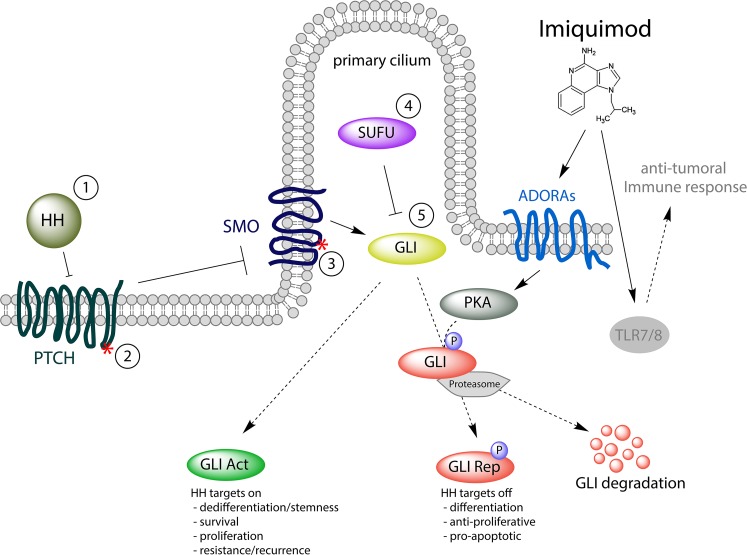
Figure 1. IMQ represses HH/GLI signaling via ADORA/PKA activation.
Classical Hedgehog (HH) signaling is activated by secreted HH protein binding to its receptor PTCH (1). In cancer, loss of function mutations in PTCH (2), activating mutations in SMO (3), genetic loss of SUFU (4) or GLI1/2 amplification/overexpression (5) result in aberrant HH signaling and an increased GLI activator (GLI Act) to GLI repressor (GLI Rep) ratio, inducing HH target gene expression (e.g. GLI1, HHIP) and oncogenic transformation. Imiquimod (IMQ) activates Protein Kinase A (PKA) by engaging adenosine receptors (ADORAs), leading to GLI phosphorylation and functional inactivation via proteasome-mediated GLI repressor formation and/or GLI degradation. We propose that IMQ can block HH signaling in all pathway-activating events illustrated, even in settings where SMO inhibitors may no longer be effective (i.e. in settings 4 and 5, where GLI activation occurs in a SMO-independent manner, including GLI activation by other oncogenic pathways, for details see main text).