Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to observe the efficacy and toxicities of capecitabine-based chemotherapy and capecitabine monotherapy as maintenance therapy in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
Patients and methods
A total of 98 MBC patients were treated with capecitabine combined with vinorelbine (NX).
Results
The median number of treatment was 6 cycles (1-7 cycles). There were two cases of complete remission (CR), 58 partial remission, 27 stable disease (SD), 11 progression disease. The overall response rate (ORR) (CR + PR) was 61.2%. The clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 75.5%. Fifty of effective patients received with capecitabine monotherapy as maintenance therapy. The ORR (CR + PR) was 4%. The CBR was 48%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12 months. In maintenance therapy or not, the median post metastasis survival rate (MSR) was 63 and 28 months, respectively. In the combination therapy group, the major grade 3/4 toxicities included hand-foot syndrome (3.1%), skin pigmentation (2.0%), diarrhoea and abdominal distension (5.1%), stomatitis (1.0%), and leukopenia (20.4%).
Conclusions
Capecitabine-based combination therapy and single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy were well tolerated and effective to MBC.
Keywords: Metastatic breast cancer (MBC), capecitabine, maintenance therapy
Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common non-cutaneous malignancy, accounting for nearly one in three cancers diagnosed among women in the United States, and the second leading cause of cancer death around the world (1,2), 20% of patients with lymph node-negative breast cancer and 50-60% of patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer suffer from tumor metastasis within 5 years after surgery (3,4). Since metastatic breast cancer (MBC) still cannot be cured, the objectives were to extend the overall survival, relieve tumor-related symptoms, and delay tumor progression while maintaining the optimal quality of life (5).
Along with the wide application of anthracyclines or taxanes as the adjuvant chemotherapy or front-line and salvage chemotherapy regimens for advanced breast cancer, the salvage treatment for the anthracycline- or taxane-resistant advanced breast cancer has become a major challenge for medical oncologists (6). Capecitabine (Xeloda) is a novel oral a fluoropyrimidine carbamate with cytotoxic activity. It can be rapidly absorbed, with low toxicity (7). When used alone or in combination with many other chemotherapy drugs, it is effective for advanced breast cancer (7,8). As a maintenance therapy for MBC, capecitabine can significantly prolong the patients’ survival time and improve the quality of life (9).
In the current study, we tried to detect the efficacy and safety of capecitabine combined with vinorelbine in treating MBC as well as the capecitabine monotherapy for maintenance treatment after the effective combination therapy.
Patients and methods
Patients
A total of 98 MBC patients who had received capecitabine combined with vinorelbine (among whom 50 received capecitabine monotherapy as maintenance therapy) in the Department of Breast Diseases, Henan Cancer Hospital, from December 2009 to December 2013, were studied. Eligibility criteria included the patients preferred chemotherapy; prior anthracycline- and taxane-based therapies failed; HER2-positive patients could not afford the trastuzumab (Herceptin)-based targeted therapy; previous endocrine therapy failed in hormone receptor-positive patients. All the patients were women, with a median age of 53 years. In these subjects, there were at least one measurable lesion, and routine liver function, kidney function, blood, and urine tests showed that there was no contraindication for chemotherapy. Their Karnofsky performance status (KPS) scores were ≥70 (Table 1).
Table 1. Clinical data of 98 patients with metastatic breast cancer.
| Clinical features | Combination group, n (%) | X maintenance group, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≥60 years | 18 (18.4) | 13 (26.0) |
| <60 years | 80 (81.6) | 37 (74.0) |
| Hormone receptor | ||
| Positive | 53 (54.1) | 31 (62.0) |
| Negative | 45 (45.9) | 19 (38.0) |
| Her-2 | ||
| Positive | 43 (43.9) | 22 (44.0) |
| Negative | 55 (56.1) | 28 (56.0) |
| Previous treatment | ||
| First-line | 53 (54.1) | 30 (60.0) |
| Second-line and above | 45 (45.9) | 20 (40.0) |
| Metastatic sites | ||
| Viscera | 77 (78.6) | 39 (78.0) |
| Non-viscera | 21 (21.4) | 11 (22.0) |
| DFS | ||
| >2 years | 44 (44.9) | 23 (46.0) |
| ≤2 years | 54 (55.1) | 27 (54.0) |
X, capecitabine; DFS, disease-free survival.
Treatment
A total of 98 patients received the combination treatment using capecitabine and vinorelbine, among whom 43 were HER2-positive, 22 further received the maintenance treatment. All did not receive the trastuzumab (Herceptin)-based targeted therapy due to economic concerns. The dosages in the combination group were as follows: capecitabine 1,000 mg/m2, orally, twice daily, d 1-d 14; and vinorelbine 25 mg/m2, d 1 and d 8, 21 days as one cycle. Patients in the combination group with a disease control rate (CR + PR + SD) ≥6 months entered the maintenance group: capecitabine 1,000 mg/m2, orally, twice daily, d 1-d 14, 21 days as one cycle.
Statistical analysis
The therapeutic efficacy was evaluated using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.0 every two cycles. The efficacy was evaluated as complete remission (CR), partial responses (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD). The overall response rate (ORR) = (CR + PR)/case number ×100%; clinical benefit rate (CBR) = (CR + PR + SD) ≥6 months/case number ×100%. The progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time elapsed between combined treatment initiation and tumor progression, loss to follow-up, or death during the combination therapy or maintenance therapy. The post-metastasis survival (PMS) was defined as the time elapsed between the first onset of metastasis and loss to follow-up/death. The National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events was applied in this study.
Statistical analysis was performed using 17.0 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Particularly, the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed, and univariate analysis of prognostic factors was performed using the log-rank test. A value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Efficacy and safety
A total of 98 MBC patients completed 1-7 cycles of chemotherapy (median, 6 cycles); all these patients were regarded as evaluable cases. Upon the completion of the 1-7 cycles of combination chemotherapy, the efficacies were as follows: CR 2 cases, PR 58 cases, SD 27 cases, and PD 11 cases (Table 2). The ORR was 61.2% (60/98), and the CBR was 75.5% (74/98). In the combination group, the ORR and CBR were not significantly associated with age, estrogen/progesterone receptor status, HER2 status, previous chemotherapy lines, metastatic locations, and DFS (Table 3).
Table 2. Therapeutic efficiencies in the combination group and the maintenance group.
| Clinical data | Combination group (%) | Maintenance group (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CR | 2.0 (2.0) | 1 (2.0) |
| PR | 58 (59.2) | 1 (2.0) |
| SD ≥6 months | 14 (14.3) | 19 (38.0) |
| SD <6 months | 13 (13.3) | 11 (22.0) |
| PD | 11 (11.2) | 18 (36.0) |
CR, complete remission; PR, partial responses; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease.
Table 3. Comparison of the therapeutic efficacies in the combination group.
| Clinical data | NX combination group (%) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | ORR (%) | P value | CBR (%) | P value | |
| Age | 0.991 | 0.82 | |||
| ≥60 years | 18 | 11 (61.1) | 15 (83.3) | ||
| <60 years | 80 | 49 (61.2) | 62 (77.5) | ||
| Hormone receptor | 0.547 | 0.351 | |||
| Positive | 53 | 31 (58.5) | 42 (79.2) | ||
| Negative | 45 | 29 (64.4) | 32 (71.1) | ||
| Her-2 | 0.891 | 0.802 | |||
| Positive | 43 | 26 (60.5) | 33 (76.7) | ||
| Negative | 55 | 34 (61.8) | 41 (74.5) | ||
| Previous treatment | 0.289 | 0.644 | |||
| First-line | 53 | 35 (66.0) | 41 (77.4) | ||
| Second-line and above | 45 | 25 (55.6) | 33 (73.3) | ||
| Metastatic sites | 0.942 | 0.935 | |||
| Viscera | 77 | 47 (61.0) | 58 (75.3) | ||
| Non-viscera | 21 | 13 (61.9) | 16 (76.2) | ||
| DFS | 0.101 | 0.714 | |||
| >2 years | 44 | 23 (52.3) | 34 (77.3) | ||
| ≤2 years | 54 | 37 (68.5) | 40 (74.1) | ||
NX, vinorelbine combined with capecitabine; ORR, overall response rate; CBR, clinical benefit rate; DFS, disease-free survival.
Totally 87 patients archived CR + PR + SD, although 18 patients withdrew from the treatment; 2 patients were converted to other regimens based on their own preference; 14 patients were converted to other therapies due to drug resistance or disease progression during the combined treatment; 2 patients entered endocrine drug maintenance therapy; 1 patient entered single-agent vinorelbine maintenance therapy after one cycle of combined treatment because he could not tolerate capecitabine; and 50 patients entered single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy.
In the maintenance group, PD was noted in 15 cases; in 21 cases, the efficacy of combined treatment was maintained, the efficacy of combined treatment was stable and even slightly improved; in one case who had achieved PR during the combined treatment, the lesion further shrank and the efficacy reached “CR”; and in one case, the disease was slightly improved after one cycle of combined treatment but then the patient began to receive the single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy due to abdominal distension, in whom the lesion further shrank and the efficacy reached “PR”. The ORR of the single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy was 4% (2/50), and the CBR was 48% (24/50). The ORR and CBR of the single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy were significantly superior in the estrogen/progesterone receptor-negative group than in the estrogen/progesterone receptor-positive group (P=0.009) and in HER2-negative group than in HER2-positive Group (P=0.049) (Table 4). They were not significantly associated with age, previous chemotherapy lines, metastatic locations, and DFS (P>0.05).
Table 4. Comparison of the therapeutic efficacies in the maintenance group.
| Clinical data | X maintenance group |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | ORR (%) | P value | CBR (%) | P value | |
| Age | 0.064 | 0.764 | |||
| ≥60 years | 13 | 2 (15.4) | 5 (38.5) | ||
| <60 years | 37 | 0 (0) | 16 (43.2) | ||
| Hormone receptor | 1 | 0.009 | |||
| Positive | 31 | 1 (3.2) | 8 (25.2) | ||
| Negative | 19 | 1 (5.3) | 12 (63.2) | ||
| Her-2 | 0.497 | 0.049 | |||
| Positive | 22 | 0 (0) | 5 (22.7) | ||
| Negative | 28 | 2 (7.1) | 16 (50.0) | ||
| Previous treatment | 0.57 | 0.128 | |||
| First-line | 30 | 2 (6.7) | 10 (33.3) | ||
| Second-line and above | 20 | 0 (0) | 11 (55.0) | ||
| Metastatic sites | 1 | 1 | |||
| Viscera | 39 | 2 (5.1) | 16 (41.0) | ||
| Non-viscera | 11 | 0/11 (0) | 5 (45.5) | ||
| DFS | 1 | 0.145 | |||
| >2 years | 23 | 1 (4.3) | 12 (52.2) | ||
| ≤2 years | 27 | 1 (3.6) | 9 (33.3) | ||
X, capecitabine; ORR, overall response rate; CBR, clinical benefit rate; DFS, disease-free survival.
Progression-free survival (PFS)
The follow-up ended December 31, 2013. Up to the follow-up, the number of deaths were 24 in the non-maintenance group (24/48) and 16 in the maintenance group (16/50). In the maintenance group, the median PFS was 12 months (95% CI: 10.5-13.5 months). Univariate analysis using the log-rank test showed that age, estrogen/progesterone receptor status, Her-2 status, DFS, number of salvage treatment lines, and visceral metastasis were not significantly correlated with the PFS.
Post-metastasis survival (PMS)
The PMS was 63 months (95% CI: 18.4-107.6 months) and 28 months (95% CI: 15.5-40.5 months) in the maintenance group and the non-maintenance group, showing significant difference (P=0.006) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
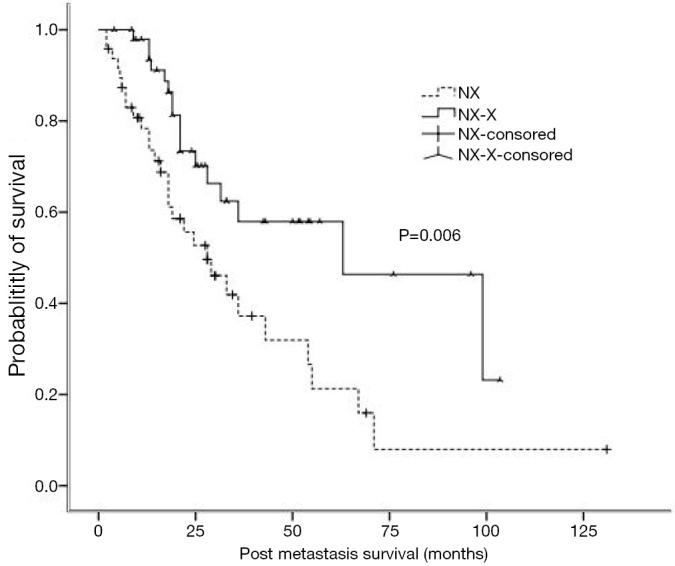
The post-metastasis survival (PMS) in the non-maintenance group (NX) and the maintenance group (NX-X).
Toxicities
In the combination group (n=98), the main grade 3/4 toxicities were neutropenia, hand-foot syndrome, abdominal distension, diarrhea, stomatitis, and skin pigmentation, seen in 20 patients (20.4%). These symptoms mainly occurred 10-13 days after the chemotherapy and were resolved after symptomatic management using granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Meanwhile, the main non-hematologic grade 3/4 toxicities included hand-foot syndrome (n=3, 3.1%), gastrointestinal reactions (n=5, 5.1%), stomatitis (n=1, 1%), and skin pigmentation (n=2, 2%); after symptomatic management, the patients could continue to receive the following treatment cycles. In the maintenance group (n=50), the main adverse reaction was skin pigmentation (n=6, 12.0%), which was considered to be due to the administration of capecitabine. Nevertheless, all patients in the maintenance group could tolerate the maintenance treatment (Table 5).
Table 5. Grade 3/4 toxicities in the combination group and maintenance group.
| Grade 3/4 toxicities | NX combination group, n (%) | X maintenance group, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Leukopenia | 20 (20.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| Diarrhoea | 3 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| Abdominal distension | 2 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Hand-foot syndrome | 3 (3.1) | 1 (1.0) |
| Stomatitis | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Skin pigmentation | 2 (2.0) | 6 (12.0) |
NX, vinorelbine combined with capecitabine; X, capecitabine.
Discussion
The role of capecitabine combined with vinorelbine in treatment of advanced breast cancer has been studied (10-13). It was reported that vinorelbine combined with capecitabine was applied in the treatment of 31 patients with advanced breast cancer, achieving a response rate of 49%, which included CR in 4 cases and PR in 11 cases; the TTP was 7.6 months, and the median survival time was 27.2 months (10). In this study, we applied capecitabine combined with vinorelbine in treating patients with advanced MBC that had been resistant to anthracyclines/taxanes and archived an ORR of 61.2% and CBR of 75.5%, with a median PFS of 12 months, which was basically consistent with previous studies (10-13). This strategy has shown good efficacy in terms of improving symptoms, relieving pain, increasing KPS score, and improving patients’ quality of life.
Maintenance treatment was usually applied in patients who have achieved CR, PR, or SD after the initial combination therapy by the prolonged administration of a single agent in the combination regimen, with an attempt to control the disease. Capecitabine with its high efficacy and low toxicities, has shown unique advantages in the maintenance treatment of breast cancer. According to a retrospective analysis, in patients with recurrent MBC who had achieved CR, PR, or SD after capecitabine-based combination treatment, subsequent single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy achieved a CBR of 32.2% and maintained the original efficacy in 81% of the patients; the median TTP was 4 months (14). Data from over 70 research centers worldwide have shown that the response rates of capecitabine monotherapy in treating advanced breast cancer ranged 20-40%; no prophylactic or adjunctive medication is required during the treatment; in addition, this strategy is quite safe, and the patients can enjoy good quality of life (15). In the current study, the median MSR was 63 months and 28 months in the maintenance group and non-maintenance group. Obviously, the survival was significantly superior in patients who had received the maintenance treatment than those who had not received the maintenance treatment due to various reasons (disease progression during the combined treatment, or treatment interruptions).
The common toxicities of capecitabine included diarrhoea, gastrointestinal disorders, hand-foot syndrome, and bone marrow suppression. It was found that the toxicity types of capecitabine are associated with factors such as the treatment regimens and medication frequency (16). We also observed the treatment-related mild and moderate adverse reactions in our cohort. However, no treatment-associated death was noted. The most common grade 3/4 toxicity was bone marrow suppression (20.4%). In contrast, the main non-hematologic adverse events included gastrointestinal reactions, hand-foot syndrome, stomatitis, and skin pigmentation, with an overall incidence of 11.2%. The incidence of skin pigmentation increased in the maintenance group, while the incidences of other toxicities did not.
In conclusion, capecitabine combined with vinorelbine plus single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy is a safe, effective, and tolerated strategy for the treatment of MBC. As a preferred drug for the maintenance therapy, capecitabine provides an option for the multidisciplinary management of advanced breast cancer. However, this findings needs to be confirmed by prospective randomised control trials.
Acknowledgements
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Colditz GA, Bohlke K. Priorities for the primary prevention of breast cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 2014;64:186-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, et al. Report of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010. Ann Transl Med 2014;2:61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dong X, Alpaugh KR, Cristofanilli M. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in breast cancer: a diagnostic tool for prognosis and molecular analysis. Chin J Cancer Res 2012;24:388-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Assi HA, Khoury KE, Dbouk H, et al. Epidemiology and prognosis of breast cancer in young women. J Thorac Dis 2013;5Suppl 1:S2-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jung SY, Sereika SM, Linkov F, et al. The effect of delays in treatment for breast cancer metastasis on survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011;130:953-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nakhlis F, Golshan M.Bevacizumab: where do we go from here in breast cancer? Transl Cancer Res 2012;1:55-6. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Molina-Garrido MJ, Mora-Rufete A, Guillen-Ponce C. Oral chemotherapy in elderly women with metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2014;14:665-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park JS, Jeung HC, Rha SY, et al. Phase II gemcitabine and capecitabine combination therapy in recurrent or metastatic breast cancer patients pretreated with anthracycline and taxane. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2014;74:799-808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gligorov J, Doval D, Bines J, et al. Maintenance capecitabine and bevacizumab versus bevacizumab alone after initial first-line bevacizumab and docetaxel for patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (IMELDA): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15:1351-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Estévez LG, Batista N, Sánchez-Rovira P, et al. A Phase II study of capecitabine and vinorelbine in patients with metastatic breast cancer pretreated with anthracyclines and taxanes. Clin Breast Cancer 2008;8:149-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fan Y, Xu B, Yuan P, et al. Prospective study of vinorelbine and capecitabine combination therapy in Chinese patients with metastatic breast cancer pretreated with anthracyclines and taxanes. Chemotherapy 2010;56:340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jones A, O’Brien M, Sommer H, et al. Phase II study of oral vinorelbine in combination with capecitabine as second line chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer patients previously treated with anthracyclines and taxanes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2010;65:755-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Orphanos G, Alexopoulos A, Malliou S, et al. A Phase II trial of the combination of vinorelbine and capecitabine as second-line treatment in metastatic breast cancer previously treated with taxanes and/or anthracyclines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2010;136:115-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kamal AH, Camacho F, Anderson R, et al. Similar survival with single-agent capecitabine or taxane in first-line therapy for metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012;134:371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huang H, Jiang Z, Wang T, et al. Single-agent capecitabine maintenance therapy after response to capecitabine-based combination chemotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2012;23:718-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mikhail SE, Sun JF, Marshall JL. Safety of capecitabine: a review. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2010;9:831-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


