Abstract
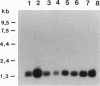
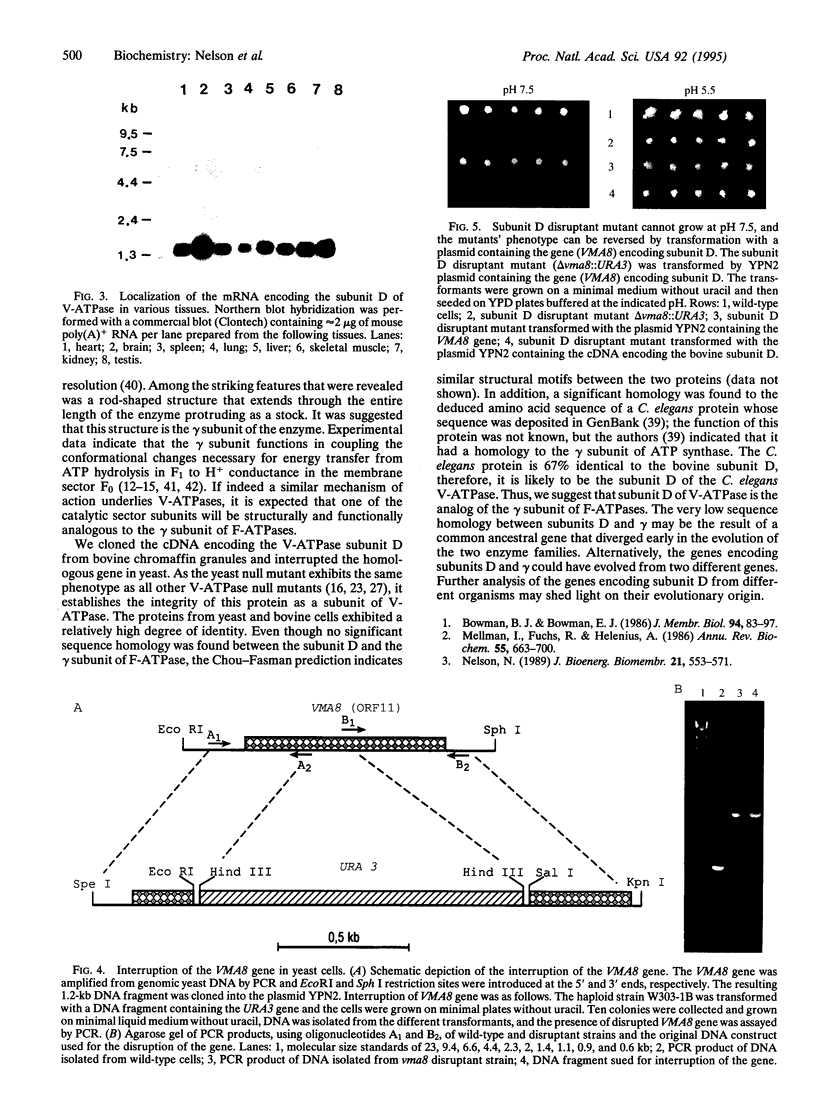
Subunit D of vacuolar H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) from bovine chromaffin granules was subjected to partial proteolysis and amino acid sequencing. A cDNA encoding this subunit was isolated and sequenced. The predicted open reading frame encodes a protein of 247 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 28,336. Northern blot analysis revealed an mRNA distribution with higher transcript amounts in tissues that are active in secretion. A homologous gene was identified as open reading frame 11 in chromosome V of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The two proteins exhibit 55% identity with several conservative replacements. Interruption of the yeast gene, denoted as VMA8, resulted in the null mutant delta vma8::URA3 that, like all the other V-ATPase null mutants, did not grow on medium buffered at pH 7.5 and showed no accumulation of quinacrine into their vacuoles. Transformation of the null mutant with a plasmid containing the VMA8 gene restored the wild-type phenotype. This supports the conclusion that subunit D is an integral subunit of the catalytic sector of V-ATPase and its structural analysis suggests analogy to the gamma subunit of F-ATPases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams J. P., Lutter R., Todd R. J., van Raaij M. J., Leslie A. G., Walker J. E. Inherent asymmetry of the structure of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria at 6.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1775–1780. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Terres G., Pink S., Forgac M. Topography and subunit stoichiometry of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8796–8802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán C., Kopecky J., Pan Y. C., Nelson H., Nelson N. Cloning and mutational analysis of the gene encoding subunit C of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):774–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Bowman E. J. H+-ATPases from mitochondria, plasma membranes, and vacuoles of fungal cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01871190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denda K., Konishi J., Hajiro K., Oshima T., Date T., Yoshida M. Structure of an ATPase operon of an acidothermophilic archaebacterium, Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21509–21513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denda K., Konishi J., Oshima T., Date T., Yoshida M. The membrane-associated ATPase from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius is distantly related to F1-ATPase as assessed from the primary structure of its alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6012–6015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger B. O. Adaptation of the Bradford protein assay to membrane-bound proteins by solubilizing in glucopyranoside detergents. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):765–796. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F. The 31-kDa polypeptide is an essential subunit of the vacuolar ATPase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18554–18560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Noumi T., Maeda M. ATP synthase (H+-ATPase): results by combined biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:111–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräf R., Lepier A., Harvey W. R., Wieczorek H. A novel 14-kDa V-ATPase subunit in the tobacco hornworm midgut. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3767–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata R., Ohsumk Y., Nakano A., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Anraku Y. Molecular structure of a gene, VMA1, encoding the catalytic subunit of H(+)-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6726–6733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Strauss A., Masood K., Lee S., Sukhatme V., Gluck S. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the 31-kDa subunit of bovine kidney vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. N., Hirata R., Umemoto N., Ohya Y., Takatsuki A., Stevens T. H., Anraku Y. VMA13 encodes a 54-kDa vacuolar H(+)-ATPase subunit required for activity but not assembly of the enzyme complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18286–18292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketcham S. R., Davenport J. W., Warncke K., McCarty R. E. Role of the gamma subunit of chloroplast coupling factor 1 in the light-dependent activation of photophosphorylation and ATPase activity by dithiothreitol. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7286–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. Cold inactivation of vacuolar proton-ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3577–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. The purified ATPase from chromaffin granule membranes is an anion-dependent proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9175–9180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Mandiyan S., Nelson N. A conserved gene encoding the 57-kDa subunit of the yeast vacuolar H+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1775–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Mandiyan S., Nelson N. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae VMA7 gene encodes a 14-kDa subunit of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase catalytic sector. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24150–24155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Mandiyan S., Noumi T., Moriyama Y., Miedel M. C., Nelson N. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the C subunit of H(+)-ATPase from bovine chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20390–20393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Nelson N. Disruption of genes encoding subunits of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase causes conditional lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3503–3507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Evolution of organellar proton-ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 May 20;1100(2):109–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(92)90072-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Organellar proton-ATPases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90086-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, molecular genetics, and evolution of vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Oct;21(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00808113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Taiz L. The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noumi T., Beltrán C., Nelson H., Nelson N. Mutational analysis of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1938–1942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puopolo K., Kumamoto C., Adachi I., Magner R., Forgac M. Differential expression of the "B" subunit of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase in bovine tissues. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3696–3706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E. The proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:7–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. B., Gibson K. D., Scheraga H. A., McCarty R. E. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer mapping of the fourth of six nucleotide-binding sites of chloroplast coupling factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17276–17285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solioz M., Davies K. Operon of vacuolar-type Na(+)-ATPase of Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9453–9459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Fried V. A., Stone D. K., Johnston P. A., Xie X. S. Human endomembrane H+ pump strongly resembles the ATP-synthetase of Archaebacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6067–6071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takase K., Kakinuma S., Yamato I., Konishi K., Igarashi K., Kakinuma Y. Sequencing and characterization of the ntp gene cluster for vacuolar-type Na(+)-translocating ATPase of Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11037–11044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Moriyama Y., Mandel M., Hulmes J. D., Pan Y. C., Danho W., Nelson H., Nelson N. Cloning of cDNA encoding a 32-kDa protein. An accessory polypeptide of the H+-ATPase from chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17638–17642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]