Abstract
IFN regulatory factors (IRFs) are a family of transcription factors that play an essential role in the homeostasis and function of immune systems. Recent studies indicated that IRF-8 is critical for the development of CD11blowCD8α+ conventional dendritic cells (DCs) and plasmacytoid DCs. Here we show that IRF-4 is important for CD11bhighCD8α– conventional DCs. The development of CD11bhigh DCs from bone marrow of IRF-4–/– mice was severely impaired in two culture systems supplemented with either GM-CSF or Flt3-ligand. In the IRF-4–/– spleen, the number of CD4+CD8α– DCs, a major subset of CD11bhigh DCs, was severely reduced. IRF-4 and IRF-8 were expressed in the majority of CD11bhighCD4+CD8α– DCs and CD11blowCD8α+ DCs, respectively, in a mutually exclusive manner. These results imply that IRF-4 and IRF-8 selectively play critical roles in the development of the DC subsets that express them.
Dendritic cells (DCs) are professional antigen-presenting cells that link the innate and adaptive immune systems. They express CD11c and are composed of heterogeneous cell populations with different functions (1). At present, murine DCs have been divided into two major groups, B220– conventional DCs and B220+ plasmacytoid DCs (2–5). In lymphoid organs, the conventional DCs can be divided into two subsets, CD11bhighCD8α– and CD11blowCD8α+ DCs, based on the expression of surface markers (1). In the spleen, the CD11bhighCD8α– subset can be further divided into CD4+ and CD4– DCs (6, 7). In vitro, CD11bhighCD8α– DCs can be generated in two bone marrow (BM) culture systems, supplemented with either granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) or Flt3 ligand (Flt3L) (8–10). CD11blowCD8α+ DCs can also be generated from a BM culture supplemented with Flt3L, although further stimulation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is needed to induce the expression of CD8α (10). The molecular phenomena that regulate the differentiation of these distinct subsets of DCs are poorly understood.
Transcription factors of the IFN-regulatory factor (IRF) family participate in the early host response to pathogens, immunomodulation, and hematopoietic differentiation (11). A member of the family, IRF-4, was cloned independently as a homologous member of the IRF gene family (12) and as an interacting partner of PU.1 (Pip) (13). PU.1 is an Ets family member involved in B lymphocyte and myeloid lineage development (14, 15) and is essential for the development of CD8α– DCs (16, 17). Upon their association, IRF-4 and PU.1 undergo conformational changes, followed by binding to the DNA-binding element (18). IRF-4 is expressed at all stages of B cell development, in mature T cells (12), adult T cell leukemia cell lines (19, 20), and in macrophages (21, 22). The analysis of mice lacking IRF-4 (IRF-4–/–) revealed that IRF-4 is essential for the function and homeostasis of both mature B and T lymphocytes (23, 24). IRF-8 (originally named IFN consensus sequence binding protein, ICSBP) is another member of the IRF family, and its structure is closely related to that of IRF-4. It can interact with PU.1 and binds to a DNA sequence similar to that bound by IRF-4 (22). Recent studies indicated that IRF-8 is critical for the development of CD11blowCD8α+ conventional DCs and plasmacytoid DCs (25–28). Here, we show that bone marrow cells from IRF-4 knockout mice have intrinsic defects in the development of CD11bhigh DCs in two culture systems supplemented with either GM-CSF or Flt3-ligand. Mice lacking the IRF-4 gene have selective defects in splenic CD11bhighCD8α– conventional DCs. IRF-4 is expressed in this subset of DCs, indicating that IRF-4 plays a critical role in the development of the DC subset that expresses it.
Methods
Mice. C57BL/6J mice were purchased from CLEA Japan (Osaka). IRF-4-deficient mice (23) and OT-II transgenic mice (29), expressing the T cell receptor specific for OVA323–339 and I-Ab, were maintained at the Laboratory Animal Center for Biomedical Research, Nagasaki University School of Medicine.
BM Cultures. The GM-CSF-supplemented BM culture was performed as described (9). The culture supernatant from a Chinese hamster ovary cell line transfected with the murine GM-CSF gene was used as the source of GM-CSF. At day 10, the nonadherent cells were harvested by gentle pipeting and were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS (Escherichia coli 0127:B8, Sigma) for 48 h. The Flt3L-supplemented BM culture was performed as described (10), except mouse Flt3L (Genzyme/Techne) was used. At day 9, the nonadherent cells were harvested by gentle pipeting and were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS for 24 h. For the experiments using the six-well transwell plates (Corning, NY), 5.2 × 105 BM cells (low cell density) in the lower chamber and 5 × 106 BM cells (high cell density) in the upper chamber were cultured in 4.1 ml of McCoy's medium, supplemented with 100 ng/ml Flt3L, for 10 days as described (10). For details see Supporting Text, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site.
Cell Preparation from Lymphoid Organs. Cells from thymuses and spleens were prepared as described (6). Low-density cells from spleen were also prepared as described (6).
Flow Cytometry. The cells were blocked with anti-CD16/32 antibody, rat IgG, and mouse IgG. All antibodies were purchased from BD Pharmingen, except where noted. In addition to the isotype controls, the following antibodies were used: Anti-CD16/32, FITC-conjugated anti-MHC class II (MHC-II), anti-CD8, and anti-Gr-1; phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD11c; CyChrome-conjugated anti-CD4; peridinin chlorophyll-α protein (PerCP)-conjugated anti-B220; biotin-conjugated anti-CD11b, anti-B220, and anti-Ly6c; PE-conjugated anti-CD40, anti-CD80, and anti-CD86 from Immunotech; biotin-conjugated anti-CD8 and anti-MHC-II, PE-conjugated anti-CD3, and allophycocyanin-conjugated anti-CD4 from eBioscience; and anti-IRF-4 and anti-IRF-8 from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. The binding of biotinylated antibodies was detected with PerCP-Cy5.5- or CyChrome-conjugated streptavidin. Analyses of stained cells were performed on a FACScan or FACSCalibur with the cellquest software (BD Bioscience).
Intracellular Staining. For the analysis of neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPTII), cells were fixed and permeabilized with the Fix and Perm kit (Caltag), and were incubated with anti-NPTII (Upstate Biotechnology) followed by ant-rabbit IgG-biotin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and streptavidin-CyChrome. For analyses of IRF-4 and IRF-8, cells were fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde (Wako) and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Wako). The permeabilized cells were incubated with the anti-IRF-4 or IRF-8 antibody, followed by anti-goat IgG-Alexa Fluor 488 (Molecular Probes)
Western Blot Analysis. Cell lysates were prepared as described (30), with modifications (see supporting information). Immunoblotting was performed as described (31).
RT-PCR. Total RNA was prepared from cells as described (31). The cDNA synthesized from the total RNA by using ReverTra Ace (Toyobo) was subjected to PCR amplification using EX Taq (Takara) and the following primers: CIITA (sense), type I exon1: GACTTTCTTGAGCTGGGTCTG; type III exon1: CTGGCCCTTCTGGGTCTTAC; CIITA (antisense), common exon2: TCTTCATCCAGTTCCATGTCC. All of the other primer sequences are available on request.
Antigen-Presentation Assay. The ability of DCs to activate antigen-specific T cells was monitored by the secretion of IL-2 from CD4+ T cells of OT-II mice. Purified CD4+ T cells from OT-II mice (4 × 105 per well) were stimulated with ovalbumin (OVA) or its peptide and various numbers of DCs. After 48 h, the IL-2 level in the culture supernatant was determined by a sandwich ELISA with a biotin-conjugated anti-IL-2 antibody (BD Pharmingen) and avidin-alkaline phosphatase (Jackson ImmunoResearch).
Results
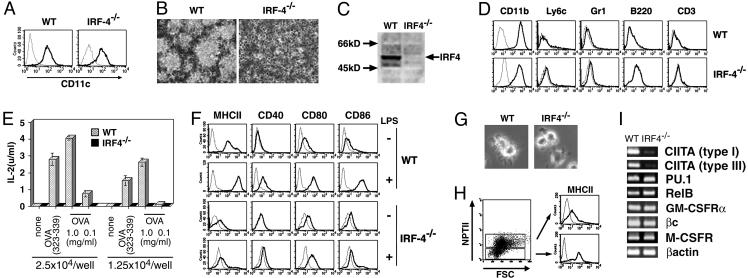
Defective DC Development in IRF-4–/– BM Culture. During analyses of the DC-specific regulatory mechanisms of the gp91phox gene, which is expressed in a cell type-specific manner (32–34), we found that the IRF-4 protein was expressed in human DCs and bound to the Ets/IRF composite element of the promoter together with PU.1 (data not shown). This observation was consistent with the recent studies on DC-associated factors, which revealed the expression of IRF-4 mRNA in human DCs (35, 36). Therefore, we used the GM-CSF-supplemented cultures of BM from IRF-4–/– mice to determine the role of IRF-4 in DC development and function. Nonadherent CD11c+ cells were generated from BM cells of IRF-4–/– mice as well as wild-type mice (Fig. 1A). Surprisingly, CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM failed to form DC clusters (Fig. 1B) and showed no veil processes (Fig. 5, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site). A Western blot analysis demonstrated that CD11c+ cells from wild-type mice expressed the IRF-4 protein, but those from IRF-4–/– mice did not (Fig. 1C). Flow cytometry analysis showed that CD11c+ cells from both wild-type and IRF-4–/– BM expressed CD11b at high levels but did not express B220, CD3, Gr-1, and Ly6c (Fig. 1D).
Fig. 1.
Impaired DC development in the IRF-4–/– BM culture with GM-CSF. (A) The CD11c expression on nonadherent cells from GM-CSF BM cultures at day 10 was analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Photographs of the cultures by phase contrast microscopy, taken at day 10. (C) The expression of IRF-4 in the CD11c+ cells was assessed by immunoblotting. Lysates from 2.5 × 105 cells were subjected to electrophoresis. (D) The lineage marker expression on the CD11c+ cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. (E) The antigen-presenting ability of the CD11c+ cells for whole OVA and its peptide (323–339 amino acid residues) to OVA-specific CD4+ T cells was examined. (F) MHC-II and costimulatory factor expression by the nonstimulated and LPS-stimulated CD11c+ cells was examined. (G) The morphology of LPS-stimulated CD11c+ cells was observed by phase contrast microscopy. (H) Wild-type and IRF-4–/– BM cells were cocultured. After 10 days, the expression of MHC-II on the cells was analyzed. NPTII expression by the wild-type and the IRF-4–/– cells was distinguished by flow cytometry with anti-MHC-II and anti-NPTII. (I) The expression of several transcription factor and cytokine receptor genes involved in DC development was analyzed by RT-PCR.
Next, we evaluated their ability to present the OVA protein (1 and 0.1 mg/ml) or its peptide (323–339 amino acid residues) to OVA-specific CD4+ T cells from OT-II mice (29). The wild-type DCs stimulated IL-2 production of the T cells in antigen dose- and DC number-dependent manners. However, CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM were unable to stimulate IL-2 production by OVA-specific T cells (Fig. 1E). We also analyzed their expression of the surface antigens associated with antigen presentation (Fig. 1F). The expression of MHC-II on CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM was extremely low, consistent with their defects in antigen presentation. The expression of CD40, CD80, and CD86 on CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM was similar to that of wild-type DCs. Strong up-regulation of the surface antigens was observed in wild-type DCs after stimulation with LPS. However, the up-regulation was not observed in most, if not all, CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM. Morphologically, the CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM did not develop the sheet-like veil structure after LPS stimulation (Fig. 1G). These results indicate that CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM fail to respond normally to LPS.
To determine whether the impaired DC development of CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM was caused by their intrinsic defects or environmental defects in the support of DC development in a GM-CSF-supplemented culture, we examined the generation of DCs from IRF-4–/– BM after a coculture with wild-type BM cells (Fig. 1H). The wild-type and IRF-4–/– BM could be distinguished by their expression of NPTII, whose gene was inserted when the IRF-4 gene was disrupted (23). Cells derived from IRF-4–/– BM cells (NPTII+) in the mixed culture system did not express MHC-II at high levels, unlike those derived from wild-type BM (NPTII–). This result indicates that the impaired DC development from IRF-4–/– BM cells is caused by cell autonomous defects.
To investigate the mechanisms underlying the impaired development of DCs from IRF-4–/– BM, we analyzed the mRNA expression of class II transactivator isoforms (CIITA types I and III), which are essential for the constitutive expression of MHC-II in DCs (37, 38) by an RT-PCR analysis. CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM expressed the CIITA type I and III mRNAs at almost negligible levels, as compared with the wild-type DCs (Fig. 1I), which might be responsible for the low-MHC-II expression level. CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– and wild-type BM expressed similar levels of the mRNAs encoding PU.1 and RelB, which are critical transcription factors for DC development (16, 17, 39, 40), the GM-CSF receptor components (α and cβ), and the M-CSF receptor, responsible for the interference of DC differentiation by M-CSF (41). Therefore, it is unlikely that the impaired DC development from IRF-4–/– BM cells is caused by the abnormal behaviors of PU.1 and RelB or abnormal responses to GM-CSF and M-CSF.
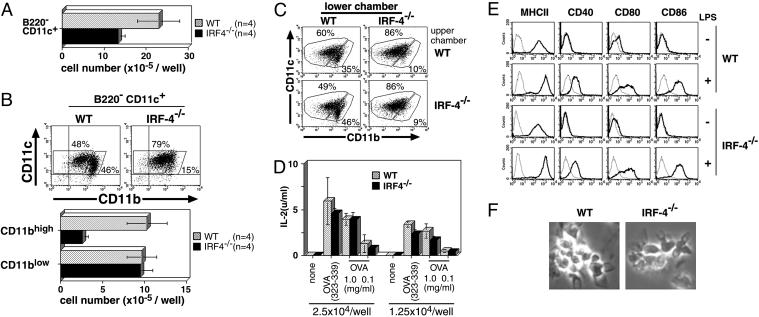
Defective Development Is Limited to CD11bhigh DCs. We next used the Flt3L-supplemented BM culture system, which can give rise to B220–CD11c+ conventional DCs and B220+CD11c+ plasmacytoid DCs (42, 43). It is demonstrated that the conventional DCs from the culture contain two types of subsets, CD11bhigh and CD11blow DCs (10), and the plasmacytoid DCs do not express CD11b (42, 43). The number of B220–CD11c+ conventional DCs developed from IRF-4–/– BM was reduced to ≈60% of that produced by wild-type BM (Fig. 2A). The number of B220+CD11c+CD11b– plasmacytoid DCs that developed from IRF-4–/– BM, however, was similar to that from wild-type BM (Fig. 6, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site). We analyzed the expression of CD11b on B220–CD11c+ cells from the Flt3L-supplemented BM culture. The proportion of CD11bhigh cells to CD11c+ cells from the wild-type BM culture was 46%, whereas that from the IRF-4–/– BM was 15%. The absolute number of CD11c+CD11bhigh cells derived from IRF-4–/– BM was severely reduced, as compared with that from wild-type BM, whereas the absolute number of CD11c+CD11blow cells was unchanged (Fig. 2B). These results suggest that IRF-4 plays an important role in the development of CD11bhigh conventional DCs, and is not essential for that of CD11blow conventional DCs and plasmacytoid DCs in the Flt3L-supplemented BM culture. This defect of IRF-4–/– CD11bhigh DCs could be due to the lack of soluble factor production by the IRF-4–/– BM cells. Therefore, we cultured IRF-4–/– and wild-type BM cells in the presence of Flt3L by using a transwell system as described (10). BM cells were cultured at low density in the lower chamber and at high density in the upper chamber in the presence of Flt3L (Fig. 2C). At the end of the culture, the generation of DCs in the lower chamber was analyzed by flow cytometry. In this system, the development of DCs from the wild-type BM cells in the lower chamber depended on the presence of wild-type BM cells at high density in the upper chamber (S.S. and A.K., unpublished data). Wild-type BM cells gave rise to a CD11c+CD11bhigh population when IRF-4–/– BM cells were cultured in the upper chamber (Fig. 2C Lower Left), suggesting that IRF-4–/– BM cells generated soluble factors that support DC development from the wild-type BM in the presence of Flt3L. On the contrary, the proportion of the CD11bhigh population derived from IRF-4–/– BM cells remained low, even after they were cultured with wild-type BM in the upper chamber at high density (Fig. 2C Upper Right). Taken together, these results suggest that the defect in the generation of a CD11c+CD11bhigh population from IRF-4–/– BM in the presence of Flt3L is an intrinsic characteristic of these cells.
Fig. 2.
Impaired development of the CD11bhigh DC subset in the IRF-4–/– BM culture with Flt3L. Cells were stained with anti-CD11b-FITC, anti-CD11c-PE, and anti-B220-PerCP. (A) The number of B220–CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM was compared with that from wild-type BM cells at 9 days after culture. (B) Analysis of the DC subsets in the Flt3L culture was performed, based on the expression of B220, CD11b, and CD11c. The values (%) indicate the proportion of each DC subset to B220– cells (Upper). The number per well of CD11blow and CD11bhigh CD11c+ DCs from IRF-4–/– BM cells was compared with that from wild-type BM cells (Lower). (C) Soluble factors from BM cells stimulated by Flt3L were assessed by using transwell plates. BM cells at low density (5.2 × 105 cells) were cultured in the lower chambers of transwell plates, separated by a 0.4-μm filter from BM cells at high density (5 × 106 cells) in the upper chambers. Analysis of the DC subsets in the lower chambers was performed, based on the expression of CD11b and CD11c. (D) The antigen-presenting ability was examined as described in Fig. 1E. (E) The expression of MHC-II and costimulatory factors on DCs was analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) The morphology of LPS-stimulated DCs was observed by phase-contrast microscopy.
Next, we examined the properties of the CD11c+ cells generated from IRF-4–/– BM in the Flt3L-supplemented culture. The CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM were able to present whole OVA and its peptide (323–339 amino acid residues) to naive CD4+ T cells from OT-II mice (Fig. 2D). They expressed MHC-II, CD40, CD80, and CD86 on the cell surface at levels similar to those of DCs from wild-type BM, before and after LPS stimulation (Fig. 2E). The CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– and wild-type BM were morphologically indistinguishable (Fig. 2F). Because the majority of the IRF-4–/– DCs were CD11blow conventional DCs (Figs. 2B and 6), these results suggest that the CD11blow DCs in IRF-4–/– DCs are not impaired in their antigen-presenting function and responsiveness to LPS.
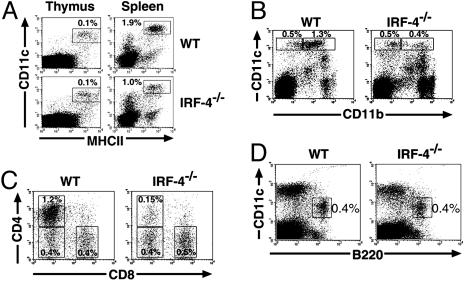
Defects of CD11bhigh DCs in IRF-4–/– Spleen. Next, we examined the levels of conventional DCs in vivo. The majority of thymic and splenic conventional DCs belong to the CD11blow and CD11bhigh DC subsets, respectively (1). The proportion of conventional DCs in the thymus of IRF-4–/– mice was similar to that of the wild-type (0.1%), whereas it was reduced by ≈50% in the spleen (Fig. 3A). Among these DCs in the spleen, the proportion of CD11bhigh DCs was markedly reduced, whereas that of CD11blow DCs was not (Fig. 3B). Because the total splenic cell numbers were comparable (Table 1), the absolute number of CD11bhigh DCs was selectively reduced in the IRF-4–/– spleen, consistent with the essential role of IRF-4 in the generation of CD11bhigh DCs in vitro. Splenic CD11bhigh DCs can be further subdivided into CD4+CD8α– and CD4–CD8α– subsets (6, 7). We further classified the splenic DCs, based on the expression of CD4 and CD8α. Flow cytometry analyses revealed that the CD4+CD8α– splenic DCs in IRF-4–/– mice were selectively reduced to ≈10% of the number in wild-type mice (Fig. 3C). As shown in Table 1, the absolute number of CD4+CD8α– DCs in the IRF-4–/– spleen was ≈10% of that found in the wild-type, resulting in the lower total number of CD11chighMHC-II+ DCs. These results demonstrated that the splenic CD11bhighCD4+CD8α– subset was selectively reduced among the conventional DCs in the IRF-4–/– mouse. We also examined the level of plasmacytoid DCs in the IRF-4–/– spleen. CD19+and NK1.1+ cells were gated out to exclude B cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which are B220+ and CD11clow, respectively (44). The proportion and the absolute number of CD11cintB220+ plasmacytoid DCs in IRF-4–/– spleen were not significantly different from those of the wild-type spleen (Fig. 3D and Table 1). Taken together, these results suggest that IRF-4 is critical for the development of the majority of CD11bhighCD4+CD8α– splenic conventional DCs, but not for that of CD11bhighCD4–CD8α– and CD11blowCD4–CD8α+ splenic conventional DCs as well as plasmacytoid DCs.
Fig. 3.
Splenic CD11bhighCD4+CD8α– conventional DCs are selectively reduced in IRF-4–/– mice. Six-week-old male mice were used. (A) Thymic and splenic cells were stained with anti-MHC-II-FITC, anti-CD11c-PE, and anti-B220-PerCP. The CD11chighMHC-IIhigh cells were analyzed after the B220+ population was electrically gated out. (B) Splenic cells were stained with anti-CD11b-FITC, anti-CD11c-PE, and anti-B220-PerCP. Expression of CD11b on CD11chigh DCs was analyzed after the B220+ population was electrically gated out. (C) Splenic cells were stained with anti-CD8α FITC, anti-CD11c-PE, and anti-CD4-CyChrome, and then the expression of CD4 and CD8α on CD11chigh DCs was analyzed. (D) Splenic cells were stained with anti-CD19-FITC and anti-NK1.1-FITC, anti-CD11c-PE, and anti-B220-biotin. The CD11c versus B220 profile is shown, after the CD19- or NK1.1-positive populations were electrically gated out to exclude B and NK cells. The biotinylated B220 antibody was detected with streptavidin-PerCP-Cy5.5. The values (%) indicate the proportion of gated populations to total thymic or splenic cells.
Table 1.
Reduced number of CD4+CD8– DCs in IRF-4–/– spleen
| Wild type | IRF-4-/- | |
|---|---|---|
| Splenocytes | 1,040 ± 240 | 1,030 ± 190 |
| CD11chighMHC-II+ | 22.5 ± 3.2 | 11.7 ± 3.1 |
| CD11bhighCD4+CD8- | 12.8 ± 2.1 | 1.5 ± 0.5 |
| CD11bhighCD4-CD8- | 4.6 ± 1.2 | 5.0 ± 1.3 |
| CD11blowCD4-CD8+ | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 5.1 ± 1.5 |
| CD11clntB220+ | 5.1 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 0.5 |
Results represent the number of cells per spleen. Values are the means ± SD (× 10-5) of eight mice aged 6 weeks.
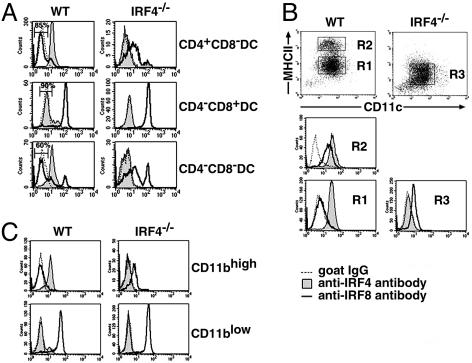
IRF-4/IRF-8 Expression in Distinct DC Subsets. We next analyzed the expression of IRF-4 and IRF-8 in each splenic conventional DC subset at the single cell level, using four-color flow cytometry after triple staining of cell surface markers and intracellular IRFs (Fig. 4A). IRF-8 is another member of the IRF family that is important for DC development (25–28). In the wild-type spleen, all of the CD4+CD8α– DCs expressed IRF-4 and a small population (≈15%) expressed IRF-8, indicating that most of the CD4+CD8α– DCs express IRF-4 alone, and a minor population expresses both IRFs. In contrast, the majority of CD4–CD8α+ DCs in the wild-type spleen expressed IRF-8 and only ≈10% expressed IRF-4, indicating that most CD4–CD8α+ DCs express IRF-8, but not IRF-4. The majority of CD4–CD8α– splenic DCs expressed IRF-4 in wild-type mice, whereas ≈40% expressed IRF-8. In the IRF4–/– mouse spleen, all of the CD4–CD8α+ DCs expressed IRF-8, as expected. Interestingly, the small population of CD4+CD8α– DCs that remained in IRF4–/– mice expressed IRF-8, unlike the majority of these cells in wild-type mice. In addition, the majority of the CD4–CD8α– DCs, of which ≈60% did not express IRF-8 in wild-type mice, also expressed IRF-8 in the IRF-4–/– spleen. Taken together, these results indicate that the IRF-4 defect specifically affected the CD4+CD8α– and CD4–CD8α– DC subsets, which both preferentially expressed IRF-4 in wild-type mice.
Fig. 4.
IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression in various DC subsets. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression in splenic conventional DCs. After low-density cells from wild-type and IRF-4–/– spleen were stained with anti-CD11c-PE, anti-CD4-allophycocyanin, and anti-CD8α-PerCP-Cy5.5, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-IRF-4 or anti-IRF-8, followed by the Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated second antibody. CD11chigh DCs were gated on, and divided into the three subsets. Each subset was gated on, and IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression was examined. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression in DCs from the GM-CSF culture. The wild-type and IRF-4–/– DCs were stained with anti-MHC-II-biotin and anti-CD11c-PE, followed by intracellular staining as described in A. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression in DCs from the Flt3L culture. The wild-type and IRF-4–/– DCs were stained with anti-CD11b-biotin and anti-CD11c-PE, followed by intracellular staining as described in A. Cells were divided into CD11bhigh and CD11blow DCs as shown in Fig. 2 A. Each population was gated on, and IRF-4 and IRF-8 expression was examined. The biotinylated antibodies used in B and C were detected with streptavidin-PerCP-Cy5.5.
The expression levels of IRF-4 and -8 in CD11c+ cells from the BM culture with GM-CSF were analyzed by flow cytometry (Fig. 4B). IRF-4 was expressed in both immature (R1) and mature (R2) wild-type DCs. However, IRF-8 was not expressed in immature wild-type DCs, suggesting a role of IRF-8 in the maturation of wild-type DCs, as reported (25–27), but not for their development in the GM-CSF-supplemented culture. The stimulation of the immature DCs with LPS induced IRF-8 expression, concomitant with their maturation (data not shown). In contrast, the majority of CD11c+ cells from IRF-4–/– BM (R3) expressed IRF-8. The aberrant expression of IRF-8 in these cells was insufficient to compensate for the lack of IRF-4, because these cells were unable to become functional DCs (Fig. 1).
We also analyzed the expression of IRF-4 and -8 in CD11bhigh and CD11blow DCs from the BM culture with Flt3L (Fig. 4C). The majority of CD11bhigh cells from wild-type BM expressed IRF-4, but not IRF-8, whereas the majority CD11blow cells expressed IRF-8, but not IRF-4. Interestingly, the majority of CD11bhigh cells that were generated from IRF-4–/– BM expressed significant levels of IFR-8, unlike those derived from wild-type BM. This result is consistent to the in vivo observation that most CD11bhigh splenic DCs express IRF-8 in the IRF-4–/– mouse (Fig. 4A).
Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrated that IRF-4 is important for most DCs of the CD11bhighCD8α– subset, but not of the CD11blowCD8α+ subset. We show that IRF-4 is expressed in most DCs of the CD11bhighCD8α– subset, but not of CD11blowCD8α+ subset in mouse spleen. The expression of IRF-4 in this DC subset was also confirmed in two BM culture systems. The DCs derived from BM in the presence of GM-CSF were uniformly CD11bhigh, and most of them expressed IRF-4. Both CD11bhigh and CD11blow conventional DCs developed from BM in cultures supplemented with Flt3L; however, IRF-4 was preferentially expressed in the CD11bhigh DC populations. Studies with mice lacking IRF-4 also determined that IRF-4 plays a critical role in these DC subsets. The development of CD11bhigh DCs from IRF-4–/– BM in vitro was severely impaired in both culture systems. Furthermore, the number of CD4+CD8α– DCs, a major subset of CD11bhigh DCs, was severely reduced in the spleen in mice lacking IRF-4. These results indicate that IRF-4 is selectively expressed in the CD11bhigh subset of conventional DCs and plays critical roles in their development.
Comparative analyses of the expression of IRF-4 and IRF-8 in DCs revealed that conventional DCs can be grouped into three subpopulations: IRF-4(+)IRF-8(–), IRF-4(–)IRF-8(+), and IRF-4(+)IRF-8(+). The IRF-4(+)IRF-8(–) subpopulation preferentially belongs to the both CD11bhighCD4+ and CD11bhighCD4– subsets, whereas the IRF-4(–)IRF-8(+) subpopulation preferentially belongs to the CD11blowCD8– DC subset. This observation may yield insight into the complicated developmental pathways of DCs. In mice lacking IRF-4, most of the DCs in CD11bhighCD8– subset expressed IRF-8, although the majority of the DCs in this subset did not express IRF-8 in the wild-type mouse. These results suggest that a subset of IRF-8(–) DCs could not be generated in the absence of the IRF-4 gene, implying that IRF-4 is essential for the development of IRF-8(–), but not IRF-8(+), DCs. In contrast to the CD11bhigh DC subsets, we did not detect any significant abnormality in the CD11blowCD8α+ DCs in IRF-4–/– mice. This subpopulation of DCs in the spleens of wild-type and IRF-4–/– mice is IRF-8(+). The DCs that develop from the BM of IRF-4–/– mice in the Flt3L-supplemented culture are also IRF-8(+), suggesting that IRF-4 is not essential for the development and maturation of CD11blowCD8α+ conventional DCs. Taken together, it is clear that all of the DC subsets that were examined expressed IRF-4 and/or IRF-8, suggesting the intriguing possibility that the function of either IRF-4 or IRF-8 is essential for the development of DCs.
The development of CD11bhigh CD4+ DCs was severely impaired in mice lacking the RelB subunit of NF-κB (45). This defect in the DC subset is similar to the defects in IRF-4–/– mice. The expression of the IRF-4 gene is activated by c-Rel, another member of the NF-κB family, in B cells (46). RelB can bind to the same recognition DNA sequence as c-Rel in DCs (47). These findings suggest that IRF-4 might be regulated by RelB in DCs. In addition, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which operates in the activation of NF-κB, is required for the development of conventional CD4+ DCs (45), suggesting that IRF-4 might also be regulated through TRAF6. The elucidation of the regulatory mechanisms for IRF-4 gene expression would help to clarify the developmental mechanisms of DCs.
Functional differences between CD11bhighCD8α– and CD11blowCD8α+ DCs have been suggested in a number of studies. These two subclasses of DCs regulate the development of T helper (Th) cells secreting discrete sets of lymphokines: CD11bhighCD8α– DCs induce Th2-type responses and CD11blowCD8α+ DCs induce Th1-type responses (48). The preferential induction of Th1 responses by CD11blowCD8α+ DCs is mainly caused by their production of IL-12. In this study, we showed that IRF-4 and IRF-8 are expressed preferentially in CD11bhighCD8α– and CD11blowCD8α+ DCs, respectively. These IRFs may dictate not only the differentiation but also the function of these DC subsets. IRF-8 directs the expression of IL-12 (49) and IL-18 (50), promoting Th1-biased immune responses. On the other hand, IRF-4 is involved in the Th2-bias, by promoting IL-4 production by CD4+ T-cells and regulating their responsiveness to IL-4 (24, 51, 52). Therefore, it is intriguing to speculate that the IRF-4 expressed in the CD11bhighCD8α– subset of DCs is involved in Th2-biased immune responses, by inducing certain Th2-promoting cytokines. In addition, the IRF-4 expressed in B cells is critical for their Ab production, further supporting the role of IRF-4 in humoral immune responses (23). Taken together, these results strongly suggest that the IRF-4 expressed in T and B lymphocytes, as well as in the CD11bhighCD8α– subset of DCs, is a crucial transcription factor for promoting humoral immune responses. In other words, IRF-4 polarizes the Th2 response extrinsically as well as intrinsically. Further analyses of DCs and DC precursors, based on the expression and functions of IRF members, should provide important insights into the present controversy regarding both the developmental origin of DCs and the functional distinctions among DC subsets.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank T. Moriuch and M. Nakamura for animal care and Drs. W. Heath and H. Kosaka for providing the OT-II mice. We also thank Dr. T. Sudo for the GM-CSF-producing and -indicator cells, Drs. K. Yamashita and K. Miyazaki for technical advice, and Dr. S. Yoshinaga for helpful discussions and comments. This work was supported by 21st Century COE Program of Nagasaki University and a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientist (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
This paper was submitted directly (Track II) to the PNAS office.
Abbreviations: DC, dendritic cell; BM, bone marrow; Flt3L, Flt3 ligand; GM-CSF, granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IRF, IFN-regulatory factor; PE, phycoerythrin; PerCP, peridinin chlorophyll-α protein; NPTII, neomycin phosphotransferase II; OVA, ovalbumin; MHC-II, MHC class II; NK, natural killer.
References
- 1.Shortman, K. & Liu, Y. J. (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 151–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bjorck, P. (2001) Blood 98, 3520–3526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Asselin-Paturel, C., Boonstra, A., Dalod, M., Durand, I., Yessaad, N., Dezutter-Dambuyant, C., Vicari, A., O'Garra, A., Biron, C., Briere, F. & Trinchieri, G. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2, 1144–1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nakano, H., Yanagita, M. & Gunn, M. D. (2001) J. Exp. Med. 194, 1171–1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ardavin, C. (2003) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 582–590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vremec, D., Pooley, J., Hochrein, H., Wu, L. & Shortman, K. (2000) J. Immunol. 164, 2978–2986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Martin, P., del Hoyo, G. M., Anjuere, F., Ruiz, S. R., Arias, C. F., Marin, A. R. & Ardavin, C. (2000) Blood 96, 2511–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Inaba, K., Inaba, M., Romani, N., Aya, H., Deguchi, M., Ikehara, S., Muramatsu, S. & Steinman, R. M. (1992) J. Exp. Med. 176, 1693–1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lutz, M. B., Kukutsch, N., Ogilvie, A. L., Rossner, S., Koch, F., Romani, N. & Schuler, G. (1999) J. Immunol. Methods 223, 77–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brasel, K., De Smedt, T., Smith, J. L. & Maliszewski, C. R. (2000) Blood 96, 3029–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Taniguchi, T., Ogasawara, K., Takaoka, A. & Tanaka, N. (2001) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 623–655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matsuyama, T., Grossman, A., Mittrucker, H. W., Siderovski, D. P., Kiefer, F., Kawakami, T., Richardson, C. D., Taniguchi, T., Yoshinaga, S. K. & Mak, T. W. (1995) Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 2127–2136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eisenbeis, C. F., Singh, H. & Storb, U. (1995) Genes Dev. 9, 1377–1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Scott, E. W., Simon, M. C., Anastasi, J. & Singh, H. (1994) Science 265, 1573–1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.McKercher, S. R., Torbett, B. E., Anderson, K. L., Henkel, G. W., Vestal, D. J., Baribault, H., Klemsz, M., Feeney, A. J., Wu, G. E., Paige, C. J. & Maki, R. A. (1996) EMBO J. 15, 5647–5658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Anderson, K. L., Perkin, H., Surh, C. D., Venturini, S., Maki, R. A. & Torbett, B. E. (2000) J. Immunol. 164, 1855–1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guerriero, A., Langmuir, P. B., Spain, L. M. & Scott, E. W. (2000) Blood 95, 879–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Perkel, J. M. & Atchison, M. L. (1998) J. Immunol. 160, 241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yamagata, T., Nishida, J., Tanaka, S., Sakai, R., Mitani, K., Yoshida, M., Taniguchi, T., Yazaki, Y. & Hirai, H. (1996) Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 1283–1294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Imaizumi, Y., Kohno, T., Yamada, Y., Ikeda, S., Tanaka, Y., Tomonaga, M. & Matsuyama, T. (2001) Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92, 1284–1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rosenbauer, F., Waring, J. F., Foerster, J., Wietstruk, M., Philipp, D. & Horak, I. (1999) Blood 94, 4274–4281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marecki, S., Atchison, M. L. & Fenton, M. J. (1999) J. Immunol. 163, 2713–2722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mittrucker, H. W., Matsuyama, T., Grossman, A., Kundig, T. M., Potter, J., Shahinian, A., Wakeham, A., Patterson, B., Ohashi, P. S. & Mak, T. W. (1997) Science 275, 540–543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tominaga, N., Ohkusu-Tsukada, K., Udono, H., Abe, R., Matsuyama, T. & Yui, K. (2003) Int. Immunol. 15, 1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schiavoni, G., Mattei, F., Sestili, P., Borghi, P., Venditti, M., Morse, H. C., III, Belardelli, F. & Gabriele, L. (2002) J. Exp. Med. 196, 1415–1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aliberti, J., Schulz, O., Pennington, D. J., Tsujimura, H., Reis e Sousa, C., Ozato, K. & Sher, A. (2003) Blood 101, 305–310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tsujimura, H., Tamura, T., Gongora, C., Aliberti, J., Reis e Sousa, C., Sher, A. & Ozato, K. (2003) Blood 101, 961–969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsujimura, H., Tamura, T. & Ozato, K. (2003) J. Immunol. 170, 1131–1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barnden, M. J., Allison, J., Heath, W. R. & Carbone, F. R. (1998) Immunol. Cell Biol. 76, 34–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yu, D., Imajoh-Ohmi, S., Akagawa, K. & Kanegasaki, S. (1996) J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 119, 23–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kumatori, A., Yang, D., Suzuki, S. & Nakamura, M. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9103–9111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Skalnik, D. G., Dorfman, D. M., Perkins, A. S., Jenkins, N. A., Copeland, N. G. & Orkin, S. H. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 8505–8509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Suzuki, S., Kumatori, A., Haagen, I. A., Fujii, Y., Sadat, M. A., Jun, H. L., Tsuji, Y., Roos, D. & Nakamura, M. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6085–6090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yang, D., Suzuki, S., Hao, L. J., Fujii, Y., Yamauchi, A., Yamamoto, M., Nakamura, M. & Kumatori, A. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9425–9432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hashimoto, S. I., Suzuki, T., Nagai, S., Yamashita, T., Toyoda, N. & Matsushima, K. (2000) Blood 96, 2206–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ahn, J. H., Lee, Y., Jeon, C., Lee, S. J., Lee, B. H., Choi, K. D. & Bae, Y. S. (2002) Blood 100, 1742–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chang, C. H., Guerder, S., Hong, S. C., van Ewijk, W. & Flavell, R. A. (1996) Immunity 4, 167–178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Muhlethaler-Mottet, A., Otten, L. A., Steimle, V. & Mach, B. (1997) EMBO J. 16, 2851–2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Burkly, L., Hession, C., Ogata, L., Reilly, C., Marconi, L. A., Olson, D., Tizard, R., Cate, R. & Lo, D. (1995) Nature 373, 531–536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wu, L., D'Amico, A., Winkel, K. D., Suter, M., Lo, D. & Shortman, K. (1998) Immunity 9, 839–847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miyamoto, T., Ohneda, O., Arai, F., Iwamoto, K., Okada, S., Takagi, K., Anderson, D. M. & Suda, T. (2001) Blood 98, 2544–2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brawand, P., Fitzpatrick, D. R., Greenfield, B. W., Brasel, K., Maliszewski, C. R. & De Smedt, T. (2002) J. Immunol. 169, 6711–6719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gilliet, M., Boonstra, A., Paturel, C., Antonenko, S., Xu, X. L., Trinchieri, G., O'Garra, A. & Liu, Y. J. (2002) J. Exp. Med. 195, 953–958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lian, Z. X., Okada, T., He, X. S., Kita, H., Liu, Y. J., Ansari, A. A., Kikuchi, K., Ikehara, S. & Gershwin, M. E. (2003) J. Immunol. 170, 2323–2330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kobayashi, T., Walsh, P. T., Walsh, M. C., Speirs, K. M., Chiffoleau, E., King, C. G., Hancock, W. W., Caamano, J. H., Hunter, C. A., Scott, P., et al. (2003) Immunity 19, 353–363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Grumont, R. J. & Gerondakis, S. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 191, 1281–1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Boffa, D. J., Feng, B., Sharma, V., Dematteo, R., Miller, G., Suthanthiran, M., Nunez, R. & Liou, H. C. (2003) Cell Immunol. 222, 105–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Maldonado-Lopez, R. & Moser, M. (2001) Semin. Immunol. 13, 275–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Giese, N. A., Gabriele, L., Doherty, T. M., Klinman, D. M., Tadesse-Heath, L., Contursi, C., Epstein, S. L. & Morse, H. C., III (1997) J. Exp. Med. 186, 1535–1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim, Y. M., Kang, H. S., Paik, S. G., Pyun, K. H., Anderson, K. L., Torbett, B. E. & Choi, I. (1999) J. Immunol. 163, 2000–2007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rengarajan, J., Mowen, K. A., McBride, K. D., Smith, E. D., Singh, H. & Glimcher, L. H. (2002) J. Exp. Med. 195, 1003–1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lohoff, M., Mittrucker, H. W., Prechtl, S., Bischof, S., Sommer, F., Kock, S., Ferrick, D. A., Duncan, G. S., Gessner, A. & Mak, T. W. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11808–11812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.