Abstract
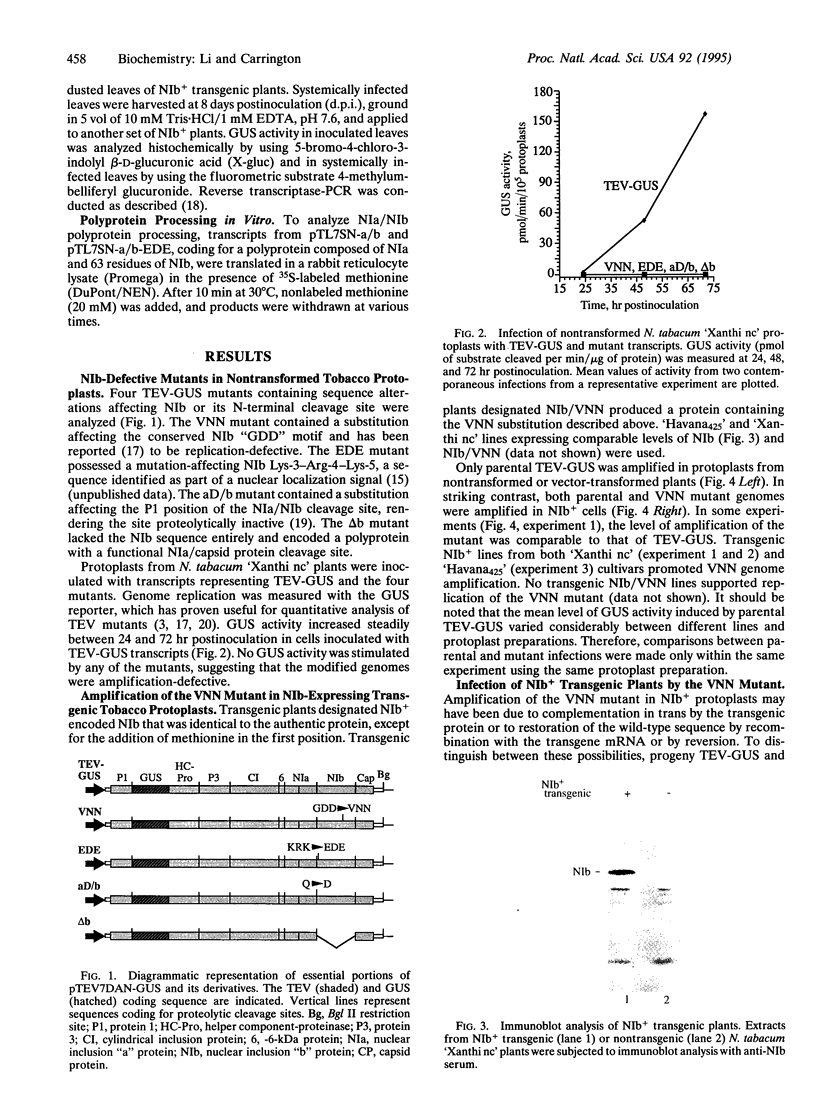
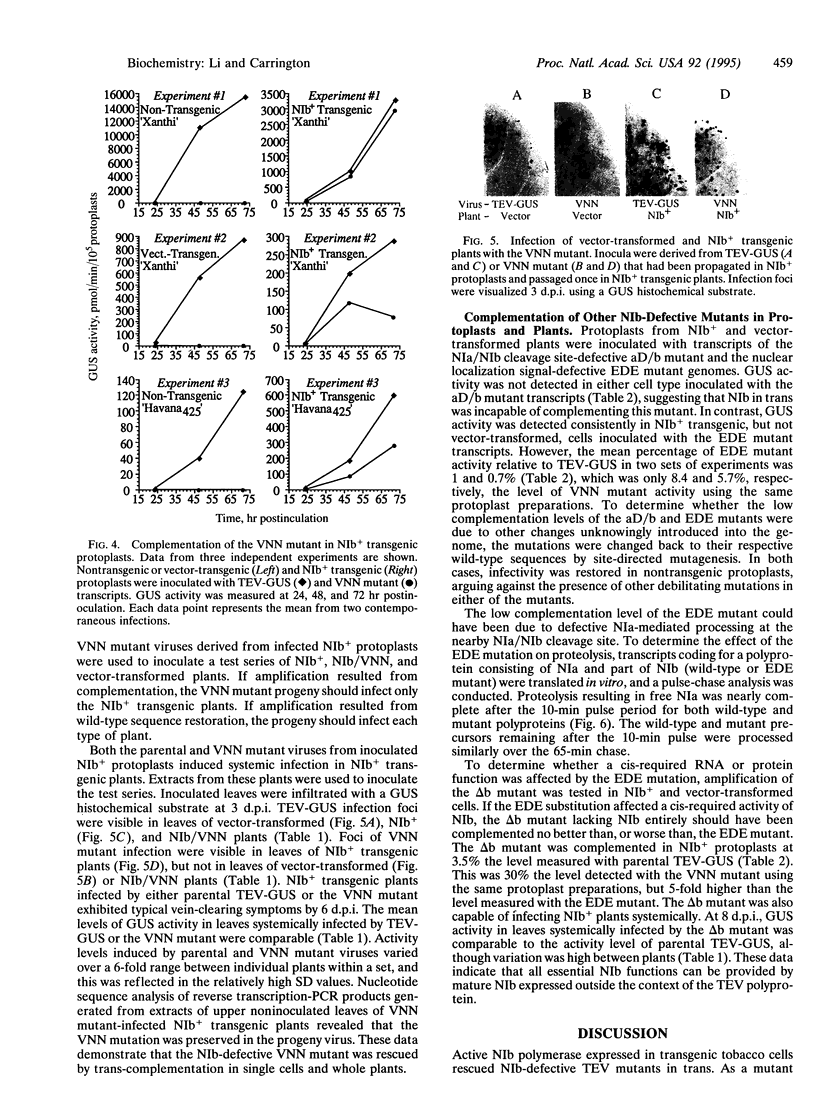
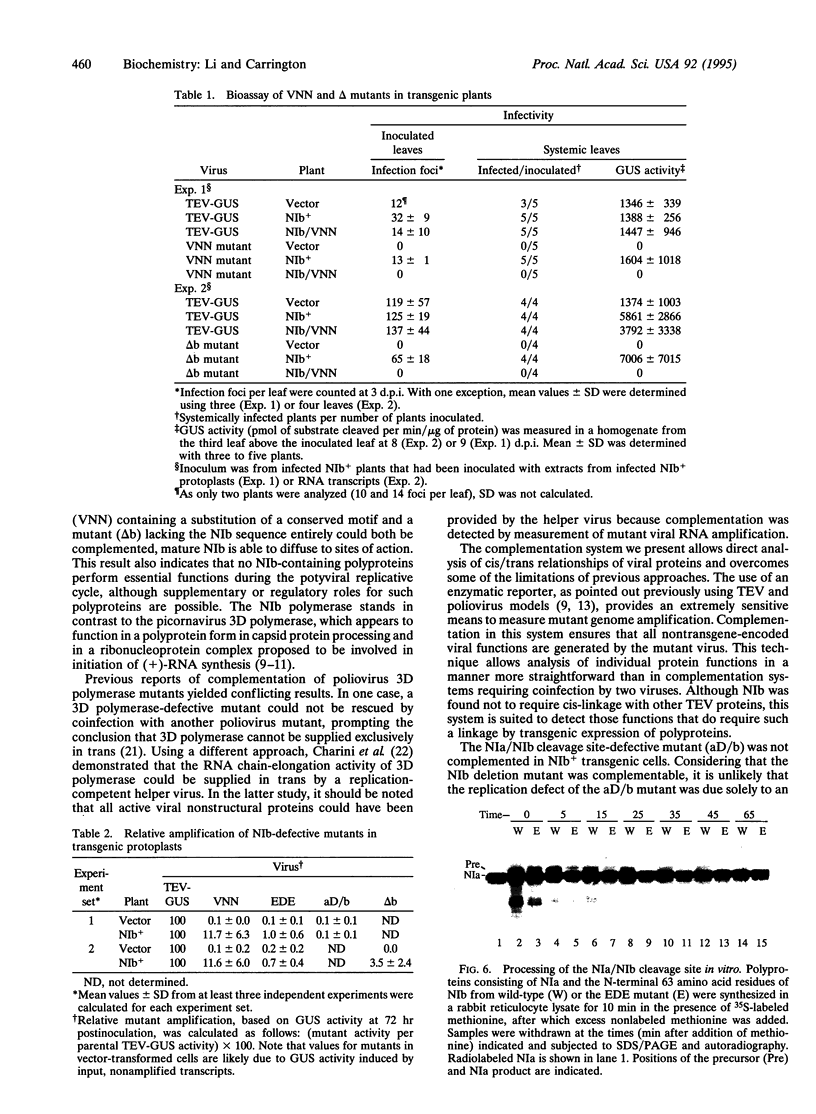
A genetic complementation system was developed in which tobacco etch virus (TEV) polymerase (NIb)-expressing transgenic plants or protoplasts were inoculated with NIb-defective TEV mutants. A beta-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene integrated into the genomes of parental and four mutant viruses was used to assay RNA amplification. Two mutants (termed VNN and EDE) contained substitutions affecting the conserved "GDD" polymerase motif or a nuclear localization signal sequence, respectively; one (aD/b) contained a mutation debilitating the NIb N-terminal cleavage site, whereas the other (delta b) lacked the entire NIb sequence. Each mutant was unable to amplify in nontransformed tobacco protoplasts. In contrast, the VNN, EDE, and delta b mutants were complemented to various degrees in NIb-expressing cells, whereas the aD/b mutant was not complemented. The VNN mutant was complemented most efficiently, reaching an average of 11-12% the level of parental TEV-GUS, although in some experiments the level was near 100%. This mutant also replicated in, and spread through, whole transgenic plants to the same level as parental virus. The EDE mutant was complemented relatively poorly, reaching 1% or less of the level of parental TEV-GUS. Despite the close proximity of the EDE substitution to the N-terminal cleavage site, proteolytic processing of NIb was unaffected in an in vitro assay. The delta b mutant was complemented to an intermediate degree in protoplasts, reaching 3.5% the level of parental virus, and replicated and moved systemically in transgenic plants. These data indicate that free NIb supplied entirely in trans can provide all NIb functions essential for RNA amplification. The relative inefficient complementation of the EDE mutant suggests that the resulting mutant protein was transinhibitory.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Achacoso P. L., Baltimore D. Poliovirus RNA synthesis utilizes an RNP complex formed around the 5'-end of viral RNA. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3587–3598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audy P., Palukaitis P., Slack S. A., Zaitlin M. Replicase-mediated resistance to potato virus Y in transgenic tobacco plants. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1994 Jan-Feb;7(1):15–22. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-7-0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Dougherty W. G. Mutational analysis of tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing: cis and trans proteolytic activities of polyproteins containing the 49-kilodalton proteinase. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2313–2320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2313-2320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Haldeman R., Dolja V. V., Restrepo-Hartwig M. A. Internal cleavage and trans-proteolytic activities of the VPg-proteinase (NIa) of tobacco etch potyvirus in vivo. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):6995–7000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.6995-7000.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charini W. A., Burns C. C., Ehrenfeld E., Semler B. L. trans rescue of a mutant poliovirus RNA polymerase function. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2655–2665. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2655-2665.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolja V. V., Haldeman R., Robertson N. L., Dougherty W. G., Carrington J. C. Distinct functions of capsid protein in assembly and movement of tobacco etch potyvirus in plants. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1482–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolja V. V., Herndon K. L., Pirone T. P., Carrington J. C. Spontaneous mutagenesis of a plant potyvirus genome after insertion of a foreign gene. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):5968–5975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.5968-5975.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolja V. V., McBride H. J., Carrington J. C. Tagging of plant potyvirus replication and movement by insertion of beta-glucuronidase into the viral polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorssers L., van der Krol S., van der Meer J., van Kammen A., Zabel P. Purification of cowpea mosaic virus RNA replication complex: Identification of a virus-encoded 110,000-dalton polypeptide responsible for RNA chain elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1951–1955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty W. G., Cary S. M., Parks T. D. Molecular genetic analysis of a plant virus polyprotein cleavage site: a model. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):356–364. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemboski D. B., Lomonossoff G. P., Zaitlin M. Plants transformed with a tobacco mosaic virus nonstructural gene sequence are resistant to the virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6311–6315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jore J., De Geus B., Jackson R. J., Pouwels P. H., Enger-Valk B. E. Poliovirus protein 3CD is the active protease for processing of the precursor protein P1 in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1627–1636. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Ahlquist P. Identification of the domains required for direct interaction of the helicase-like and polymerase-like RNA replication proteins of brome mosaic virus. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7293–7302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7293-7302.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. RNA helicase: a novel activity associated with a protein encoded by a positive strand RNA virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7003–7006. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. H., Carrington J. C. Nuclear transport of tobacco etch potyviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is highly sensitive to sequence alterations. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):951–958. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martín M. T., García J. A. Plum pox potyvirus RNA replication in a crude membrane fraction from infected Nicotiana clevelandii leaves. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):785–790. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T. D., Smith H. A., Dougherty W. G. Cleavage profiles of tobacco etch virus (TEV)-derived substrates mediated by precursor and processed forms of the TEV NIa proteinase. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):149–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo-Hartwig M. A., Carrington J. C. The tobacco etch potyvirus 6-kilodalton protein is membrane associated and involved in viral replication. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2388–2397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2388-2397.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann J. L., Laín S., García J. A. Highlights and prospects of potyvirus molecular biology. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahabuddin M., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. Mapping of the tobacco vein mottling virus VPg cistron. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):635–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]