Abstract
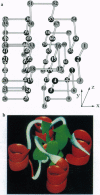
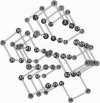
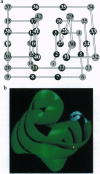
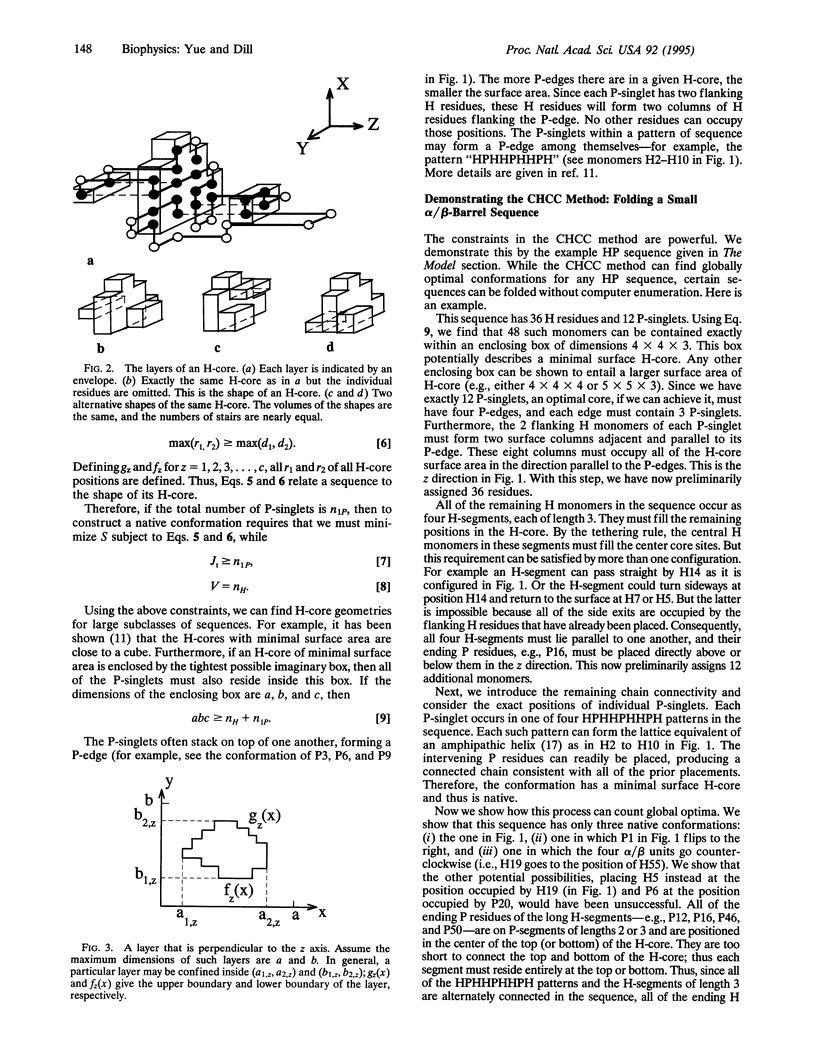
The tertiary structures of globular proteins have remarkable and complex symmetries. What forces cause them? We find that a very simple model reproduces some of those symmetries. Proteins are modeled as copolymers of specific sequences of hydrophobic (H) and polar (P) monomers (HP model) configured as self-avoiding flights on simple three-dimensional cubic lattices. The model has no parameters; we just seek the conformations that have the global maximum number of HH contacts for any given sequence. Finding global optima for chains in this model has not been computationally possible before for chains longer than 36-mers. We report here a procedure that can find all the globally optimal conformations, the number of which defines the degeneracy of a sequence, for chains up to 88 monomers long. It is about 37 orders of magnitude faster than previous exact methods. We find that degeneracy is an important aspect of sequence design. So far, we have found that four-helix bundles, alpha/beta-barrels, and parallel beta-helices are globally optimal conformations of polar/nonpolar sequences that have minimal degeneracy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan H. S., Dill K. A. Origins of structure in globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Wasserman Z. R., Lear J. D. Protein design, a minimalist approach. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2464850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A. Dominant forces in protein folding. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7133–7155. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Weiss R. M., Terwilliger T. C. The hydrophobic moment detects periodicity in protein hydrophobicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):140–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Experimental support for the "hydrophobic zipper" hypothesis. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):536–536. doi: 10.1126/science.8290964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C., Ogden R. C. De novo design, expression, and characterization of Felix: a four-helix bundle protein of native-like sequence. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):884–891. doi: 10.1126/science.2392678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDREW J. C., BODO G., DINTZIS H. M., PARRISH R. G., WYCKOFF H., PHILLIPS D. C. A three-dimensional model of the myoglobin molecule obtained by x-ray analysis. Nature. 1958 Mar 8;181(4610):662–666. doi: 10.1038/181662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamtekar S., Schiffer J. M., Xiong H., Babik J. M., Hecht M. H. Protein design by binary patterning of polar and nonpolar amino acids. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1680–1685. doi: 10.1126/science.8259512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. F., Dill K. A. Theory for protein mutability and biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):638–642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Chothia C. Structural patterns in globular proteins. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):552–558. doi: 10.1038/261552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Sauer R. T. Reverse hydrophobic effects relieved by amino-acid substitutions at a protein surface. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):363–364. doi: 10.1038/344363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Chan H. S., Dill K. A. Modeling the effects of mutations on the denatured states of proteins. Protein Sci. 1992 Feb;1(2):201–215. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick J., Kolinski A. Dynamic Monte Carlo simulations of a new lattice model of globular protein folding, structure and dynamics. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):499–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80070-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D. P., Dill K. A. Families and the structural relatedness among globular proteins. Protein Sci. 1993 Jun;2(6):884–899. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder M. D., Keen N. T., Jurnak F. New domain motif: the structure of pectate lyase C, a secreted plant virulence factor. Science. 1993 Jun 4;260(5113):1503–1507. doi: 10.1126/science.8502994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue K., Dill K. A. Inverse protein folding problem: designing polymer sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4163–4167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue K, Dill KA. Sequence-structure relationships in proteins and copolymers. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1993 Sep;48(3):2267–2278. doi: 10.1103/physreve.48.2267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]