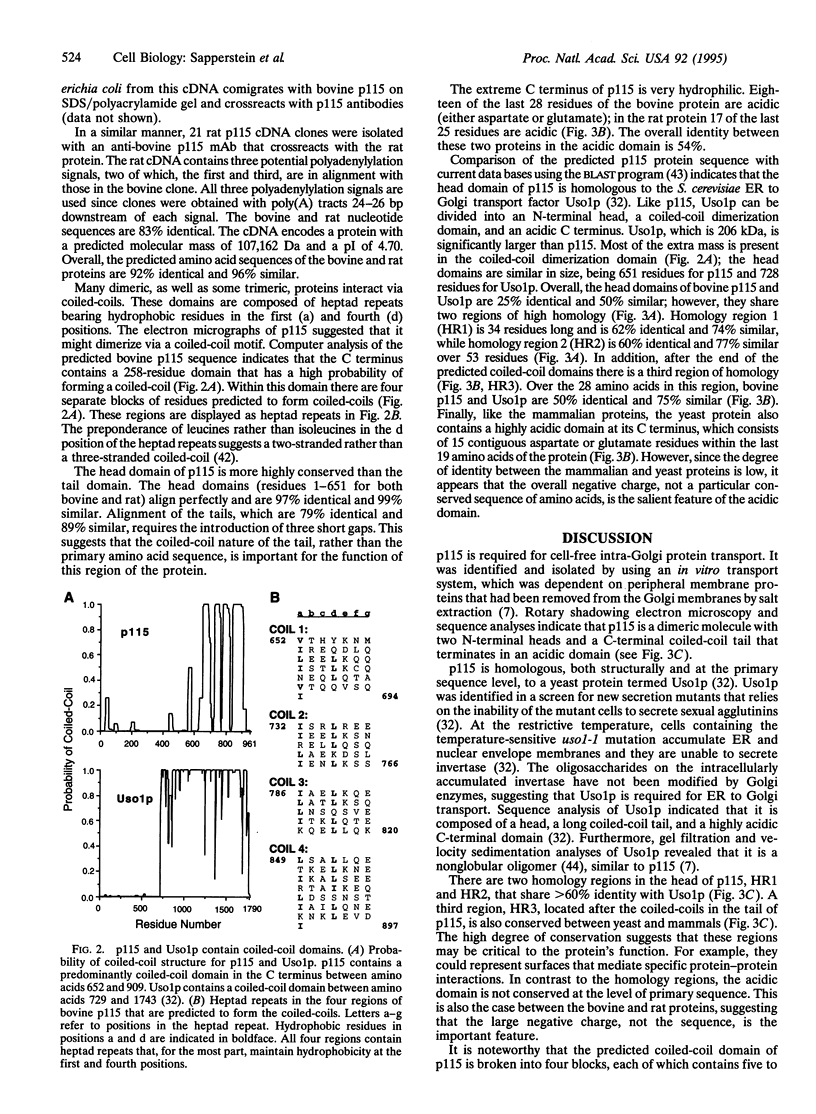
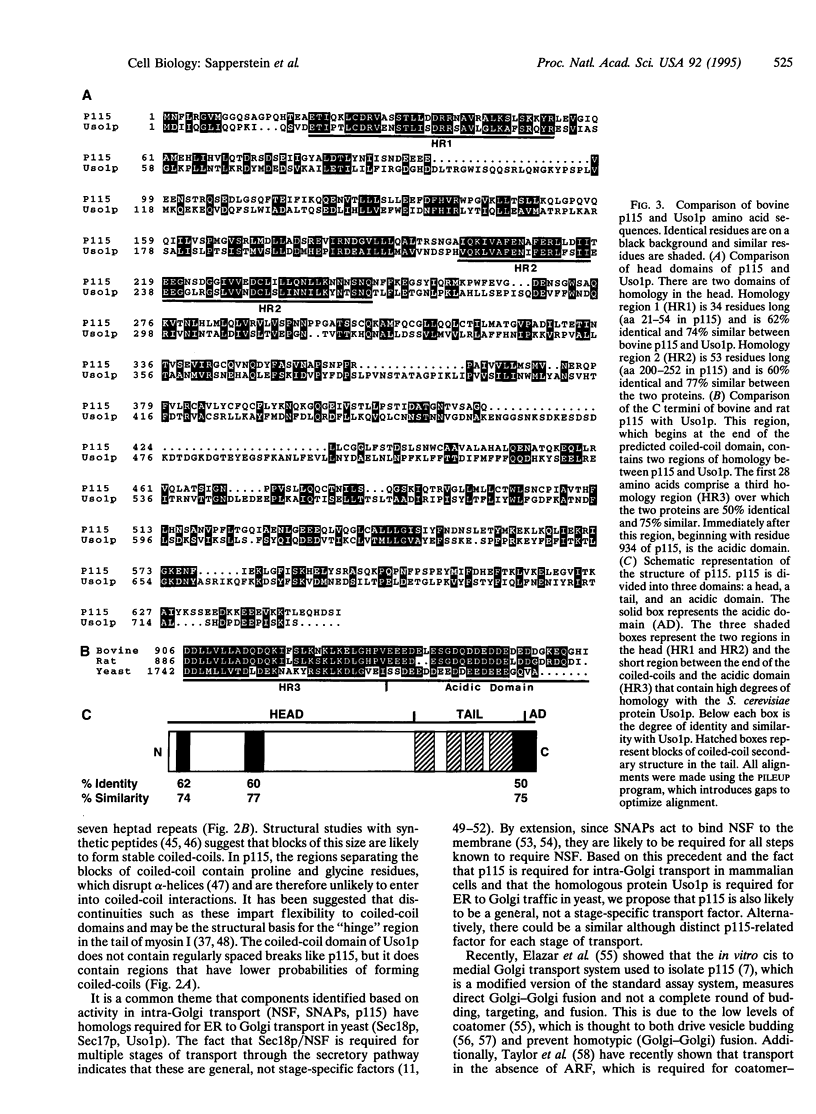
Abstract
A recently discovered vesicular transport factor, termed p115, is required along with N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) and soluble NSF attachment proteins for in vitro Golgi transport. p115 is a peripheral membrane protein found predominantly on the Golgi. Biochemical and electron microscopic analyses indicate that p115 is an elongated homodimer with two globular "heads" and an extended "tail" reminiscent of myosin II. We have cloned and sequenced cDNAs for bovine and rat p115. The predicted translation products are 90% identical, and each can be divided into three domains. The predicted 108-kDa bovine protein consists of an N-terminal 73-kDa globular domain followed by a 29-kDa coiled-coil dimerization domain, a linker segment of 4 kDa, and a highly acidic domain of 3 kDa. p115 is related to Uso1p, a protein required for endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicular transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which has a similar "head-coil-acid" domain structure. The p115 and Uso1p heads are similar in size, have approximately 25% sequence identity, and possess two highly homologous regions (62% and 60% identity over 34 and 53 residues, respectively). There is a third region of homology (50% identity over 28 residues) between the coiled-coil and acidic domains. Although the acidic nature of the p115 and Uso1p C termini is conserved, the primary sequence is not. We discuss these results in light of the proposed function of p115 in membrane targeting and/or fusion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark I. C. Structure of the chicken gene for SNAP-25 reveals duplicated exon encoding distinct isoforms of the protein. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):67–76. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barroso M., Nelson D. S., Sztul E. Transcytosis-associated protein (TAP)/p115 is a general fusion factor required for binding of vesicles to acceptor membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):527–531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Block M. R., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E., Balch W. E. Vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stack requires the NEM-sensitive fusion protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):397–398. doi: 10.1038/339397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. The molecular machinery for secretion is conserved from yeast to neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Griff I. C., Rothman J. E. SNAPs, a family of NSF attachment proteins involved in intracellular membrane fusion in animals and yeast. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):709–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90482-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. Purification of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment proteins from bovine brain microsomes. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:319–330. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. Purification of three related peripheral membrane proteins needed for vesicular transport. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):10109–10117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Mayorga L. S., Weidman P. J., Rothman J. E., Stahl P. D. Vesicle fusion following receptor-mediated endocytosis requires a protein active in Golgi transport. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):398–400. doi: 10.1038/339398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Pfeffer S. R., Clary D. O., Wattenberg B. W., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Yeast and mammals utilize similar cytosolic components to drive protein transport through the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Bernstein M., Emr S. D. Characterization of a component of the yeast secretion machinery: identification of the SEC18 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4098–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Orci L., Ostermann J., Amherdt M., Tanigawa G., Rothman J. E. ADP-ribosylation factor and coatomer couple fusion to vesicle budding. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):415–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink L. A., Trimble W. S., Scheller R. H. Two vesicle-associated membrane protein genes are differentially expressed in the rat central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11061–11064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Emr S. D. Compartmental organization of Golgi-specific protein modification and vacuolar protein sorting events defined in a yeast sec18 (NSF) mutant. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):207–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griff I. C., Schekman R., Rothman J. E., Kaiser C. A. The yeast SEC17 gene product is functionally equivalent to mammalian alpha-SNAP protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12106–12115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. B., Zhang T., Kim P. S., Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1401–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.8248779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick K. G., Pelham H. R. SED5 encodes a 39-kD integral membrane protein required for vesicular transport between the ER and the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):513–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E. Procedure for freeze-drying molecules adsorbed to mica flakes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):155–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Murofushi H., Okuhara K., Sato R., Masuda Y., Sakai H., Hirokawa N. The molecular structure of adrenal medulla kinesin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):264–272. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. S., Semchuk P. D., Taneja A. K., Kay C. M., Parker J. M., Mant C. T. Protein design using model synthetic peptides. Pept Res. 1988 Sep-Oct;1(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosobuchi M., Kreis T., Schekman R. SEC21 is a gene required for ER to Golgi protein transport that encodes a subunit of a yeast coatomer. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):603–605. doi: 10.1038/360603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Orci L., Glick B. S., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Role of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive transport component in promoting fusion of transport vesicles with cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90554-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Hirata A., Ogawa Y., Yonehara T., Yoda K., Yamasaki M. A cytoskeleton-related gene, uso1, is required for intracellular protein transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):245–260. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oas T. G., Endow S. A. Springs and hinges: dynamic coiled coils and discontinuities. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orcl L., Palmer D. J., Amherdt M., Rothman J. E. Coated vesicle assembly in the Golgi requires only coatomer and ARF proteins from the cytosol. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):732–734. doi: 10.1038/364732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyler G. A., Higgins G. A., Hart R. A., Battenberg E., Billingsley M., Bloom F. E., Wilson M. C. The identification of a novel synaptosomal-associated protein, SNAP-25, differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3039–3052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R. Clues to brain function from bakers' yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):1987–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryer N. K., Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. Vesicle-mediated protein sorting. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:471–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Warren G. Implications of the SNARE hypothesis for intracellular membrane topology and dynamics. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):220–233. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seog D. H., Kito M., Igarashi K., Yoda K., Yamasaki M. Molecular characterization of the USO1 gene product which is essential for vesicular transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):647–653. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns T., Willingham M. C., Botstein D., Kahn R. A. ADP-ribosylation factor is functionally and physically associated with the Golgi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1238–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenbeck G., Schreiner R., Herrmann D., Auerbach S., Lottspeich F., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. Gamma-COP, a coat subunit of non-clathrin-coated vesicles with homology to Sec21p. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 14;314(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80973-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztul E., Colombo M., Stahl P., Samanta R. Control of protein traffic between distinct plasma membrane domains. Requirement for a novel 108,000 protein in the fusion of transcytotic vesicles with the apical plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1876–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor T. C., Kanstein M., Weidman P., Melançon P. Cytosolic ARFs are required for vesicle formation but not for cell-free intra-Golgi transport: evidence for coated vesicle-independent transport. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Feb;5(2):237–252. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Spudich J. A. Myosin structure and function in cell motility. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:379–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Clary D. O., Rothman J. E. A novel 115-kD peripheral membrane protein is required for intercisternal transport in the Golgi stack. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1015–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Serafini T., Rothman J. E. 'Coatomer': a cytosolic protein complex containing subunits of non-clathrin-coated Golgi transport vesicles. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):248–251. doi: 10.1038/349248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman P. J., Melançon P., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Binding of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein to Golgi membranes requires both a soluble protein(s) and an integral membrane receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1589–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Whiteheart S. W., Wiedmann M., Brunner M., Rothman J. E. A multisubunit particle implicated in membrane fusion. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):531–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Wilcox C. A., Flynn G. C., Chen E., Kuang W. J., Henzel W. J., Block M. R., Ullrich A., Rothman J. E. A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):355–359. doi: 10.1038/339355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]