Abstract
Molecular events responsible for modulation of neoantigenic expressions of a defined molecule have been explored in relation to three hypothetical molecular models (see below). Fibrinogen and its cleavage-associated neoantigen have been used as a prototype system. Physicochemical and enzymatic factors influencing neoantigenic expression were evaluated. The cleavage-associated neoantigen was not only exposed by plasmin and enzymes of similar specificity, but also in a qualitatively and quantitatively deficient fashion by enzymes of differing specificities. Denaturation of fibrinogen via reduction or pH alteration did not induce the neoantigen, but oxidation of the native fibrinogen molecule did elicit this neoantigenic expression. The neoantigen, once exposed on the D-fragment, was relatively stable to physical and chemical denaturation. These results are inconsistent with proposed cleavage site specific and neoconformational determinant models and are consistent with a steric model, which postulates that the cleavage-associated neoantigenic determinant is buried in native fibrinogen but is exposed in certain altered molecular species. The importance of molecular conformation in the exposure of antigenic expressions of a molecule and in modulation of the binding affinity of a neoantigen for specific antibody is demonstrated.
Keywords: blood coagulation, fibrinogen cleavage products, fibrinolysis, molecular conformation
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTEL A. H., CAMPBELL D. H. Some immunochemical differences between associated and dissociated hemocyanin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN R. K. Studies on the antigenic structure of ribonuclease. III. Inhibition by peptides of antibody to performic acid-oxidized ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1162–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzyński A. Z., Stahl M., Kopeć M., Latallo Z. S., Wegrzynowicz Z., Kowalski E. High molecular weight products of the late stage of fibrinogen proteolysis by plasmin and their structural relation to the fibrinogen molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Schubert D., Schwartz S. A. Amino acid sequence studies on artiodactyl fibrinopeptides. I. Dromedary camel, mule deer, and cape buffalo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Feb;118(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W. Immunochemical specificity: recent conceptual advances. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIZAKA T., CAMPBELL D. H., ISHIZAKA K. Internal antigenic determinants in protein molecules. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:5–9. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latallo Z. S., Teisseyre E., Wegrzynowicz Z., Kopéc M. Degradation of fibrinogen by proteolytic enzymes. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1971;13:15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1971.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence T. G., Jr, Williams R. C., Jr Studies of human anti-gamma-globulin factors reacting with pepsin-digested gamma-globulins. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):233–248. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer H. I., Van Vunakis H. Immunochemical studies on carboxypeptidase A. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo Gerfo P., Krupey J., Hansen H. J. Demonstration of an antigen common to several varieties of neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 15;285(3):138–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107152850302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. P., Sanchez-Avalos J. Degradation of fibrinogen by proteolytic enzymes. II. Effect of the products on coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Nov 15;20(1):15–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niléhn J. E. Split products of fibrinogen after prolonged interaction with plasmin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Aug 15;18(1-2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTERLAND C. K., HARBOE M., KUNKEL H. G. Anti-gamma-globulin factors in human sera revealed by enzymatic splitting of anti-Rh antibodies. Vox Sang. 1963 Mar-Apr;8:133–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K. Properties of leucocytic protease. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 May;32(3):399–405. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
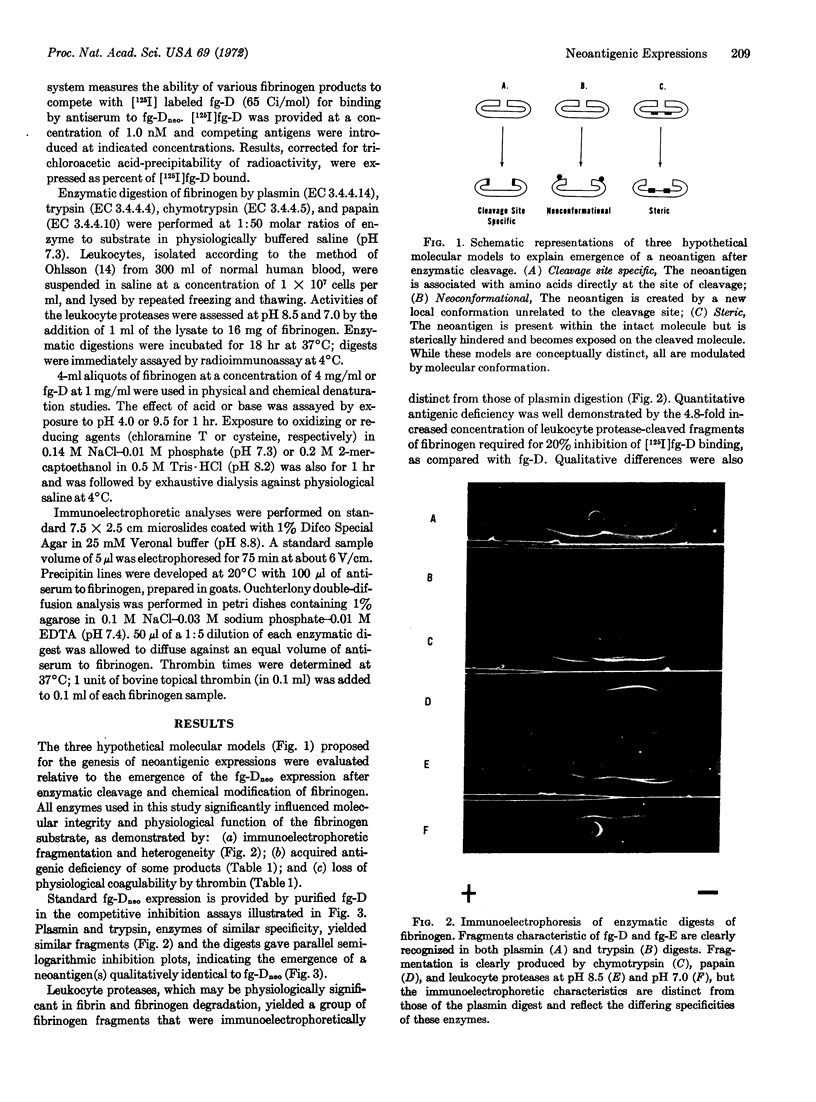
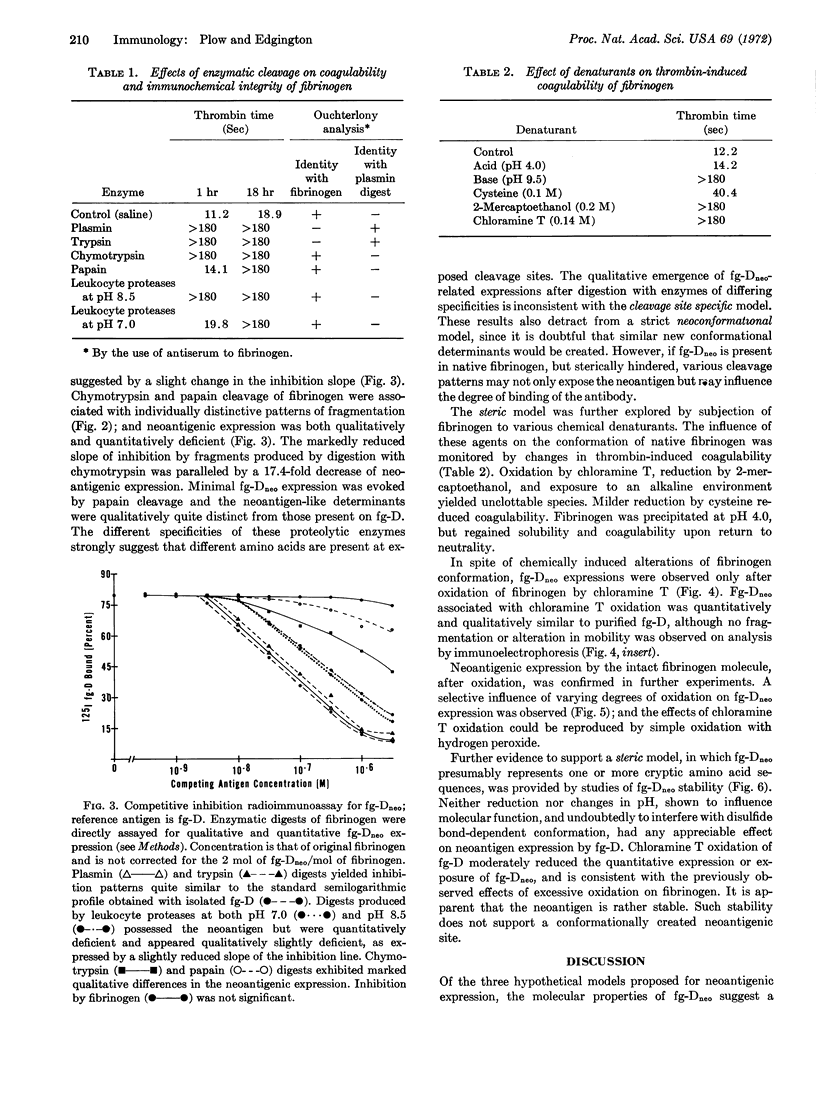
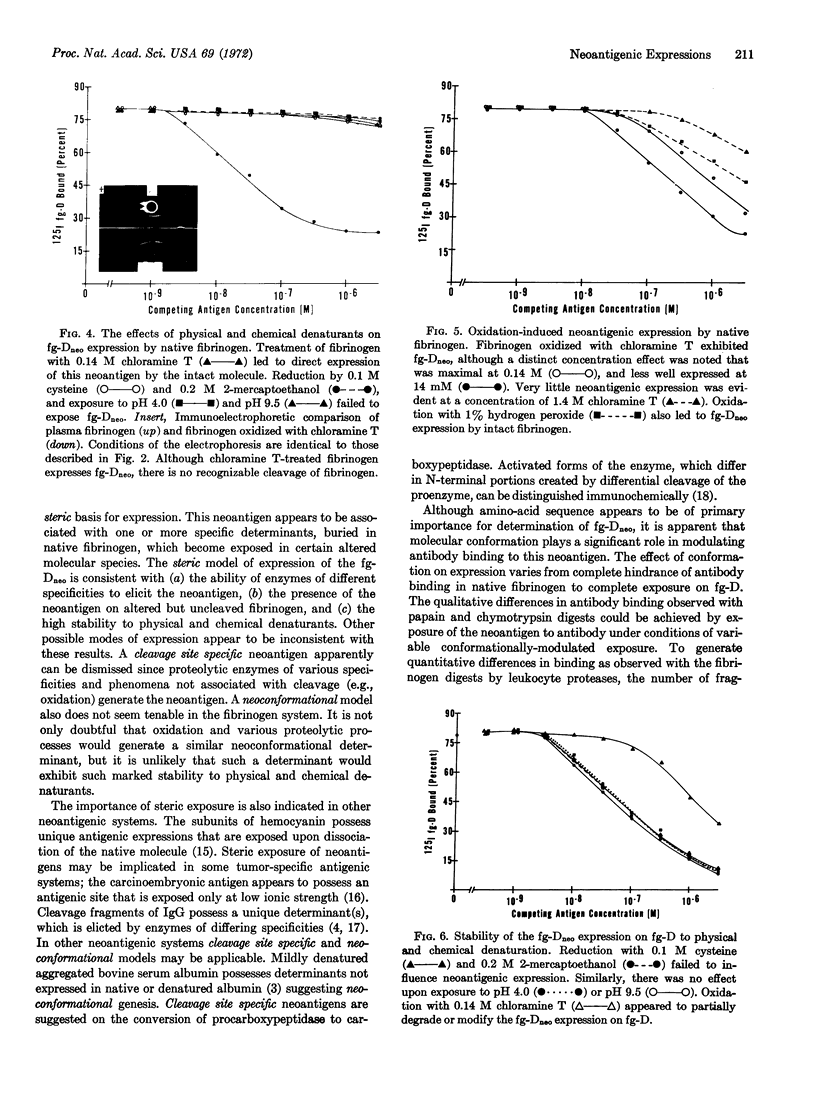
- Plow E. F., Hougie C., Edgington T. S. Neoantigenic expressions engendered by plasmin cleavage of fibrinogen. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1496–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela M. Antigenicity: some molecular aspects. Science. 1969 Dec 12;166(3911):1365–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3911.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., Liu C. T., Adler F. L. Passive hemagglutination. II. Titration of antibody against determinants unique for aggregated denatured bovine serum albumin and further studies on gelatin. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):797–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]