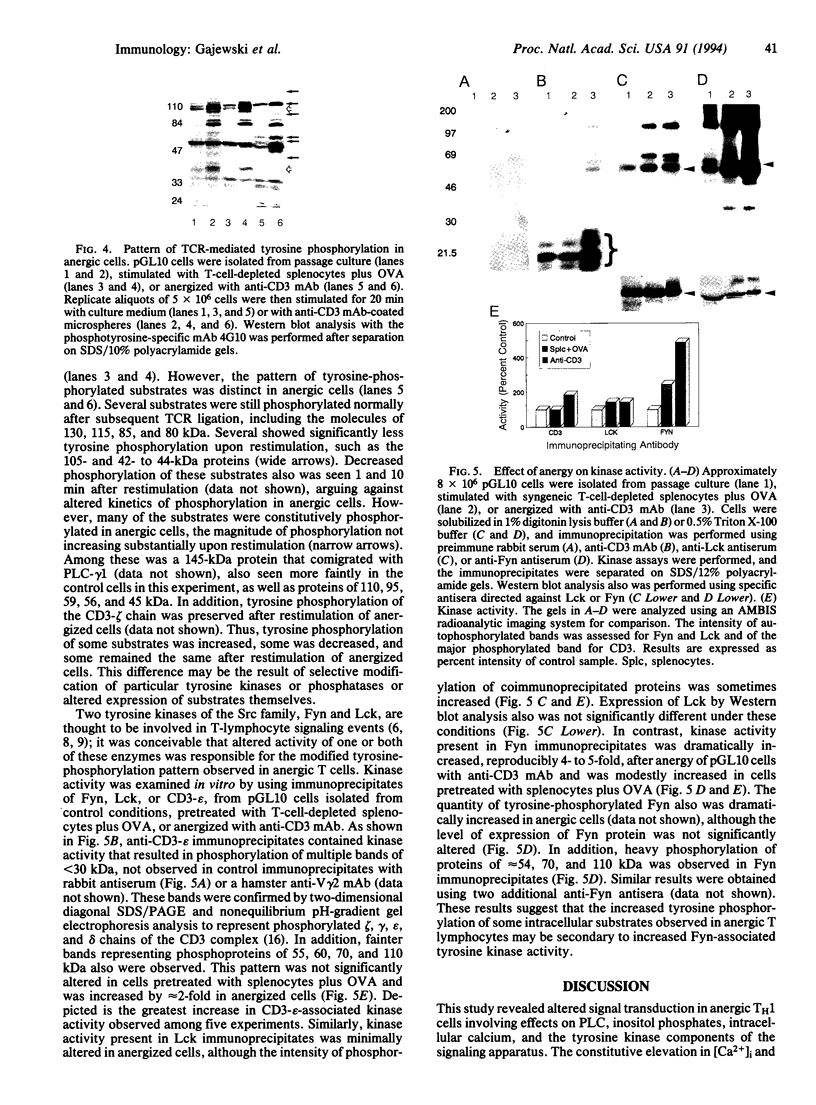
Abstract
Full activation of TH1 helper T lymphocytes requires ligation of the specific T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) and a second signal provided by costimulator molecule(s) expressed on particular antigen-presenting cells. Stimulation via the TCR complex alone generates a subsequent unresponsive state characterized by an inability to produce interleukin 2. We report here that such anergic cells exhibit multiple alterations in TCR-associated signaling. The basal levels of intracellular free calcium and phosphatidylinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate are elevated in anergic cells, and the levels fail to increase significantly upon subsequent restimulation. Examination of phospholipase C-gamma 1 reveals evidence for post-translational modification, correlating with increased tyrosine phosphorylation of the molecule. Tyrosine phosphorylation of additional substrates identified from whole-cell lysates also is altered compared to untreated cells, suggesting a modification in net tyrosine kinase activity. Although the level of kinase activity present in TCR/CD3 or Lck immunoprecipitates is modestly altered after induction of anergy, there is a dramatic increase in specific Fyn-associated tyrosine kinase activity in anergic cells and increased phosphorylation of a 110-kDa protein that is coimmunoprecipitated with Fyn. These results are consistent with a model in which anergic TH1 lymphocytes display a fundamental alteration in TCR-mediated tyrosine kinase activity, associated with changes in phospholipase C-gamma 1, inositol phosphates, and intracellular free calcium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan A. C., Irving B. A., Fraser J. D., Weiss A. The zeta chain is associated with a tyrosine kinase and upon T-cell antigen receptor stimulation associates with ZAP-70, a 70-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9166–9170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M., Forbush K. A., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by a src family protein-tyrosine kinase (p59fyn). Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90162-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Fitch F. W. Anti-proliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. IV. Murine CTL clones produce IL-3 and GM-CSF, the activity of which is masked by the inhibitory action of secreted IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):548–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Joyce J., Fitch F. W. Antiproliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. III. Differential selection of TH1 and TH2 murine helper T lymphocyte clones using recombinant IL-2 and recombinant IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Pinnas M., Wong T., Fitch F. W. Murine Th1 and Th2 clones proliferate optimally in response to distinct antigen-presenting cell populations. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1750–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski T. F., Schell S. R., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating utilization of different T cell receptor-associated signaling pathways by TH1 and TH2 clones. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4110–4120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go C., Lancki D. W., Fitch F. W., Miller J. Anergized T cell clones retain their cytolytic ability. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsi E. D., Siegel J. N., Minami Y., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell activation induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a limited number of cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Schieven G. L., Siegel J. N., Phillips A. F., Samelson L. E. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7722–7726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. M., Beverly B., Tran A. C., Brorson K., Schwartz R. H., Lenardo M. J. Transactivation by AP-1 is a molecular target of T cell clonal anergy. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1134–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Kim J. W., Zilberstein A., Margolis B., Kim J. G., Schlessinger J., Rhee S. G. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-gamma 1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Cooke M. P., Mellins E. D., Gearn M. E., Samelson L. E., Wilson C. B., Miller A. D., Perlmutter R. M. Lymphocyte activation provokes modification of a lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck). J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2430–2437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. J., Rho H. W., Rhee S. G. CD3 stimulation causes phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 on serine and tyrosine residues in a human T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5453–5456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian D., Griswold-Prenner I., Rosner M. R., Fitch F. W. Multiple components of the T cell antigen receptor complex become tyrosine-phosphorylated upon activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4488–4493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Riley M. P., Cho E. A., Casnellie J. E., Reed J. C., Torigoe T. Anergic Th1 cells express altered levels of the protein tyrosine kinases p56lck and p59fyn. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2887–2893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F., Fowlkes B. J. Maintenance of in vivo tolerance by persistence of antigen. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1130–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. A cell culture model for T lymphocyte clonal anergy. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1349–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.2113314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






