Figure 1.
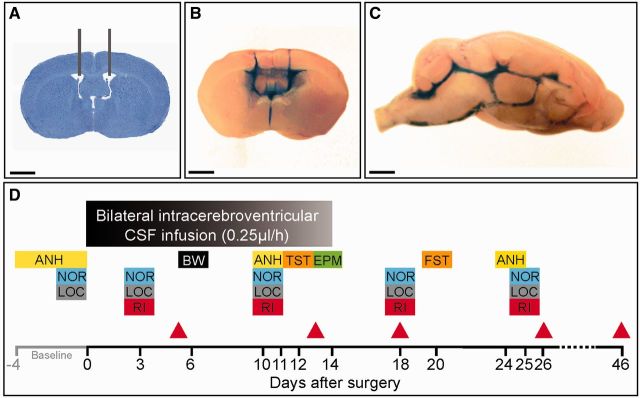
Experimental design and placement of ventricular catheters. (A) Representative coronal mouse brain section with catheter placement. Scale bar = 2 mm. (B and C) Coronal and sagittal mouse brain sections demonstrating cerebroventricular diffusion of methylene blue after ventricular infusion. Scale bars = 2 mm. (D) Schedule of cognitive testing and animal sacrifice. At Day 0, catheters and osmotic pumps were placed and bilateral ventricular infusion of patients’ or control CSF started. Infusion lasted for 14 days. Memory [novel object recognition (NOR)], anhedonia [sucrose preference test (ANH)], depressive-like behaviour [tail suspension test (TST) and forced swimming test (FST)], anxiety [black and white test (BW) and elevated plus maze test (EPM)], aggressiveness [resident intruder test (RI)] and locomotor activity (LOC) were assessed blinded to treatment at the indicated days. The novel object recognition was assessed in open field and V-maze paradigms in two different cohorts of mice. Animals were habituated for 1 to 4 days before surgery (baseline) to novel object recognition, anhedonia, and locomotor activity. Red arrowheads indicate the days of sacrifice for studies of effects of antibodies in brain.
