Fig. 10.
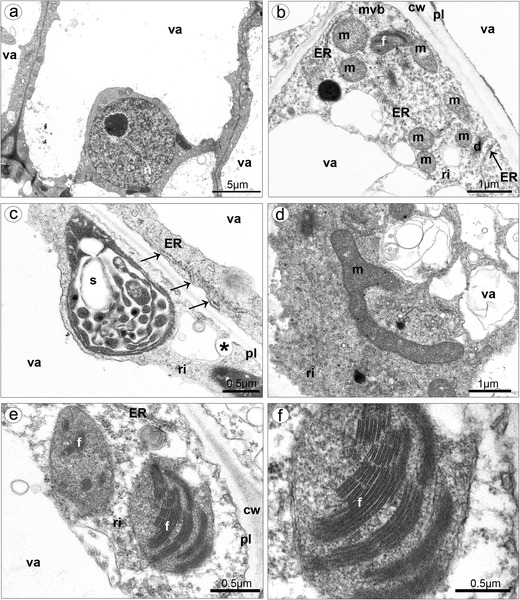
Ultrastructure of isthmus cells. a Highly vacuolated cells, with large nucleus. b In cytoplasm, presence of numerous mitochondria, plastid with phytoferritin, dictyosome, multivesicular body, free ribosomes, and ER in contact with plasmalemma. c Plastid with partially hydrolyzed starch grains, plastoglobuli, and internal membranes, ER in contact with plasmalemma (arrows), invagination of plasmalemma. d Branched mitochondrion. e Proplastids with phytoferritin. f Magnification of e (cw cell wall, d dictyosome, ER endoplasmic reticulum, f phytoferritin, l lipid body, m mitochondrion, mvl multivesicular body, pl plasmalemma, ri ribosome, s starch grain, va vacuole)
