Erratum to: Theor Appl Genet (2013) 126:1951–1964 DOI 10.1007/s00122-013-2109-6
In the original article, chromosome 6B was erroneously listed as 5A. This led to the propagation of the error from Figure 4 to Table 1 and four locations within the text. The overall scope of research and interpretation are not impacted by the error.
Revision #1 in Abstract (page no. 1951)
Incorrect: Carberry contributed resistance QTL on 4B and 5A.
Corrected to: Carberry contributed resistance QTL on 4B and 6B.
Revision #2 in Results (page no. 1955)
Incorrect: Those QTL that appeared only for traits measured in Canada were QSr.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-5A, QSr.spa-5B.1 and QPbc.spa-6A and those QTL that appeared for traits measured in Kenya and Canada were QPbc.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-4B.1 and QSr.spa-6D.
Corrected to: Those QTL that appeared only for traits measured in Canada were QSr.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-6B, QSr.spa-5B.1 and QPbc.spa-6A and those QTL that appeared for traits measured in Kenya and Canada were QPbc.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-4B.1 and QSr.spa-6D.
Revision #3 in Results (page no. 1957)
Incorrect: AC Cadillac contributed resistance at the QSr.spa-2B.1, QSr.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-5B.1, QSr.spa-6D, QSr.spa-7B and QSr.spa-7D loci while Carberry contributed resistance at the QSr.spa-4B.1 and QSr.spa-5A (Table 1).
Corrected to: AC Cadillac contributed resistance at the QSr.spa-2B.1, QSr.spa-3B.1, QSr.spa-5B.1, QSr.spa-6D, QSr.spa-7B and QSr.spa-7D loci while Carberry contributed resistance at the QSr.spa-4B.1 and QSr.spa-6B (Table 1).
Table 1.
Parental-type molecular variant mean values for each marker, most significant marker or marker interval, LOD, measure of additive effects and percent regression effect explained from Multiple QTL Mapping using MapQTL in the Carberry/AC Cadillac doubled haploid population for DArT® and SSR markers with stem rust severity and infection response from the field in Njoro, Kenya and Swift Current, Canada, and for seedling stem rust infection type against race TTKSK from containment growth chamber trials in Morden, Canada
| Chromosome | QTL | Trait | Environments | Markera/Marker interval | LODb score | Mean AC Cadillac molecular variant | Mean Carberry molecular variant | Additivec effect | PVd % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2B | QSr.spa-2B.1 | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2010 | wPt-6832 | 7.4 | 6.4 | 14 | −3.8 | 10.3 |
| QSr.spa-2B.1 | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2011 | tPt-9065 | 7 | 10.3 | 12.6 | −1.1 | 9.7 | |
| QSr.spa-2B.1 | Stem rust infection response | Kenya 2011 | wPt-6832 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 3.4 | −0.8 | 6.3 | |
| QPbc.spa-2B | PBC | Kenya 2010 | Xwmc770 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 4.9 | |
| QPbc.spa-2B | PBC | Kenya 2011 | Xwmc770 | 7.1 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 11.7 | |
| 3B | QSr.spa-3B.1 | Stem rust infection response | Canada 2011 | Xbarc147 | 3 | 1.9 | 2.4 | −0.2 | 4.6 |
| QPbc.spa-3B | PBC | Kenya 2010 | X3B042G11 | 8.1 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 13.7 | |
| QPbc.spa-3B | PBC | Canada 2012 | wPt-744251 | 12 | 1.3 | 1 | 0.2 | 18 | |
| 4B | QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2012 | wPt-744434–Xwmc617 | 3.1 | 5.9 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 2.8 |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust infection response | Kenya 2009 | wPt-744434–Xwmc617 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 0.5 | 2.4 | |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2009 | wPt-744434 | 4 | 12.3 | 7.9 | 2.2 | 5.8 | |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2010 | wPt-744434 | 4.5 | 13.4 | 7 | 3.2 | 6.1 | |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust severity | Canada 2011 | wPt-744434–Xwmc617 | 3.4 | 14.3 | 9 | 2.6 | 5.3 | |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust infection response | Canada 2011 | wPt-744434–Xwmc617 | 3 | 2.6 | 2 | 0.3 | 4.7 | |
| QSr.spa-4B.1 | Stem rust infection type | Morden combined | wPt-733745 | 3 | 6.3 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 5.1 | |
| 5B | QSr.spa-5B.1 | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2009 | wPt-9205 | 3.6 | 8.2 | 12 | −1.9 | 4.9 |
| QSr.spa-5B.1 | Stem rust infection response | Canada 2011 | wPt-5792 | 3.6 | 2 | 2.5 | −0.3 | 5.4 | |
| 6A | QPbc.spa-6A | PBC | Canada 2012 | wPt-2014 - tPt-8557 | 3.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 | −0.1 | 4.4 |
| 6B | QSr.spa-6B | Stem rust infection response | Canada 2011 | wPt-5408 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2 | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| QSr.spa-6B | Stem rust severity | Canada 2012 | wPt-2175 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 5.5 | |
| QSr.spa-6B | Stem rust severity | Canada Combined | wPt-666793 | 3.1 | 8.2 | 6 | 1.1 | 5.3 | |
| QSr.spa-6B | Stem rust infection response | Canada combined | wPt-5256 | 3.4 | 2 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 5.9 | |
| 6D | QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2012 | wPt-741955 | 34.7 | 2.5 | 7.5 | −2.5 | 42.8 |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2009 | wPt-1695 | 39.2 | 2.7 | 7.5 | −2.4 | 48.8 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection response | Kenya 2009 | wPt-1695 | 39.8 | 2.3 | 6.1 | −1.9 | 47.8 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2009 | wPt-664770 | 8.5 | 7 | 13.2 | −3.1 | 12.8 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2010 | wPt-741955 | 2.9 | 7.8 | 12.6 | −2.4 | 3.9 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection response | Kenya 2010 | wPt-741955 | 13.4 | 1.6 | 3.4 | −0.9 | 21.1 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection response | Canada 2012 | wPt-1695 | 3.4 | 1.1 | 1.4 | −0.2 | 5.8 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection type | Morden combined | wPt-741955 | 9.4 | 3.8 | 6.4 | −1.3 | 15 | |
| QSr.spa-6D | Stem rust infection response | Kenya combined | wPt-741955 | 6.7 | 2.6 | 3.7 | −0.5 | 11.1 | |
| 7B | QSr.spa-7B | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2012 | wPt-3939 | 8.6 | 3.8 | 5.8 | −1 | 7.1 |
| QSr.spa-7B | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2009 | wPt-3939 | 3.6 | 3.4 | 6.8 | −1.7 | 3.2 | |
| QSr.spa-7B | Stem rust severity | Kenya 2009 | wPt-3939 | 3.2 | 8.1 | 11.6 | −1.8 | 4.3 | |
| 7D | QSr.spa-7D | Stem rust infection type | Morden 2012 | Xwmc273 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 6 | −0.8 | 3.8 |
aMarker interval described by the markers which immediately flank the peak QTL response, or in the case of a single marker, the marker which is at the peak QTL response
bThe threshold to declare LOD scores significant ranged from 2.9 to 3.0. All LOD scores reported are significant
cA positive additive effect indicates Carberry contributed to stem rust resistance and a negative additive effect indicates AC Cadillac contributed to stem rust resistance
dPV is the proportion of the phenotypic variance explained by the QTL
Revision #4 in Discussion (page no. 1962)
Incorrect: We detected a number of less impressive main effect QTL, such as QSr.spa-5A on chromosome 5A which appeared only in the Canadian environment suggesting the gene is only effective to North American races. Njau et al. (2012) recently reported a QTL on chromosome 5A, but due to differences in markers between linkage maps it is difficult to ascertain whether their marker is the same as QSr.spa-5A.
Corrected to: We detected a number of less impressive main effect QTL, such as QSr.spa-6B on chromosome 6B which appeared only in the Canadian environment suggesting the gene is only effective to North American races.
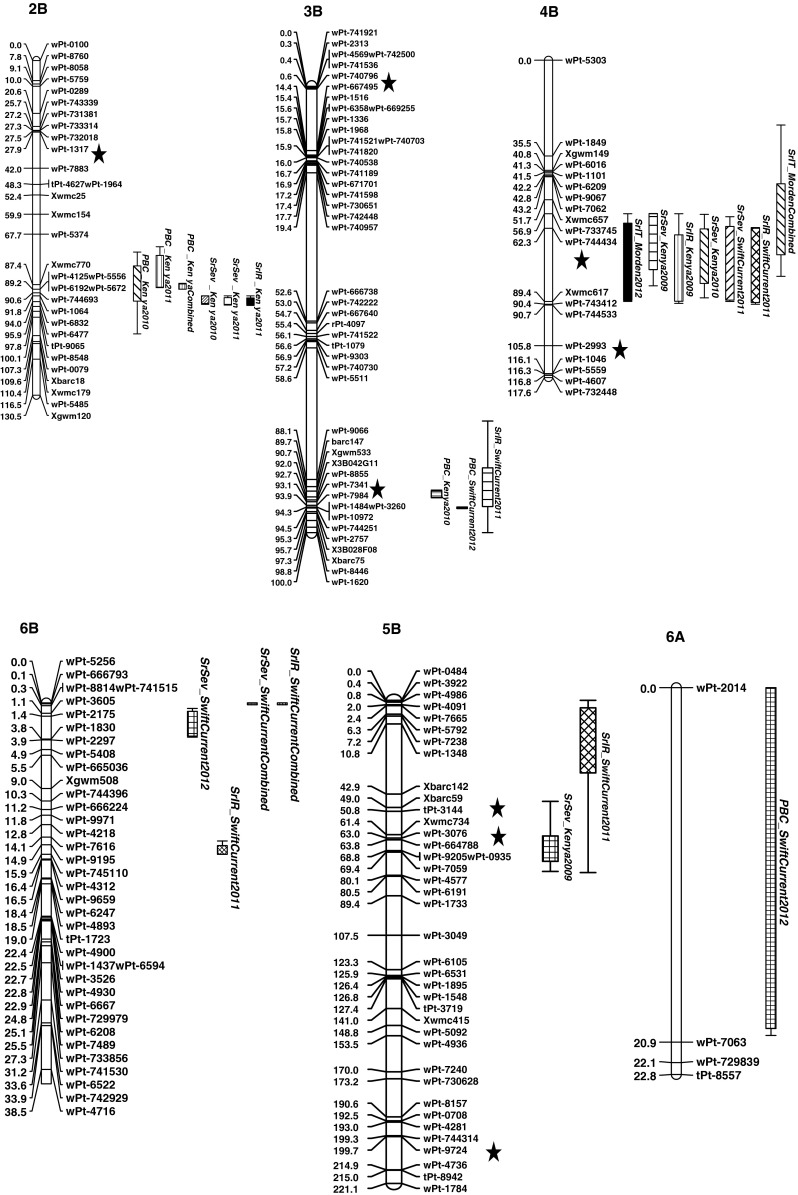
Revision # 5 in Figure 4 caption (page no. 1959)
Incorrect title: Fig. 4 Stem rust resistance QTL identified on chromosome 2B, 3B, 4B, 5, 5B, 6, 7B and 7D and pseudo-black chaff (PBC) QTL identified on chromosome 2B, 3B and 6A, using DArT and SSR markers in a doubled haploid population derived from Carberry/AC Cadillac. Disease reactions for stem rust severity, infection response and PBC were assessed near Njoro, Kenya (2009, 2010 and 2011) and near Swift Current, Canada (2011 and 2012), and seedling stem rust infection type was assessed in Morden, Canada (2009 and 2012). Location of a QTL involved in epistasis is depicted with the symbol asterisk
Corrected to: Fig. 4 Stem rust resistance QTL identified on chromosome 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 6D, 7B and 7D and pseudo-black chaff (PBC) QTL identified on chromosome 2B, 3B and 6A, using DArT and SSR markers in a doubled haploid population derived from Carberry/AC Cadillac. Disease reactions for stem rust severity, infection response and PBC were assessed near Njoro, Kenya (2009, 2010 and 2011) and near Swift Current, Canada (2011 and 2012), and seedling stem rust infection type was assessed in Morden, Canada (2009 and 2012). Location of a QTL involved in epistasis is depicted with the symbol asterisk.
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1007/s00122-013-2109-6.
Contributor Information
A. Singh, Email: dr.artisingh@yahoo.com
R. E. Knox, Email: Ron.Knox@agr.gc.ca


