Abstract
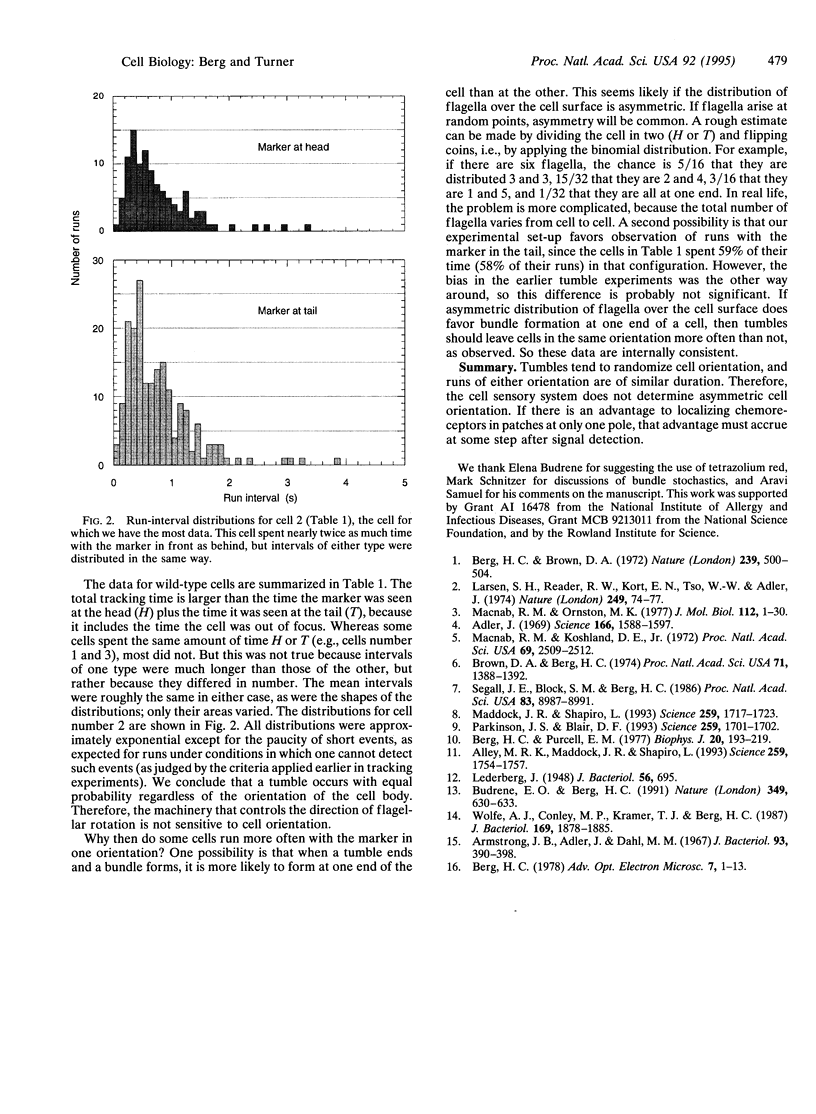
Chemotactic cells of the bacterium Escherichia coli were marked asymmetrically by growth on a rich medium containing tetrazolium red. When this dye is reduced, it tends to form a refractile granule near one end of the cell, readily visualized by dark-field microscopy. In smooth-swimming cells, the marker was found with equal probability in front or behind. In wild-type cells, tumbles changed the cell orientation nearly as often as not. Some cells formed flagellar bundles at one end more frequently than at the other, but the run-interval distributions were the same either way. We conclude that the sensory system does not favor one end of the cell over the other. Thus, chemoreceptors that appear in patches at only one pole do not serve as a nose.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley M. R., Maddock J. R., Shapiro L. Requirement of the carboxyl terminus of a bacterial chemoreceptor for its targeted proteolysis. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1754–1757. doi: 10.1126/science.8456303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Purcell E. M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys J. 1977 Nov;20(2):193–219. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85544-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Berg H. C. Temporal stimulation of chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budrene E. O., Berg H. C. Complex patterns formed by motile cells of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):630–633. doi: 10.1038/349630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. Detection of Fermentative Variants with Tetrazolium. J Bacteriol. 1948 Nov;56(5):695–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.5.695-695.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddock J. R., Shapiro L. Polar location of the chemoreceptor complex in the Escherichia coli cell. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1717–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.8456299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Blair D. F. Does E. coli have a nose? Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1701–1702. doi: 10.1126/science.8456297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Block S. M., Berg H. C. Temporal comparisons in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8987–8991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Kramer T. J., Berg H. C. Reconstitution of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1878–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1878-1885.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





