ward PR, Muller R. Smoking and stress: the double edged sword of living in a disadvantaged area. Australasian Med J 2008;1:1–17.. 10.4066/amj.2008.8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wiltshire S, Bancroft A, Parry O et al. ‘I came back here and started smoking again’: perceptions and experiences of quitting among disadvantaged smokers. Health Educ Res 2003;18:292–303. 10.1093/her/cyf031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rosenthal L, Carroll-Scott A, Earnshaw VA et al. . Targeting cessation: understanding barriers and motivations to quitting among urban adult daily tobacco smokers. Addict Behav 2013;38:1639–42. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.09.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.White S, Baird W. Disadvantaged former miners’ perspectives on smoking cessation: a qualitative study. Health Educ J 2013;72:755–60. 10.1177/0017896912468817 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Burgess D, Fu SS, Joseph AM et al. . Beliefs and experiences regarding smoking cessation among American Indians. Nicotine Tob Res 2007;9(Suppl 1):S19–28. 10.1080/14622200601083426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Choi WS, Daley CM, James A et al. . Beliefs and attitudes regarding smoking cessation among American Indians: a pilot study. Ethn Dis 2006;16:35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dawson AP, Cargo M, Stewart H et al. . Aboriginal health workers experience multilevel barriers to quitting smoking: a qualitative study. Int J Equity Health 2012;11:27 10.1186/1475-9276-11-27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Dawson AP, Cargo M, Stewart H et al. . “I know it's bad for me and yet I do it”: exploring the factors that perpetuate smoking in Aboriginal health workers––a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 2012;12:102 10.1186/1472-6963-12-102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dennis MK, Momper SL. “It's bad around here now”: tobacco, alcohol and other drug use among American Indians living on a rural reservation. J Ethn Subst Abuse 2012;11:130–48. 10.1080/15332640.2012.675244 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Fernandez C, Wilson D. Maori women's views on smoking cessation initiatives. Nurs Prax N Z 2008;24:27–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Fu SS, Burgess D, van Ryn M et al. . Views on smoking cessation methods in ethnic minority communities: a qualitative investigation. Prev Med 2007;44:235–40. 10.1016/j.ypmed.2006.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Glover M. Analysing smoking using Te Whare Tapa Wha. NZ J Psychol 2005;34:13–19. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Gould GS, Munn J, Avuri S et al. “Nobody smokes in the house if there's a new baby in it”: Aboriginal perspectives on tobacco smoking in pregnancy and in the household in regional NSW Australia. Women Birth 2013;26:246–53. 10.1016/j.wombi.2013.08.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Gryczynski J, Feldman R, Carter-Pokras O et al. . Contexts of tobacco use and perspectives on smoking cessation among a sample of urban American Indians. J Health Care Poor Underserved 2010;21:544–58. 10.1353/hpu.0.0276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Hodge FS, Struthers R. Persistent smoking among Northern Plains Indians: lenient attitudes, low harm value, and partiality toward cigarette smoking. J Cult Divers 2006;13:181–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Johnston V, Thomas DP. Smoking behaviours in a remote Australian Indigenous community: the influence of family and other factors. Soc Sci Med 2008;67:1708–16. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.09.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kaholokula J. Culturally informed smoking cessation strategies for Native Hawaiians. Nicotine Tob Res 2008;10:671–81. 10.1080/14622200801978763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Passey ME, Gale JT, Sanson-Fisher RW. “It's almost expected”: rural Australian Aboriginal women's reflections on smoking initiation and maintenance: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health 2011;11:55 10.1186/1472-6874-11-55 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Patten CA, Enoch C, Renner CC et al. . Focus groups of Alaska Native adolescent tobacco users: preferences for tobacco cessation interventions and barriers to participation. Health Educ Behav 2009;36:711–23. 10.1177/1090198107309456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wood L, France K, Hunt K et al. . Indigenous women and smoking during pregnancy: knowledge, cultural contexts and barriers to cessation. Soc Sci Med 2008;66:2378–89. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.01.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Carosella AM, Ossip-Klein DJ, Owens CA. Smoking attitudes, beliefs, and readiness to change among acute and long term care in patients with psychiatric diagnoses. Addict Behav 1999;24:331–44. 10.1016/S0306-4603(98)00096-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Davis K, Brunette M, Vorhies V et al. . A qualitative study of how individuals with severe mental illness assess smoking risks. Mental Health Subst Use 2010;3:110–23. 10.1080/17523281003738745 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Goldberg JO, Moll S, Washington A. Exploring the challenge of tobacco use and schizophrenia. Psychiatr Rehabil Skills 1996;1:55–67. 10.1080/10973435.1996.10387541 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Howard LM, Bekele D, Rowe M et al. . Smoking cessation in pregnant women with mental disorders: a cohort and nested qualitative study. BJOG 2013;120:362–70. 10.1111/1471-0528.12059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kerr S, Woods C, Knussen C et al. . Breaking the habit: a qualitative exploration of barriers and facilitators to smoking cessation in people with enduring mental health problems. BMC Public Health 2013;13:221 10.1186/1471-2458-13-221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lawn SJ, Pols RG, Barber JG. Smoking and quitting: a qualitative study with community-living psychiatric clients. Soc Sci Med 2002;54:93–104. 10.1016/S0277-9536(01)00008-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lucksted A, Dixon LB, Sembly JB. A focus group pilot study of tobacco smoking among psychosocial rehabilitation clients. Psychiatr Serv 2000;51:1544–8. 10.1176/appi.ps.51.12.1544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Morris CD, Waxmonsky JA, May MG et al. . What do persons with mental illnesses need to quit smoking? Mental health consumer and provider perspectives. Psychiatr Rehabil J 2009;32:276–84. 10.2975/32.4.2009.276.284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Nawaz S, Frounfelker R, Ferron JC et al. . Smoking and quitting beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors among smokers with severe mental illness from three race/ethnicity groups. J Dual Diagn 2012;8:180–7. 10.1080/15504263.2012.697449 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Snyder M, McDevitt J, Painter S. Smoking cessation and serious mental illness. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 2008;22:297–304. 10.1016/j.apnu.2007.08.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Solway ES. The lived experiences of tobacco use, dependence, and cessation: insights and perspectives of people with mental illness. Health Soc Work 2011;36:19–32. 10.1093/hsw/36.1.19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Tsourtos G, Ward PR, Muller R et al. . The importance of resilience and stress to maintaining smoking abstinence and cessation: a qualitative study in Australia with people diagnosed with depression. Health Soc Care Community 2011;19:299–306. 10.1111/j.1365-2524.2010.00973.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Van Dongen CJ. Smoking and persistent mental illness: an exploratory study. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv 1999;37:26–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Asher MK, Martin RA, Rohsenow DJ et al. . Perceived barriers to quitting smoking among alcohol dependent patients in treatment. J Subst Abuse Treat 2003;24:169–74. 10.1016/S0740-5472(02)00354-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Clancy N, Zwar N, Richmond R. Depression, smoking and smoking cessation: a qualitative study. Fam Pract 2013;30:587–92. 10.1093/fampra/cmt032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Prochaska JJ, Fromont SC, Wa C et al. . Tobacco use and its treatment among young people in mental health settings: a qualitative analysis. Nicotine Tob Res 2013;15:1427–35. 10.1093/ntr/nts343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Orleans CT, Hutchinson D. Tailoring nicotine addiction treatments for chemical dependency patients. J Subst Abuse Treat 1993;10:197–208. 10.1016/0740-5472(93)90045-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Ratschen E, Britton J, Doody G et al. . Smoking attitudes, behaviour and nicotine dependence among mental health acute inpatients: an exploratory study. Int J Soc Psychiatry 2010;56:107–18. 10.1177/0020764008101855 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Arnsten JH, Reid K, Bierer M et al. . Smoking behavior and interest in quitting among homeless smokers. Addict Behav 2004;29:1155–61. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2004.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Connor SE, Cook RL, Herbert MI et al. . Smoking cessation in a homeless population: there is a will, but is there a way? J Gen Intern Med 2002;17:369–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Okuyemi KS, Caldwell AR, Thomas JL et al. . Homelessness and smoking cessation: insights from focus groups. Nicotine Tob Res 2006;8:287–96. 10.1080/14622200500494971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Dickens G, Stubbs J, Popham R et al. . Smoking in a forensic psychiatric service: a survey of inpatients’ views. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 2005;12:672–8; quiz 8 10.1111/j.1365-2850.2005.00892.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Richmond R, Butler T, Wilhelm K et al. . Tobacco in prisons: a focus group study. Tob Control 2009;18:176–82. 10.1136/tc.2008.026393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Lewis S, Russell A. Young smokers’ narratives: public health, disadvantage and structural violence. Sociol Health Illn 2013;35:746–60. 10.1111/j.1467-9566.2012.01527.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Garner L, Ratschen E. Tobacco smoking, associated risk behaviours, and experience with quitting: a qualitative study with homeless smokers addicted to drugs and alcohol. BMC Public Health 2013;13:951 10.1186/1471-2458-13-951 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Patten CA. Tobacco cessation intervention during pregnancy among Alaska Native women. J Cancer Educ 2012;27(Suppl 1):S86–90. 10.1007/s13187-012-0317-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Bott MJ, Cobb AK, Scheibmeir MS et al. . Quitting: smokers relate their experiences. Qual Health Res 1997;7:255–69. 10.1177/104973239700700206 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.File SE, Dinnis AK, Heard JE et al. . Mood differences between male and female light smokers and nonsmokers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2002;72:681–9. 10.1016/S0091-3057(02)00733-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Hajek P, Taylor T, McRobbie H. The effect of stopping smoking on perceived stress levels. Addiction 2010;105:1466–71. 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.02979.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mulder I, Tijhuis M, Smit HA et al. . Smoking cessation and quality of life: the effect of amount of smoking and time since quitting. Prev Med 2001;33:653–60. 10.1006/pmed.2001.0941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Carmody TP. Affect regulation, nicotine addiction, and smoking cessation. J Psychoactive Drugs 1992;24:111–22. 10.1080/02791072.1992.10471632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.DiFranza JR, Wellman RJ. A sensitization-homeostasis model of nicotine craving, withdrawal, and tolerance: integrating the clinical and basic science literature. Nicotine Tob Res 2005;7:9–26. 10.1080/14622200412331328538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Parrott AC. Does cigarette smoking cause stress? Am Psychol 1999;54:817–20. 10.1037/0003-066X.54.10.817 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Browning KK, Ferketich AK, Salsberry PJ et al. . Socioeconomic disparity in provider-delivered assistance to quit smoking. Nicotine Tob Res 2008;10:55–61. 10.1080/14622200701704905 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Aveyard P, Begh R, Parsons A et al. . Brief opportunistic smoking cessation interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare advice to quit and offer of assistance. Addiction 2012;107:1066–73. 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03770.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Stead LF, Buitrago D, Preciado N et al. . Physician advice for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;5:CD000165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Stead M, Angus K, Holme I et al. . Factors influencing European GPs’ engagement in smoking cessation: a multi-country literature review. Br J Gen Pract 2009;59:682–90. 10.3399/bjgp09X454007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Baker , et al. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005470.pub2. Tailored interventions to overcome identified barriers to change: effects on professional practice and health care outcomes. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews; 2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Bryant J, Bonevski B, Paul C et al. . Implementing a smoking cessation program in social and community service organisations: a feasibility and acceptability trial. Drug Alcohol Rev 2012;31:678–84. 10.1111/j.1465-3362.2011.00391.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Christiansen BA, Brooks M, Keller PA et al. . Closing tobacco-related disparities: using community organizations to increase consumer demand. Am J Prev Med 2010;38(3 Suppl):S397–402. 10.1016/j.amepre.2009.11.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Bell K, Salmon A, Bowers M et al. . Smoking, stigma and tobacco ‘denormalization’: further reflections on the use of stigma as a public health tool. A commentary on Social Science & Medicine's Stigma, Prejudice, Discrimination and Health Special Issue (67: 3). Soc Sci Med 2010;70:795–9; discussion 800-1 10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.09.060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Lavack L. Denormalization of tobacco in Canada. Soc Mark Q 1999;5:82–5. 10.1080/15245004.1999.9961068 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 130.El-Guebaly N, Cathcart J, Currie S et al. . Public health and therapeutic aspects of smoking bans in mental health and addiction settings. Psychiatr Serv 2002;53:1617–22. 10.1176/appi.ps.53.12.1617 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Williams JM, Ziedonis D. Addressing tobacco among individuals with a mental illness or an addiction. Addict Behav 2004;29:1067–83. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2004.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Ziedonis DM, Guydish J, Williams J et al. . Barriers and solutions to addressing tobacco dependence in addiction treatment programs. Alcohol Res Health 2006;29:228–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Frohlich KL, Mykhalovskiy E, Poland BD et al. . Creating the socially marginalised youth smoker: the role of tobacco control. Sociol Health Illn 2012;34:978–93. 10.1111/j.1467-9566.2011.01449.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Cosh S, Maksimovic L, Ettridge K et al. . Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander utilisation of the Quitline service for smoking cessation in South Australia. Australian J Primary Health 2013;19:113–18. 10.1071/PY11152 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Bramley D, Riddell T, Whittaker R et al. . Smoking cessation using mobile phone text messaging is as effective in Maori as non-Maori. N Z Med J 2005;118:U1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Daley CM, James AS, Barnoskie RS et al. . “Tobacco has a purpose, not just a past”: feasibility of developing a culturally appropriate smoking cessation program for a pan-tribal native population. Med Anthropol Q 2006;20:421–40. 10.1525/maq.2006.20.4.421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Richmond R, Indig D, Butler T et al. . A randomized controlled trial of a smoking cessation intervention conducted among prisoners. Addiction 2013;108:966–74. 10.1111/add.12084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Richmond RL, Butler T, Belcher JM et al. . Promoting smoking cessation among prisoners: feasibility of a multi-component intervention. Aust N Z J Public Health 2006;30:474–8. 10.1111/j.1467-842X.2006.tb00467.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Siru R, Hulse GK, Tait RJ. Assessing motivation to quit smoking in people with mental illness: a review. Addiction 2009;104:719–33. 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02545.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Dani JA, Harris RA. Nicotine addiction and comorbidity with alcohol abuse and mental illness. Nat Neurosci 2005;8:1465–70. 10.1038/nn1580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1759. Prochaska JJ. Integrating tobacco treatment into mental health settings. JAMA 2010;304:2534–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Shenton AK. Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Educ Inf 2004;22:63–75. [Google Scholar]
- 143.Ward PR, Muller R, Tsourtos G et al. . Additive and subtractive resilience strategies as enablers of biographical reinvention: a qualitative study of ex-smokers and never-smokers. Soc Sci Med 2011;72:1140–8. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.01.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143a.Lawn S, Hersh D, Ward PR et al. . ‘I just saw it as something that would pull you down, rather than lift you up’: resilience in never-smokers with mental illness. Health Educ Res 2011;26:26–38. 10.1093/her/cyq065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.McGee R, Williams S, Nada-Raja S et al. . Tobacco smoking in adolescence predicts maladaptive coping styles in adulthood. Nicotine Tob Res 2013;15:1971–7. 10.1093/ntr/ntt081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Gruskin EP, Greenwood GL, Matevia M et al. . Disparities in smoking between the lesbian, gay, and bisexual population and the general population in California. Am J Public Health 2007;97:1496–502. 10.2105/AJPH.2006.090258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Weber MF, Banks E, Sitas F. Smoking in migrants in New South Wales, Australia: report on data from over 100 000 participants in the 45 and Up Study. Drug Alcohol Rev 2011;30:597–605. 10.1111/j.1465-3362.2010.00247.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration OoAS. Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings Rockville, MD.: 2008 Contract No.: DHHS Publication No. SMA 08-4343.
- 148.Fazel S, Khosla V, Doll H et al. . The prevalence of mental disorders among the homeless in western countries: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. PLoS Med 2008;5:e225 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050225 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.