Abstract
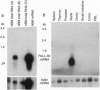
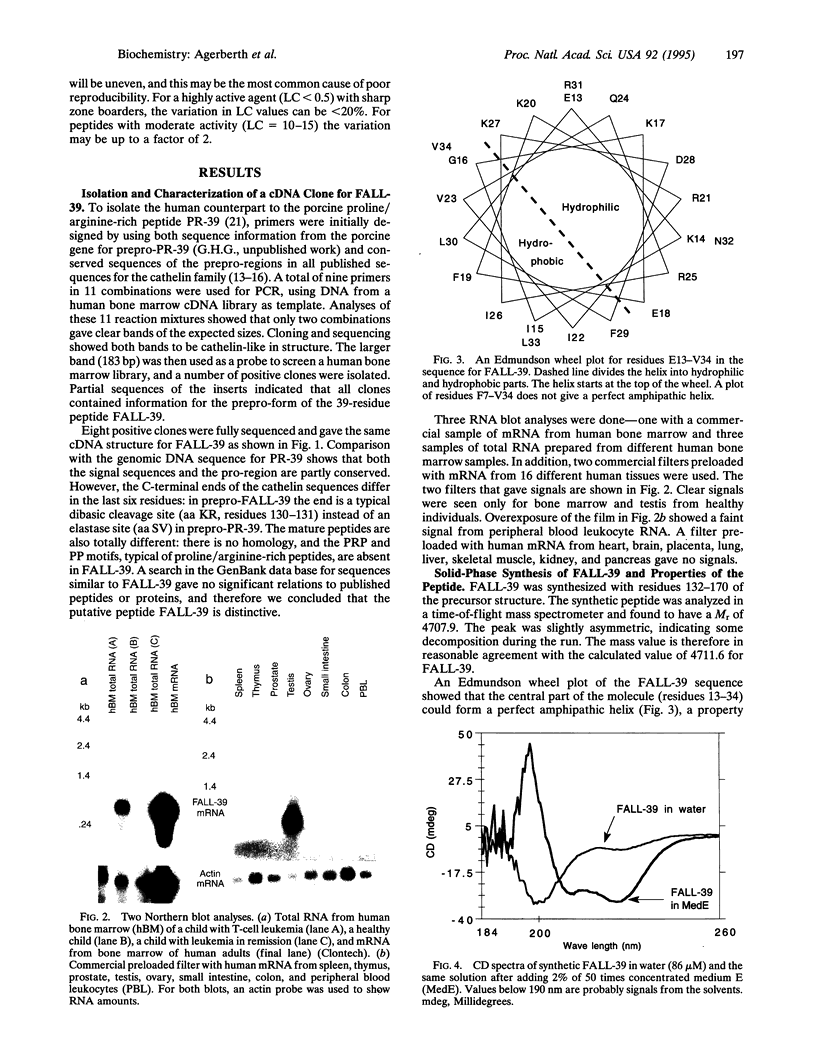
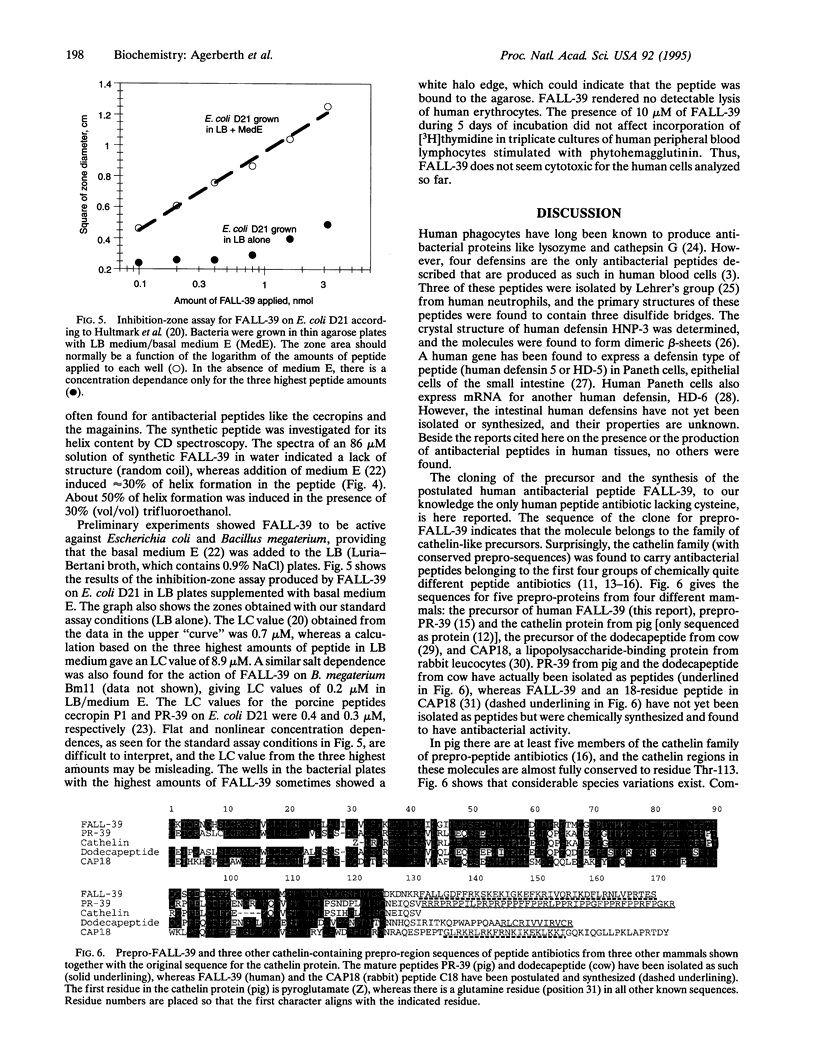
PR-39, a proline/arginine-rich peptide antibiotic, has been purified from pig intestine and later shown to originate in the bone marrow. Intending to isolate a clone for a human counterpart to PR-39, we synthesized a PCR probe derived from the PR-39 gene. However, when this probe was used to screen a human bone marrow cDNA library, eight clones were obtained with information for another putative human peptide antibiotic, designated FALL-39 after the first four residues. FALL-39 is a 39-residue peptide lacking cysteine and tryptophan. All human peptide antibiotics previously isolated (or predicted) belong to the defensin family and contain three disulfide bridges. The clone for prepro-FALL-39 encodes a cathelin-like precursor protein with 170 amino acid residues. We have postulated a dibasic processing site for the mature FALL-39 and chemically synthesized the putative peptide. In basal medium E, synthetic FALL-39 was highly active against Escherichia coli and Bacillus megaterium. Residues 13-34 in FALL-39 can be predicted to form a perfect amphiphatic helix, and CD spectra showed that medium E induced 30% helix formation in FALL-39. RNA blot analyses disclosed that the gene for FALL-39 is expressed mainly in human bone marrow and testis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agerberth B., Lee J. Y., Bergman T., Carlquist M., Boman H. G., Mutt V., Jörnvall H. Amino acid sequence of PR-39. Isolation from pig intestine of a new member of the family of proline-arginine-rich antibacterial peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):849–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurora R., Srinivasan R., Rose G. D. Rules for alpha-helix termination by glycine. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1126–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.8178170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. C., Boman I. A., Andreu D., Li Z. Q., Merrifield R. B., Schlenstedt G., Zimmermann R. Chemical synthesis and enzymic processing of precursor forms of cecropins A and B. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5852–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Agerberth B., Boman A. Mechanisms of action on Escherichia coli of cecropin P1 and PR-39, two antibacterial peptides from pig intestine. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2978–2984. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2978-2984.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Faye I., Gudmundsson G. H., Lee J. Y., Lidholm D. A. Cell-free immunity in Cecropia. A model system for antibacterial proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin G. J., Marx J. Resistance to antibiotics. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):359–359. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5157.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Storici P., Schneider C., Romeo D., Zanetti M. cDNA cloning of the neutrophil bactericidal peptide indolicidin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 31;187(1):467–472. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81517-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Liu L., Valore E. V., Oren A. Posttranslational processing and targeting of transgenic human defensin in murine granulocyte, macrophage, fibroblast, and pituitary adenoma cell lines. Blood. 1993 Jul 15;82(2):641–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. P., Yee J., Selsted M. E., Eisenberg D. Crystal structure of defensin HNP-3, an amphiphilic dimer: mechanisms of membrane permeabilization. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.2006422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. A., Hetru C. Insect defensins: inducible antibacterial peptides. Immunol Today. 1992 Oct;13(10):411–415. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90092-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Bergh S., Moks T., Uhlén M. Bidirectional solid-phase sequencing of in vitro-amplified plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):84–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 4;315(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Bevins C. L. Paneth cells of the human small intestine express an antimicrobial peptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23216–23225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Hirata M., Shimomoura Y., Yoshida M., Zheng H., Zhong J., Wright S. C. Antimicrobial activity of rabbit CAP18-derived peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Dec;37(12):2534–2539. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.12.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein A. K., Ganz T. Defensins: antimicrobial and cytotoxic peptides of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:105–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.000541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield B. Solid phase synthesis. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.3961484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritonja A., Kopitar M., Jerala R., Turk V. Primary structure of a new cysteine proteinase inhibitor from pig leucocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C., Kylsten P., Kimbrell D. A., Engström A., Hultmark D. The andropin gene and its product, a male-specific antibacterial peptide in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):163–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scocchi M., Skerlavaj B., Romeo D., Gennaro R. Proteolytic cleavage by neutrophil elastase converts inactive storage proforms to antibacterial bactenecins. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):589–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Schilling J. W., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of three human neutrophil defensins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI112121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitaram N., Nagaraj R. A synthetic 13-residue peptide corresponding to the hydrophobic region of bovine seminalplasmin has antibacterial activity and also causes lysis of red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10438–10442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Antibiotic proteins of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1381–1386. doi: 10.1172/JCI114851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storici P., Del Sal G., Schneider C., Zanetti M. cDNA sequence analysis of an antibiotic dodecapeptide from neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 14;314(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80971-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storici P., Scocchi M., Tossi A., Gennaro R., Zanetti M. Chemical synthesis and biological activity of a novel antibacterial peptide deduced from a pig myeloid cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 17;337(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storici P., Zanetti M. A cDNA derived from pig bone marrow cells predicts a sequence identical to the intestinal antibacterial peptide PR-39. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1058–1065. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storici P., Zanetti M. A novel cDNA sequence encoding a pig leukocyte antimicrobial peptide with a cathelin-like pro-sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1363–1368. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz M. N. Hospital-acquired infections: diseases with increasingly limited therapies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2420–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tossi A., Scocchi M., Skerlavaj B., Gennaro R. Identification and characterization of a primary antibacterial domain in CAP18, a lipopolysaccharide binding protein from rabbit leukocytes. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 14;339(1-2):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Del Sal G., Storici P., Schneider C., Romeo D. The cDNA of the neutrophil antibiotic Bac5 predicts a pro-sequence homologous to a cysteine proteinase inhibitor that is common to other neutrophil antibiotics. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):522–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]