Abstract
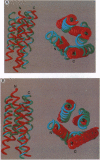
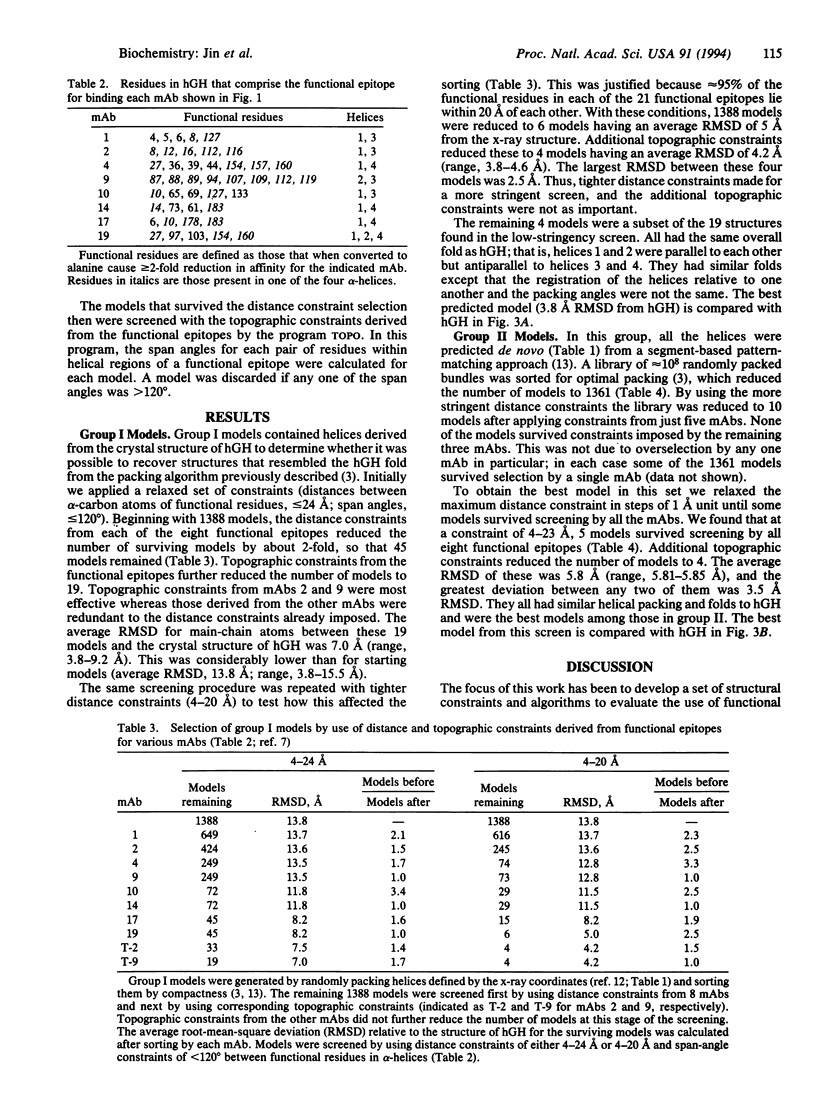
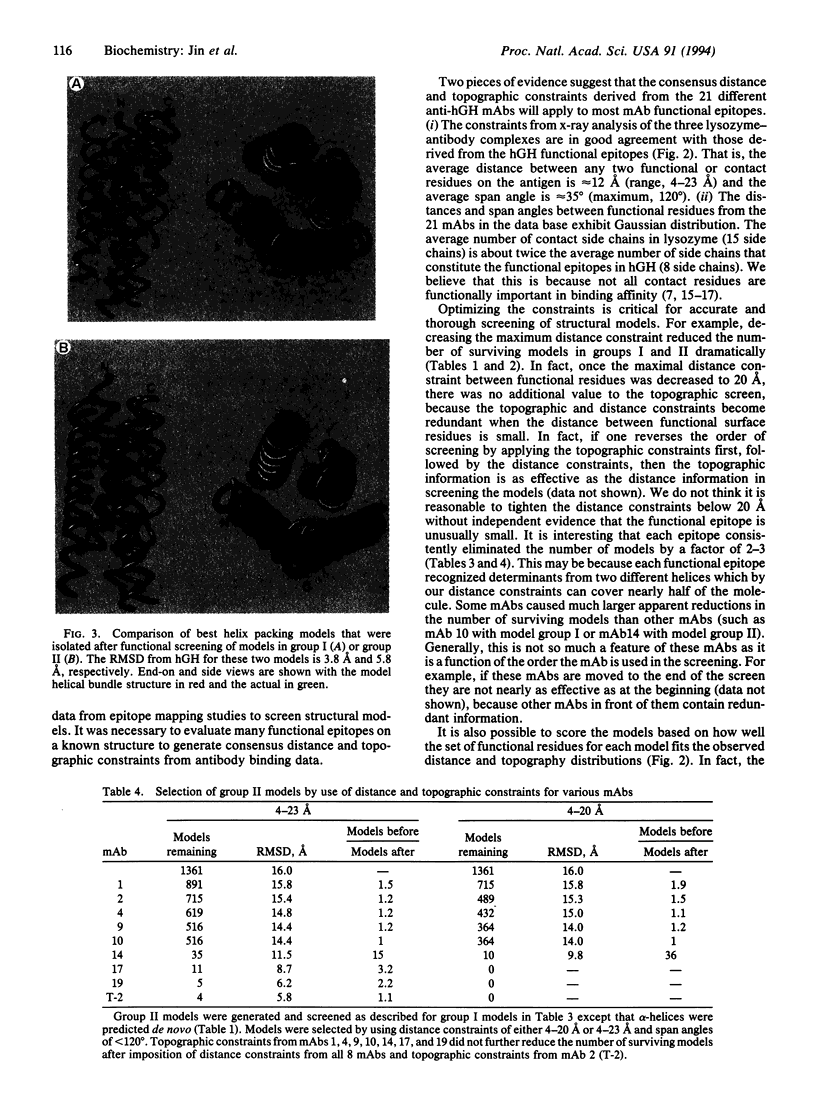
Structural constraints derived from different antibody epitopes on human growth hormone (hGH) were used to screen three-dimensional models of hGH that were generated by computer algorithms. Previously, alanine-scanning mutagenesis defined the residues that modulate binding to 21 different monoclonal antibodies to hGH. These functional epitopes were composed of 4-14 side chains whose alpha-carbons clustered within 4-23 A. Distance and topographic constraints for these functional epitopes were virtually the same as constraints derived from known x-ray structures of protein-antigen complexes. The constraints were used to evaluate about 1400 models of hGH that were computer-generated by a secondary-structure prediction and packing algorithm. On average each functional epitope reduced the number of models in the pool by a factor of 2, so that 8 monoclonal antibodies could reduce the number of possible models to < 10. The average root-mean-square deviation of alpha-carbon coordinates between the x-ray structure and either the pool of starting models or final models ranged from 13 to 16 A or 4 to 7 A, respectively, depending on the pool of starting models and the level of constraints imposed. All of the final models had the correct folding topography, and the best model was within 3.8 A root-mean-square deviation of the x-ray coordinates. This model was as close as it could have been because the models were built by using ideal helices and those in the x-ray structure are not. Our studies suggest that epitope mapping data can effectively screen structural models and, when coupled to predictive algorithms, can help to generate low-resolution models of a protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. M. The probable arrangement of the helices in G protein-coupled receptors. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1693–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass S. H., Mulkerrin M. G., Wells J. A. A systematic mutational analysis of hormone-binding determinants in the human growth hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Kuntz I. D. Prediction of the three-dimensional structure of human growth hormone. Proteins. 1987;2(2):162–166. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Richmond T. J., Richards F. M. Protein folding: evaluation of some simple rules for the assembly of helices into tertiary structures with myoglobin as an example. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. Comparison of a structural and a functional epitope. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):554–563. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J. Protein structure prediction. Biochimie. 1990 Aug;72(8):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90115-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L., Fendly B. M., Wells J. A. High resolution functional analysis of antibody-antigen interactions. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):851–865. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. F., O'Connell M. P. Thermodynamic analysis of an antibody functional epitope. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 13;32(27):6828–6835. doi: 10.1021/bi00078a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. D., Hoogenboom H. R., Bonnert T. P., McCafferty J., Griffiths A. D., Winter G. By-passing immunization. Human antibodies from V-gene libraries displayed on phage. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):581–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90498-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J., Bruccoleri R. E., Saul F. A. On the attribution of binding energy in antigen-antibody complexes McPC 603, D1.3, and HyHEL-5. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4735–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näthke I. S., Heuser J., Lupas A., Stock J., Turck C. W., Brodsky F. M. Folding and trimerization of clathrin subunits at the triskelion hub. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):899–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Silverton E. W., Sheriff S., Cohen G. H., Smith-Gill S. J., Davies D. R. Structure of an antibody-antigen complex: crystal structure of the HyHEL-10 Fab-lysozyme complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5938–5942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell S. R., Cohen B. I., Cohen F. E. A segment-based approach to protein secondary structure prediction. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):983–993. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Silverton E. W., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Smith-Gill S. J., Finzel B. C., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of an antibody-antigen complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a spectroscopic ruler. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:819–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. M., Flores T. P., Jones D. T., Swindells M. B. Protein structure. Prediction of progress at last. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):105–106. doi: 10.1038/354105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Structural determinants of the conformations of medium-sized loops in proteins. Proteins. 1989;6(4):382–394. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A. Systematic mutational analyses of protein-protein interfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:390–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]