Abstract
A cross-bridged cyclam ligand bearing two N-carboxymethyl pendant arms (1) has been found to form a copper(II) complex that exhibits significantly improved biological behavior in recent research towards 64Cu-based radiopharmaceuticals. Both the kinetic inertness and resistance to reduction of Cu–1 are believed to be relevant to its enhanced performance. To explore the influence of pendant arm length on these properties, new cross-bridged cyclam and cyclen ligands with longer N-carboxyethyl pendant arms, 2 and 4, and their respective copper(II) complexes have been synthesized. Both mono- as well as di-O-protonated forms of Cu–2 have also been isolated and structurally characterized. The spectral and structural properties of Cu–2 and Cu–4, their kinetic inertness in 5 M HCl, and electrochemical behavior have been obtained and compared to those of their N-carboxymethyl-armed homologs, Cu–1 and Cu–3. Only the cyclam-based Cu–1 and Cu–2 showed unusually high kinetic inertness towards acid decomplexation. While both of these complexes also exhibited quasi-reversible Cu(II)/Cu(I) reductions, Cu–2 is easier to reduce by a substantial margin of +400 mV, bringing it within the realm of physiological reductants. Similarly, of the cyclen-based complexes, Cu–4 is also easier to reduce than Cu–3 though both reductions are irreversible. Biodistribution studies of 64Cu-labeled 2 and 4 were performed in Sprague Dawley rats. Despite comparable acid inertness to their shorter-armed congeners, both longer-armed ligand complexes have poorer bio-clearance properties. This inferior in vivo behavior may be a consequence of their higher reduction potentials.
Introduction
Copper-based radiopharmaceuticals, especially those of 64Cu, have promise in both diagnostic and targeted-therapy applications.1–4 The biological integrity of a radiometal-labeled pharmaceutical is critical to its efficacy. As a result powerful chelators based on the 14-membered tetraazamacrocycle cyclam and its pendant-armed derivatives such as TETA (Fig. 1) have been of special interest due to their robust Cu(II) complexes. However, in spite of the excellent in vitro thermodynamic stability of Cu–TETA (log Kf 21.9), significant in vivo demetallation of the corresponding 64=Cu-labeled complexes and bioconjugates have been observed.5 Both Cu(II) displacement and copper loss following Cu(II) reduction to Cu(I) are plausible demetallation pathways. We recently reported the enhanced in vivo stability of the 64Cu-complex of a cross-bridged cyclam ligand derivative, 1 (Fig. 1) and its bioconjugate of a somatostatin analogue.6–8 It was hypothesized that the improved biological behavior of this complex may originate from its kinetic inertness to copper loss in both Cu(II) and Cu(I) oxidation states. A convenient gauge of the former is its acid-decomplexation half-life. We have found that Cu–1 is remarkably stable even in 5 M HCl solution, requiring 90 °C to initiate decomplexation with a half-life of 154(6) h.9 Furthermore, of the four carboxymethyl pendant-armed cyclam and cyclen Cu(II) complexes, only Cu–1 displayed a quasi-reversible electrochemical reduction in aqueous solution (E1/2 = − 1.08V vs. Ag/AgCl, ΔE = 101 mV).9 The solid-state structure of this complex (Fig. 2a) confirmed the good fit of Cu(II) within the ligand cleft of 1.9,10 By contrast, the related cross-bridged cyclen complex, Cu–3 has a structure with a significantly distended Cu(II) cation, indicating a mismatch within the smaller ligand's metal-binding cleft (Fig. 2b).7 In addition, this complex's dramatically reduced kinetic inertness towards acid-decomplexation (t1/2 < 1 min in 5 M HCl at 90 °C) was found to correlate with the significantly lower in vivo stability of the corresponding 64Cu-labeled complex.7,9
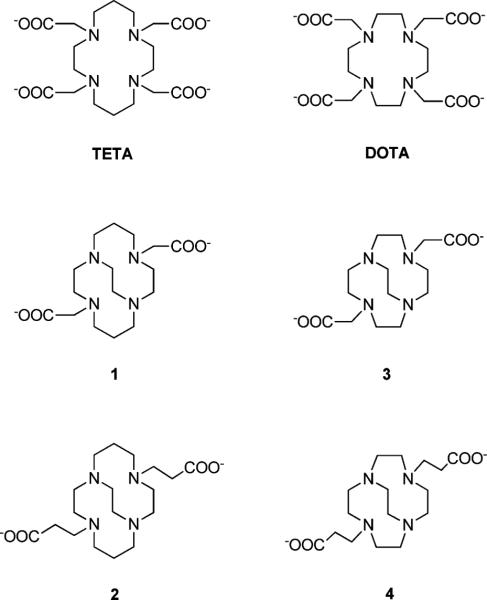
Fig. 1.
The tetraamine macrocycles TETA, DOTA, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Fig. 2.
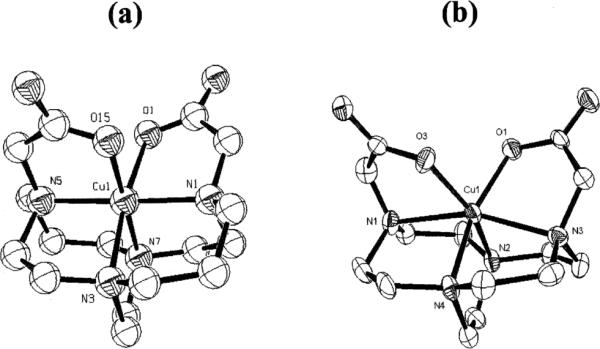
X-Ray structures of: (a) Cu–1, and (b) Cu–3.
Metal complexes of N-carboxyethyl pendant-armed cyclam and cyclen derivatives have been shown to exhibit significantly different coordination modes, as well as distinct formation, dissociation, and metal exchange kinetics from their N-carboxymethyl analogues like DOTA and TETA.11–15 Furthermore, both a macrocyclic complex's pendant arm on/off dynamics and redox chemistry can also be influenced by this variation in arm length.16,17 Herein we report new N-carboxyethyl pendant-armed cross-bridged cyclam and cyclen ligands 2 and 4 (Fig. 1) and their Cu(II) complexes. The coordination mode, spectral properties, inertness towards acid decomplexation, as well as electrochemical behavior of these complexes were assessed and compared with those of Cu– 1 and Cu–3. Animal biodistribution studies of 64Cu-labeled 2 and 4 were also carried out to discover possible correlations with these in vitro properties.
Results
Ligand syntheses
Long-arm cross-bridged dicarboxylate ligands 2 and 4 were synthesized via di-tert-butyl ester precursors 5 and 6 respectively from the corresponding parent cross-bridged tetraamines10,18 as shown in Fig. 3. While direct conjugate additions of macrocyclic polyamines to acrylic acid have been reported in the literature,19 we wished to avoid anticipated problems associated with reproducible preparation and quantification of salts of 2 and 4. Our previous work on dicarboxylate ligands 1 and 3 had shown that tert-butyl esters are ideal precursors that can be quantitatively deprotected under relatively mild conditions. However, conjugate addition products of polyamines sometimes undergo facile dealkylation.20 For example, the methyl ester analogue of 5 was readily prepared by conjugate addition of cross-bridged cyclam to methyl acrylate, but attempted acidic hydrolysis of the diester to H22·nHCl resulted in partial arm loss. Thus, it was essential to demonstrate that deprotection of 5 and 6 was clean and quantitative, with no pendant arm loss. Reactions of cross-bridged cyclam and cross-bridged cyclen with excess tert-butyl acrylate in acetonitrile (MeCN) at room temperature gave 5 and 6 in excellent yields (97% each) and high purity after removal of residual alkylating agent. 5 and 6 were deprotected with elimination of isobutylene in neat, dry CF3CO2H (TFA) at room temperature. Gratifyingly, the reactions were extremely clean, with no evidence (NMR) of dealkylative arm loss. In each case, after careful removal of as much TFA as possible, 19F NMR experiments involving addition of CF3Ph internal standard showed approximately 4 equivalents of TFA per tetraamine ligand (H22 or H24). This is consistent with di-protonation of the tetraamine and two additional equivalents of TFA hydrogen-bonded to arm-CO2H groups.
Fig. 3.
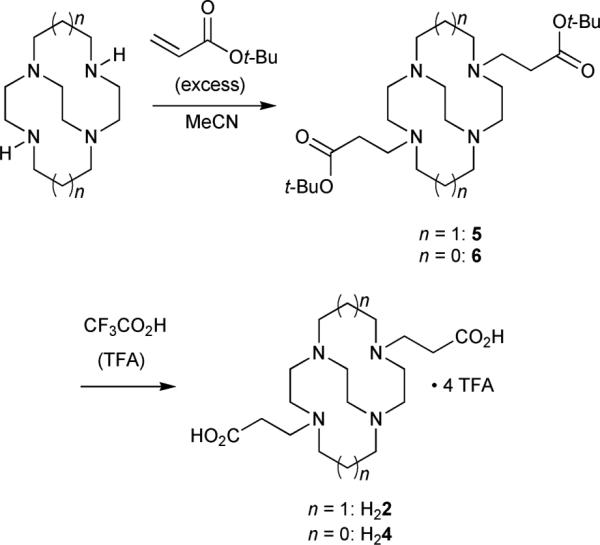
Ligand synthesis.
Synthesis of copper(II) complexes
tert-Butyl esters 5 and 6, the precursors of ligands 2 and 4 respectively, were deprotected when needed by treatment with TFA as described in the previous section. The specific ligand and copper perchlorate were dissolved in 95% ethanol followed by addition of the appropriate amount of 1 M NaOH before reflux. Subsequent workup and recrystallization from 95% ethanol by diethyl ether diffusion gave the pure complexes. Both the monoprotonated Cu– H2 and diprotonated Cu–H22 were obtained by recrystallization under increasingly acidic conditions.
Electronic spectral data
The aqueous solution electronic spectra of eleven copper(II) complexes of carboxyalkyl pendant-armed cyclam derivatives with N4O2 donor sets all revealed a single broad d–d band in the visible region with λmax values ranging from 544 to 650 nm.12,21–27 The related cyclen complex, Cu–DOTA, has a pH-dependent absorption maximum at much lower energy between 715 and 740 nm indicative of a significantly weaker ligand field due to its inferior equatorial plane metal coordination.24 By contrast, the aqueous absorption maxima of carboxylalkyl-armed copper(II) complexes for all cross-bridged cyclam and cyclen ligands we have prepared, including the title complexes, fall within a narrow 620–650 nm range as a result of their similar cis-folded N4O2 ligand environment. The low molar absorptivity of less than 100 L cm−1 mol−1 in each case is also consistent with a pseudo-octahedral solution geometry.7,10 Thus neither the longer carboxyethyl pendant arm nor the macrobicyclic size appear to affect the coordination number or ligand field strength significantly. The λmax of Cu–2 showed a minor pH-dependence; above pH 7 it was at 647 nm but decreased to 624 nm at pH 2. This shift is too small to be associated with major changes in coordination number or donor atom type but may reflect instead increased protonation of the carboxyalkyl arms, as previously reported for a di-carboxylmethyl-armed cyclam derivative.22 The λmax of Cu–4 also changed slightly with lowering pH from 643 to 635 nm. Similarly, both Cu–3 (pH > 7, ~645 nm; pH 2, 625 nm) and Cu–1 (pH > 4, 628 nm; pH < 2, 619 nm) also showed small pH-dependences in their electronic spectra. In each case, increasing carboxylate protonation resulted in a slight blue-shift of the respective λmax.
Infrared spectral data
Solid-state (KBr) spectra
Of particular interest are the prominent asymmetric carboxylate anion (1550–1620 cm−1) and carboxylic acid carbonyl (1660–1740 cm−1) stretching bands for these complexes. Their pendant arm protonation as well as coordination mode can be inferred and correlated with X-ray structural data.24,28–30 Cu–2 has a very broad band at around 1590 cm−1, consistent with overlapping coordinated carboxylate stretches as confirmed by the X-ray structure revealing both Cu(II)-and Na(I)-coordinated carboxyethyl pendant arms (vide infra). For comparison, the carboxymethyl-armed Cu–1 has two distinct Cu(II)-coordinated carboxylate bands at 1616 and 1590 cm−1. Monoprotonated [Cu–H2]+ has a sharp carboxylic acid band at 1730 cm−1 as well as a broader Cu(II)-coordinated carboxylate band at 1558 cm−1, whereas the monoprotonated [Cu–H1]+ complex has much less divergent bands at 1694 and 1616 cm−1 respectively. Finally, diprotonated [Cu–H22]2+ shows two COOH bands at 1713 and 1660 cm−1, consistent with one weakly and one strongly-coordinating propionic acid pendant arm. The Cu– 4 complex exhibited coordinated carboxylate bands at 1600 and 1555 cm−1 in the solid-state compared to Cu–3's corresponding IR bands at 1624 and 1595 cm−1.
Solution (D2O) spectra
To gain insight into the extent of carboxyethyl pendant arm protonation for both Cu–2 and Cu– 4 in aqueous solution, their FT-IR spectra in the 1500–1800 cm−1 region were recorded in DCl–D2O. As shown in Fig. 4, Cu–2 remained mostly unprotonated (1585 cm−1) down to approximately pD 4. In 1.0 M DCl however, only a broad carboxylic acid band (1680 cm−1 with 1660 cm−1 shoulder) was observed. We note that corresponding free ligand bands are at 1588 cm−1 (pD 10) and 1712 cm−1 (1.0 M DCl) respectively. Similar behavior was found for long-armed cyclen complex Cu–4, as significant protonation was observed in 0.1 M DCl (1697 cm−1) with only a very small carboxylate band at 1576 cm−1 remaining in 1.0 M DCl solution (Fig. 5a). For comparison, corresponding free ligand bands are at 1559 and 1714 cm−1 respectively in 1.0 M DCl solution. The analogous Cu–3 spectrum showed significant decomplexation with a half-life of approximately 2 h. Thus, of the four carboxyalkyl pendant-armed cross-bridged Cu(II) complexes studied, Cu–1 is unique in retention of a substantial unprotonated carboxylate band even in 1.0 M DCl (Fig. 5b).9 The propensity for protonation of carboxyalkyl-armed macrocyclic complexes is believed to be a significant facilitator of acid-assisted decomplexations.31 This is borne out by our kinetic acid inertness studies of these copper complexes (vide infra).
Fig. 4.
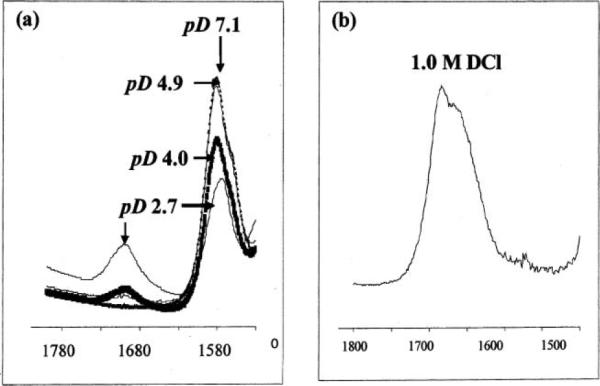
FT-IR spectra in the 1530–1800 cm−1 region of Cu–2 in: (a) DCl–D2O; and (b) 1 M DCl–D2O solutions.
Fig. 5.
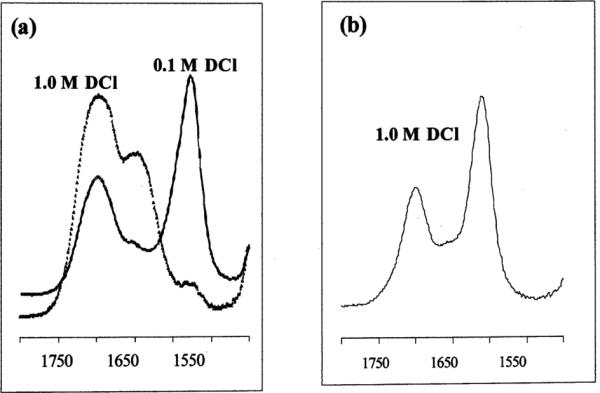
FT-IR spectra in the 1500–1800 cm−1 region of (a) Cu–4; and (b) Cu–1 in DCl–D2O solutions.
X-Ray structural studies
All copper-complex structures described below feature the cross-bridged tetraamine in the familiar cis-folded binding geometry and all but one have full ligand envelopment of the copper cation in a pseudo-octahedral cis-N4O2 geometry.
Cu–2
Both five- and six-coordinate forms of this complex were found in the solid-state along with co-crystallized NaClO4. In both complexes, the conformation of the bicyclic framework is the low-strain distorted-diamond-lattice [2323]/[2323] conformation most common in cross-bridged cyclams and observed in the Cu complex of 1.10 That portion of the structure conforms to approximate C2 symmetry. The five-coordinate complex (Fig. 6) features a Cu(II) bonded to all four ligand nitrogens but only one carboxylate pendant arm. This geometry is best described as square pyramidal (Addison and Reedjik τ value of 0.27)32 with N(5) axial having a Cu–N bond length of 2.165(4)Å. All three equatorial Cu–N bonds are shorter, between 2.042 and 2.068Å. The six-membered pendant-arm chelate ring has a N(6)–Cu(2)– O(6) angle of 93.0(2)° and a short Cu–O distance of 1.917(4)Å. The carbonyl of this chelate ring is additionally coordinated to two sodium ions in the structure. The pendant carboxylate that is not coordinated to copper is instead coordinated to three sodium cations. A good fit of the Cu(II) cation inside the cross-bridged cyclam's ligand cleft can be gauged by the internal N(6)–Cu(2)– N(8) (ideally linear) and N(5)–Cu(2)–N(7) (ideally orthogonal) angles which are 178.6(2)° and 86.0(2)° respectively. For the six-coordinate form of the complex (Fig. 7), the Jahn–Teller elongation is along the N(1)–Cu(1)–O(2) axis with Cu–N and Cu–O bond lengths of 2.287(4) and 2.322(3)Å respectively. Within the equatorial donor set, three Cu–N distances range from 2.076 to 2.095Å while the Cu(1)–O(4) bond length is 1.979(3)Å. The two six-membered pendant arms here subtend chelating angles of 93.02(15)° and 89.61(13)° at the metal center. The chelate rings of the pendant arms in the structure do not conform to C2 symmetry like the rest of the ligand. Each carbonyl is coordinated to three different sodium ions in the structure. The fit of the copper within the ligand cleft deviates slightly more from idealized values with a N(2)–Cu(1)–N(4) of 173.7(2)° and N(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) of 82.4(2)°. For comparison purposes, we have summarized these and relevant previously-reported structural data of related cross-bridged copper complexes in Table 1. The superior fit of Cu(II) within the cyclam-based ligands (trans-N–Cu–N from 173 to 180°, cis-N–Cu–N from 84 to 89°) compared to the cyclen-derived ligands (trans-N–Cu–N from 160 to 168°, cis-N–Cu–N from 81 to 86°) is clearly borne out. Other relevant structural data for Cu–2 are listed in Table 2.
Fig. 6.
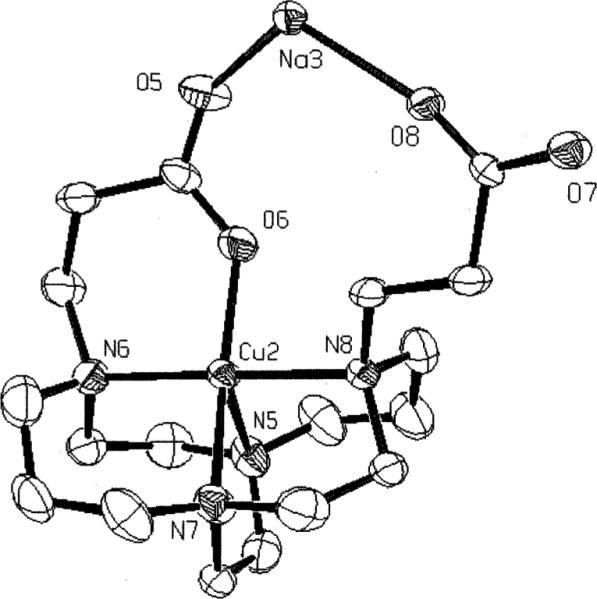
X-Ray structure of the five-coordinate Cu–2 complex.
Fig. 7.
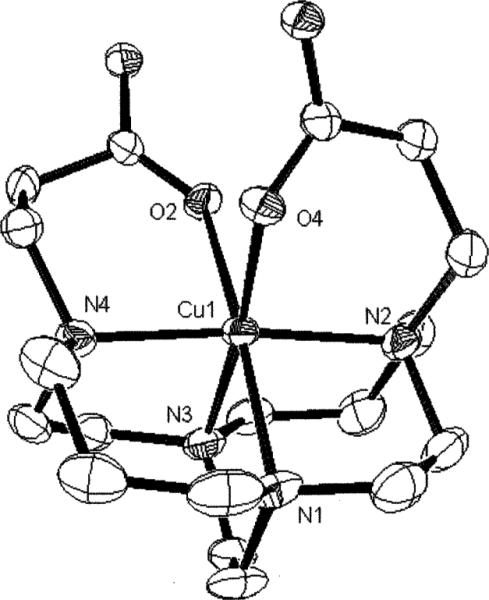
X-Ray structure of the six-coordinate Cu–2 complex.
Table 1.
Comparison of internal N–Cu–N angles for cross-bridged (CB) cyclam and cyclen copper(u) complexes
| Ligand | trans-N–Cu–N angle/° | cis-N–Cu–N angle/° | cis-N–Cu–O angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| CB-cyclam | 179.7(3) | 88.5(3) | |
| Bn2–CB-cyclam | 177.8(2) | 88.4(2) | |
| 1 | 176.5(2) | 84.5(2) | 80.28(9), 84.69(8) |
| 177.5(1) | 84.8(2) | 81.31(9), 85.63(9) | |
| H1 | 172.92(8) | 86.36(8) | 84.03(7), 76.06(7) |
| 2 | |||
| 5-coordinate | 178.6(2) | 86.0(2) | 93.0(2) |
| 6-coordinate | 173.3(2) | 82.4(2) | 93.0(2), 89.6(1) |
| H2 | 179.7(1) | 84.7(1) | 92.30(7), 87.56(6) |
| H22 | 179.3(1) | 85.3(1) | 93.22(8), 87.13(9) |
| CB-cyclen | 160.4(1) | 85.4(1) | |
| 165.3(5) | 84.7(4) | ||
| Bn2–CB-cyclen | 167.9(3) | 81.0(3) | |
| 3 | 159.0(3) | 86.4(3) | 82.6(3), 79.5(3) |
Table 2.
Relevant bond distances and angles for the X-ray structures of the Cu(ii) complexes (standard deviations in parentheses)
| Cu–2 | |||
| Cu(1)–O(4) | 1.979(3) | Cu(1)–N(3) | 2.076(4) |
| Cu(1)–N(4) | 2.094(4) | Cu(1)–N(2) | 2.095(4) |
| Cu(1)–N(1) | 2.287(4) | Cu(1)–O(2) | 2.322(3) |
| Cu(2)–O(6) | 1.917(4) | Cu(2)–N(6) | 2.042(4) |
| Cu(2)–N(7) | 2.065(5) | Cu(2)–N(8) | 2.068(4) |
| Cu(2)–N(5) | 2.165(4) | ||
| O(4)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 173.39(15) | O(4)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 88.91(15) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 86.29(16) | O(4)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 93.02(15) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 92.24(16) | N(4)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 173.72(16) |
| O(4)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 102.19(15) | N(3)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 82.37(15) |
| N(4)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 90.02(16) | N(2)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 83.73(17) |
| O(4)–Cu(1)–O(2) | 86.04(13) | N(3)–Cu(1)–O(2) | 89.39(14) |
| N(4)–Cu(1)–O(2) | 89.61(13) | N(2)–Cu(1)–O(2) | 96.49(15) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–O(2) | 171.75(14) | O(6)–Cu(2)–N(6) | 93.02(17) |
| O(6)–Cu(2)-N(7) | 162.35(18) | N(6)–Cu(2)–N(7) | 94.95(17) |
| O(6)–Cu(2)–N(8) | 87.47(16) | N(6)–Cu(2)–N(8) | 178.63(18) |
| N(7)–Cu(2)–N(8) | 84.94(17) | O(6)–Cu(2)–N(5) | 110.32(18) |
| N(6)–Cu(2)–N(5) | 85.75(17) | N(7)–Cu(2)–N(5) | 85.99(17) |
| N(8)–Cu(2)–N(5) | 92.88(18) | ||
| Cu–H2 | |||
| Cu(1)–O(1) | 1.9778(14) | Cu(1)–N(3) | 2.0611(19) |
| Cu(1)–N(1) | 2.068(2) | Cu(1)–N(4) | 2.0705(18) |
| Cu(1)–N(2) | 2.2147(19) | Cu(1)–O(3) | 2.5207(17) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 87.86(7) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 92.30(7) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 179.70(8) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 173.01(7) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 86.47(7) | N(1)–Cu(1)–(4) | 93.39(8) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 99.75(8) | N(3)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 93.99(7) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 85.74(7) | N(4)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 84.73(8) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 86.24(6) | N(3)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 87.56(6) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 92.70(7) | N(4)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 89.44(7) |
| N(2)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 173.86(7) | ||
| Cu–H22 | |||
| Cu(1)–O(1) | 2.0323(19) | Cu(1)–N(1) | 2.064(2) |
| Cu(1)–N(3) | 2.065(2) | Cu(1)–N(4) | 2.068(2) |
| Cu(1)–N(2) | 2.204(3) | Cu(1)–O(3) | 2.485(2) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 87.06(9) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 171.95(8) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 86.97(9) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 92.33(8) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 179.26(9) | N(3)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 93.68(9) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 100.54(9) | N(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 94.19(10) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 85.28(9) | N(4)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 85.51(9) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 83.16(8) | N(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 87.13(9) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 91.15(8) | N(4)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 93.22(8) |
| N(2)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 176.12(8) | ||
| Cu–4 | |||
| Cu(1)–O(1) | 1.9598(15) | Cu(1)–N(1) | 2.0254(17) |
| Cu(1)–N(4) | 2.0325(17) | Cu(1)–N(2) | 2.0407(16) |
| Cu(1)–N(3) | 2.2222(17) | Cu(1)–O(3) | 2.3713(15) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(1) | 178.81(7) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 96.31(7) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) | 83.32(7) | O(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 93.42(6) |
| N(1)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 86.73(7) | N(4)–Cu(1)–N(2) | 165.21(7) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 96.04(7) | N(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 82.80(7) |
| N(4)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 85.52(7) | N(2)–Cu(1)–N(3) | 82.39(6) |
| O(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 86.71(6) | N(1)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 94.47(7) |
| N(4)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 103.07(6) | N(2)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 88.57(6) |
| N(3)–Cu(1)–O(3) | 170.68(6) | ||
[Cu–H2]+
This monoprotonated complex is in a pseudo-octahedral geometry with both carboxylate and carboxylic acid pendant arms coordinated, the latter through the carbonyl (Fig. 8). The identity of the COOH group at C(11) is confirmed by the shorter C(11)–O(3) versus the C(11)–O(4) bond (1.212(3) and 1.319(3)Å respectively). As may be expected, the Jahn–Teller elongation is along the N(2)–Cu(1)–O(3) axis with a rather long Cu–O bond length of 2.521(2)Å and Cu–N of 2.215(2)Å. The two six-membered pendant-arm chelate rings subtend N–Cu–O angles of 92.30(7)° and 87.56(6)° at Cu(1). The bicyclic backbone adopts the [2323]/[2323] conformation and, as was observed for Cu–2, the chelate rings of the pendant arms in the structure do not conform to the approximate C2 symmetry of the remainder of the ligand. The carbonyl of the carboxylate serves as a H-bond acceptor and the OH of the COOH as an H-bond donor, each to a separate methanol in the structure. The copper cation's fit within the cyclam ligand cleft is also quite good with N(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) at 179.70(8)° and N(2)–Cu(1)–N(4) at 84.73(8)°.
Fig. 8.
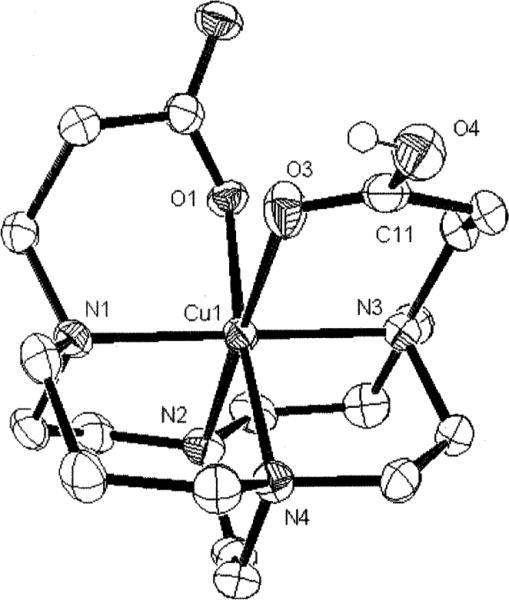
X-Ray structure of the [Cu–H2]+ complex.
[Cu–H22]2+
In this form of the complex, both carboxylic acid arms also remain coordinated with the Jahn–Teller elongation along the N(2)–Cu(1)–O(3) axis (Fig. 9). As a result, the Cu(1)– O(3) bond is 2.485(2)Å long and Cu(1)–N(2) is 2.204(3)Å. The two six-membered pendant-arm chelate rings subtend N– Cu–O angles of 93.22(8)° and 87.13(9)° respectively. Again the bicyclic backbone is [2323]/[2323] and again the chelate rings of the pendant arms are not related by C2 symmetry. Interestingly, the OH of one COOH group is H-bonded to a water molecule, and it is that COOH group that has the shorter Cu–O bond. The copper/ligand cleft fit remains good with N(1)–Cu(1)–N(4) and N(2)–Cu(1)–N(3) angles of 179.3(1)° and 85.28(9)° respectively.
Fig. 9.
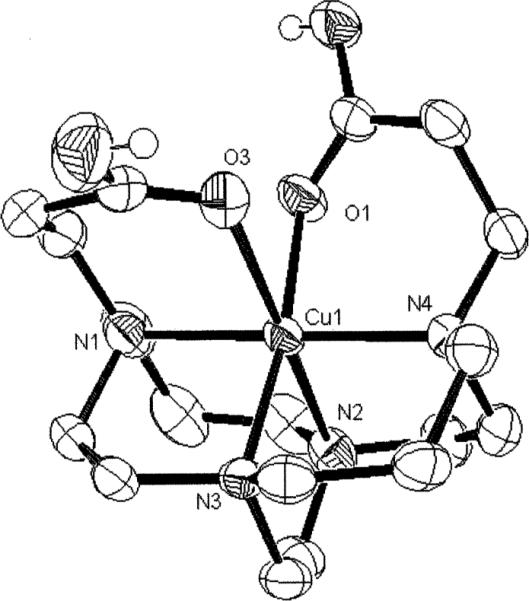
X-Ray structure of the [Cu–H22]+ complex.
Cu–4
The copper cation is also fully enveloped by the hexadentate ligand in this structure with a very distorted octahedral geometry (Fig. 10). Similar to the three other complexes described above, its Jahn–Teller elongation is again along an N–Cu–O axis with lengthened Cu(1)–O(3) (2.371(2)Å) and Cu(1)–N(3) (2.222(2)Å) bonds. In the equatorial plane, three Cu–N bonds range from 2.025 to 2.041Å and the Cu(1)–O(1) bond is at 1.960(2)Å. The two six-membered pendant-arm chelate rings here give N–Cu–O angles of 96.31(7)° and 88.57(6)° respectively. Unlike the cross-bridged cyclam structures discussed above, the conformations of the pendant-arm chelate rings in this structure are roughly related by C2 symmetry despite the different Cu– O bond lengths and different coordination geometries of each to two sodium cations. Our previously-reported structure of the carboxymethyl-armed Cu–3 differs significantly from this in having the Jahn–Teller distortion along a N–Cu–N instead of a N–Cu–O axis (Table 1, Fig. 2b).7 This is likely a consequence of the improved ability of the longer carboxyethyl arms in Cu– 4 to accommodate such an elongation along a N–Cu–O axis. In contrast to the three cyclam structures described above, the much poorer fit of Cu(II) within the smaller cyclen-derived ligand cleft of 4 is evident in the N(2)–Cu(1)–N(4) angle of only 165.21(7)° and N(1)–Cu(1)–N(3) angle of 82.80(7)°. As can be seen in Fig. 10, the metal cation is clearly protruding appreciably from the ligand cavity.
Fig. 10.
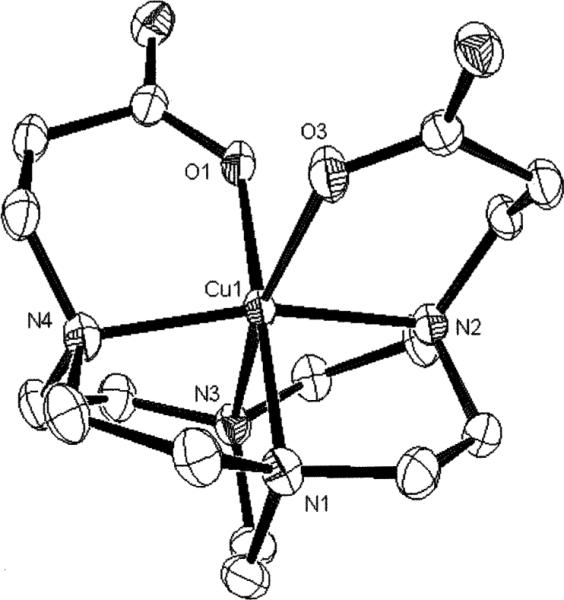
X-Ray structure of the [Cu–4] complex.
Discussion
A comparison of the views down the pseudo-C2 axes of the coordination spheres of Cu–1, Cu–2, Cu–3, and Cu–4 is shown in Fig. 11. It can be seen that the longer carboxyethyl pendant arms do result in better wrap-around of the Cu(II) centers of Cu– 2 and Cu–4, yielding more orthogonal chelate ring cis-N–Cu–O bond angles at the metals. A summary of trans-N–Cu–N and cis-N–Cu–N angles within the respective ligand cleft is also shown for the structures described above as well as related cross-bridged complexes (Table 1). The uniformly superior fit of Cu(II) within cross-bridged cyclam versus cyclen can be readily seen.
Fig. 11.
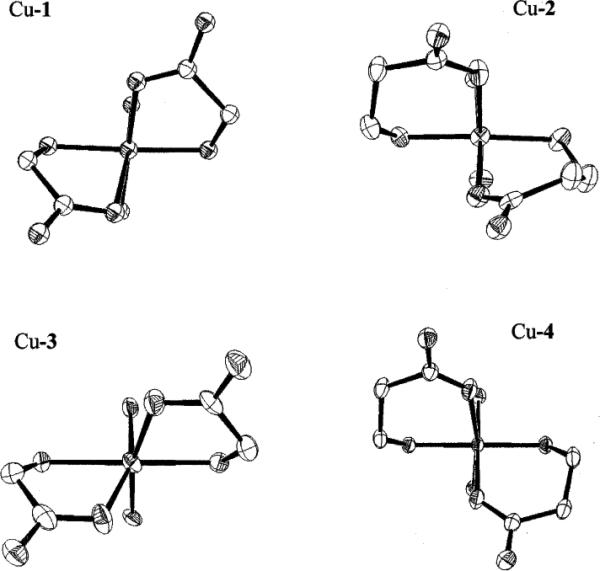
Comparative views down the pseudo-C2 axes of Cu–1, Cu–2, Cu–3, and Cu–4.
The plasticity of copper(II) bond lengths within a particular donor environment has been frequently noted.33,34 Further, applying the bond-valence sum model, crystallographic bond lengths have been used to predict copper oxidation states.35–37 It is therefore not surprising that copper(II) complexes with identical coordination spheres are likely to have a similar Cu–donor bond length sum. Thus we observe that, from the X-ray structural data of the 25 cyclam- and cyclen-derived complexes featuring two coordinated carboxylate/carboxylic acid groups (i.e. a N4O2 donor set),38 the sum of each structure's six Cu(II) bond lengths range from 12.55 to 13.20Å for an average of 12.9(2)Å. This is despite variations in the nature of the stronger-bonding equatorial donor sets (N4, N3O, or N2O2). In fact, inclusion of an additional 25 copper(II)–acyclic ligand structures from the CSD database with four sp3-amine and two carboxylate donors gave essentially the same average bond length sum of 13.0(2)Å.39
Acid decomplexation studies
Due to the strong proton sponge nature of cross-bridged cyclam ligands and the slow formation/dissociation kinetics of their copper complexes,9,10,40 determination of metal complex stability constants by traditional potentiometric methods has been limited to that of Cu–CB-cyclam.6 While this has curtailed comparisons of the thermodynamic binding strengths of these ligands, for biological applications kinetic inertness actually provides a more reliable indicator of in vivo efficacy.2,7,31 A convenient and popular gauge of relative kinetic inertness of copper–tetraamine complexes to Cu(II) extrusion in aqueous media is their acid-decomplexation half-lives.22,41–44 Several lanthanide complexes of carboxymethyl-armed tetraazamacrocyclic ligands have been shown in kinetic studies to undergo metal exchange via initial acid-decomplexation followed by transmetallation.31,45 In view of the powerful proton-sponge nature of many of the cross-bridged tetraamine ligands, such data are of additional relevance. On the other hand, since detailed kinetics and mechanisms for the acid-decomplexations we report here have not been elucidated, these results can only provide a qualitative estimate of comparative kinetic inertness. Nonetheless, the resistance of a copper chelate complex to aqueous acid decomplexation appears to serve as a useful first indicator of its likely in vivo integrity towards metal loss due to protons, competing biometals or biological ligands.
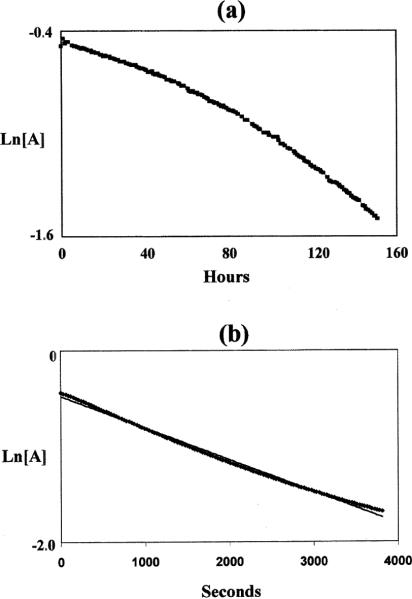
The respective copper complexes, Cu–2 and Cu–4 were dissolved in 5 M HCl and their kinetic inertness under pseudo-first-order conditions assayed by monitoring the λmax absorbance in their visible spectra. While Cu–4 had completely decomposed within sample preparation time, Cu–2 was found to be stable at 30 °C for at least one year. In fact, it required a temperature of 90 °C to give readily observable attenuation of its absorbance. However, its ln(absorbance) versus time plot showed substantial concave curvature (Fig. 12a) inconsistent with clean first-order kinetics. We have evidence that significant loss of the ligand's carboxyethyl pendant arms occurred under these forcing conditions. As a result, only an approximate half-life of about 100 h for the complex can be estimated. In 12 M HCl at 90 °C, its ln(A)/time plot more closely approached linearity (Fig. 12b), yielding a half-life of 35(5) min. Of all copper complexes of this type that we have studied, only Cu–1 has comparable inertness under such harsh conditions with 90 °C half-lives of 154(6) h in 5 M HCl and 1.6(2) h in 12 M HCl (Table 3). Indeed, the contrast between related cross-bridged cyclam and cyclen complexes is dramatic since both Cu–3 and Cu–4 decomplexed within minutes in 5 M HCl even at a lower temperature of 30 °C. In 1 M HCl at 30 °C, their respective half-lives are 4.0(1) h and 37.2(5) h. Sargeson has reported copper complexes of hexaamine sarcophagine cage ligands with high resistance to acid-assisted demetallation.46 Preliminary experiments in our laboratories have shown that even the very robust Cu–Diamsar complex decomposes within minutes in 12 M HCl at 90 °C.47 Copper(II) porphyrin complexes have also been reported in the literature to have high resistance to acid decomplexation.48–52 These studies, however, were performed in sulfuric acid solutions so direct comparisons cannot be made.
Fig. 12.
Natural log(absorbance) vs. time plots for Cu–2 at 90 °C in: (a) 5 M HCl, and (b) 12 M HCl.
Table 3.
Acid decomplexation half-lives of selected copper(u) tetraamine complexes
| Complex | [HCl]/M, T/°C | Half-life |
|---|---|---|
| Cu–1 | 5, 90 | 154(6) h |
| 12, 90 | 1.6(2) h | |
| Cu–2 | 5, 90 | ~100 h |
| 12, 90 | 39(5) min | |
| Cu–3 | 5, 90 | <3min |
| 1, 30 | 4.0(1)h | |
| Cu–4 | 5, 90 | < 3min |
| 1, 30 | 37.2(5) min | |
| Cu–CB-cyclam | 5, 90 | 11.8(2) min |
This remarkable kinetic inertness of both Cu–1 and Cu– 2 to acid decomplexation can ultimately be attributed to the reluctance of the torsionally-favored distorted-diamond-lattice binding conformation of cross-bridged cyclam to allow Cu–N bond cleavage. In fact, such a ruptured bond will be predisposed to reform immediately. It should be emphasized that the presence of coordinated carboxyalkyl pendant arms, either in protonated or unprotonated form, must contribute significantly to this kinetic inertness since the parent Cu–CB-cyclam complex does not even approach this order of robustness (Table 3). We believe that the full six-coordinate envelopment of the copper cation within the N4O2 ligand cleft can only be disrupted upon displacement of at least one of these coordinated arms before any Cu–N bond cleavage can occur. Solution FT-IR data (vide supra) support the persistent coordination of these pendant groups even under acidic conditions. Despite the absence of detailed mechanistic studies and other reservations,53 we have found these acid-decomplexation data to be a convenient first gauge of the viability of a copper(II) chelator towards in vivo demetallation processes.6,7,9
Electrochemical studies
The cyclic voltammograms of Cu–2 and Cu–4 in aqueous solution at neutral pH are shown in Fig. 13. A quasi-reversible reduction wave was found for Cu–2 with E1/2 = −0.68 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) and ΔE = 118 mV (differential pulse voltammetry (DVP) 0.68 V). This reduction potential is 400 mV more positive than− that for Cu–1 (E1/2 = −1.08 V) (DPV −1.06 V), a somewhat surprising difference in view of the very similar solid-state coordination spheres of both complexes. Further, their respective λmax at pH 7 of 647 nm and 628 nm in aqueous solution are not significantly different, suggesting similar solution coordination environments. Numerous factors are known to affect the Cu(II)/Cu(I) reduction potential in complexes with similar donor sets, including ligand flexibility and hydrophobicity.54,55 While the additional methylene unit in the longer pendant arms of Cu–2 can increase overall hydrophobicity to stabilize its reduced form, this should be a relatively minor factor. More plausible may be the decreased thermodynamic stability of Cu(II)–2 compared to Cu(II)–1 and/or the enhanced stabilization of the preferred tetrahedral Cu(I)–2 coordination sphere due to the increased flexibility of its pendant arms. Rorabacher has successfully correlated Cu(II)–complex stability constants with their reduction potentials while finding little dependence on the stability of Cu(I)–complexes.56 Whatever the origin of this discrepancy, it is significant that this relative ease of reduction now places Cu–2 within the realm of biological reductants, which should render it vulnerable to in vivo demetallation in a Cu(I) state.57,58
Fig. 13.
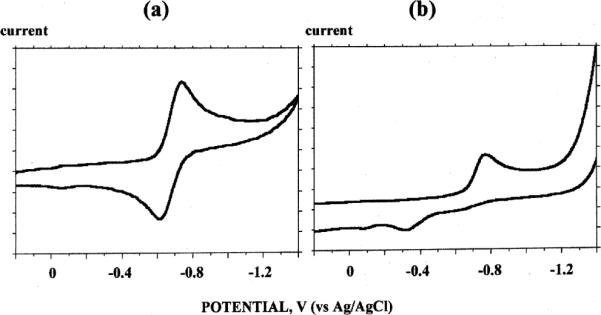
Cyclic voltammograms (sweep rate 200 mV s−1) in 0.1 N NaOAc (adjusted to pH 7) of: (a) Cu–2, and (b) Cu–4.
The reduction of Cu–4 is irreversible with a peak potential Epc of −0.78 V (DPV −0.67 V) (Fig. 13b). This can be compared with Cu–3's Epc value of −0.92 V (DPV −0.85 V). Here too, the longer-armed complex is easier to reduce by about 140 mV. Our data to date indicate that cross-bridged cyclam but not cross-bridged cyclen copper(II) complexes typically exhibit quasi-reversible reductions, suggesting that the former macrobicycle can adapt somewhat to the coordination preferences of Cu(I). Confirmation of this can be found in the published isolation and X-ray structures of both Cu(I) and Cu(II) complexes of the N,N ′′dibenzyl-CB-cyclam ligand.59
Radiochemistry
The radio-labeling of ligand 4 occurred under relatively mild conditions. A single product peak (Rf = 0.6) corresponding to 64Cu–4 was verified by radio-TLC using a mobile phase of 2 : 1 MeOH–10% NH4OAc on silica plates. The presence of 64Cu–acetate at the origin of the plate was negligible indicating that the formation of the complex was complete.
The conditions employed to label 2 with 64Cu were more rigorous and required a pre-incubation of the ligand with Cs2CO3 in ethanol at 43 °C before the addition of 64CuCl2. Formation of the desired product was also verified by radio-TLC using a mobile phase of 3 : 7 10% NH4OAc–MeOH on C-18 plates. A single product peak (Rf 0.6) and the absence of 64Cu–acetate at the origin confirmed=the formation of this complex.
Biodistribution of 64Cu–2 and 64Cu–4
The biodistribution of 64Cu–2 and 64Cu–4 was determined in normal female Sprague Dawley rats, and these data can be found in Tables 4 and 5 respectively as well as Fig. 14. Clearance of 64Cu–4 from the blood, liver and kidney occurred more rapidly than clearance of 64Cu–2 at earlier time points, but by 24 h post-injection, both 64Cu-complexes were effectively cleared from these tissues. Over time, the clearance properties of these two complexes were comparable to or better than the clearance properties of other non-cross bridged 64Cu–tetraazamacrocycles. For example, 64Cu–4 demonstrated comparable clearance in the blood, liver, and kidney with 64Cu–DOTA at 24 h post-injection (%ID per organ at 24 h) (blood, 0.66 ± 0.15 vs. 0.58 ± 0.19; liver, 1.31 ± 0.14 vs. 1.05 ± 0.16; and kidney, 0.25 ± 0.027 vs. 0.54 ± 0.08).60 Likewise 64Cu–2 demonstrated similar clearance properties as 64Cu–TETA (%ID per organ; 24 h) (blood, 0.22 ± 0.036 vs. 0.21 ± 0.05; liver, 0.62 ± 0.049 vs. 0.49 ± 0.11; and kidney, 0.10 ± 0.013 vs. 0.21 ± 0.03).6 However, when compared to 64Cu–3, the longer-arm complex 64Cu–4 exhibited slower blood, liver and kidney clearance (%ID per organ at 24 h) (blood, 0.66 ± 0.15 vs. 0.14 ± 0.059; liver, 1.31 ± 0.14 vs. 0.39 ± 0.03; and kidney, 0.25 ± 0.027 vs. 0.051 ± 0.0089).7 Similarly, 64Cu–2 cleared significantly more slowly than 64Cu–1 from blood, liver and kidney (%ID per organ; 24 h) (blood, 0.22 ± 036 vs. 0.032 ± 0.014; liver, 0.62 ± 0.049 vs. 0.14 ± 0.039; and kidney, 0.10 ± 0.013 vs. 0.064 ± 0.012).7 These data suggest that the substitution of carboxylmethyl by carboxyethyl pendant arms decreased the in vivo stability of the corresponding 64Cu– cross-bridged tetraamine complexes.
Table 4.
Rat biodistribution data of 64Cu–2 in selected organsa
| Organ | 1h | 2h | 4h | 24 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 0.2090 ± 0.0717 | 0.0514 ± 0.0173 | 0.0335 ± 0.0136 | 0.0227 ± 0.0036 |
| Lung | 0.1643 ± 0.0439 | 0.0655 ± 0.0128 | 0.0491 ± 0.0074 | 0.0269 ± 0.0025 |
| Liver | 1.5643 ± 0.2074 | 1.1229 ± 0.1209 | 0.5999 ± 0.0422 | 0.1042 ± 0.0114 |
| Spleen | 0.0737 ± 0.0164 | 0.0640 ± 0.0200 | 0.0479 ± 0.0080 | 0.0248 ± 0.0037 |
| Kidney | 2.8723 ± 0.2016 | 1.7981 ± 0.1155 | 0.8934 ± 0.0411 | 0.1497 ± 0.0112 |
| Muscle | 0.0569 ± 0.0164 | 0.0312 ± 0.0147 | 0.0218 ± 0.0101 | 0.0070 ± 0.0003 |
| Fat | 0.0454 ± 0.0162 | 0.0439 ± 0.0291 | 0.0401 ± 0.0149 | 0.0037 ± 0.0015 |
| Heart | 0.0961 ± 0.0284 | 0.0362 ± 0.0101 | 0.0260 ± 0.0052 | 0.0224 ± 0.0013 |
| Brain | 0.0125 ± 0.0036 | 0.0152 ± 0.0080 | 0.0088 ± 0.0027 | 0.0032 ± 0.0002 |
| Bone | 0.0981 ± 0.0422 | 0.1003 ± 0.0368 | 0.1040 ± 0.0592 | 0.0221 ± 0.0039 |
Presented as %ID per gram ± SD (n = 5).
Table 5.
Rat biodistribution data of 64Cu–4 in selected organsa
| Organ | 1h | 2h | 4h | 24 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | 0.1216 ± 0.0311 | 0.0511 ± 0.0021 | 0.0524 ± 0.0089 | 0.0516 ± 0.0139 |
| Lung | 0.1096 ± 0.0224 | 0.0610 ± 0.0144 | 0.0549 ± 0.0065 | 0.0394 ± 0.0066 |
| Liver | 0.4340 ± 0.0532 | 0.3390 ± 0.0348 | 0.2902 ± 0.0389 | 0.2023 ± 0.0408 |
| Spleen | 0.0471 ± 0.0115 | 0.0294 ± 0.0047 | 0.0315 ± 0.0027 | 0.0374 ± 0.0033 |
| Kidney | 1.6535 ± 0.3497 | 1.2060 ± 0.2359 | 1.1530 ± 0.3151 | 0.3290 ± 0.0383 |
| Muscle | 0.0577 ± 0.0098 | 0.0286 ± 0.0256 | 0.0163 ± 0.0103 | 0.0079 ± 0.0017 |
| Fat | 0.0361 ± 0.0196 | 0.0125 ± 0.0049 | 0.0106 ± 0.0039 | 0.0031 ± 0.0016 |
| Heart | 0.0477 ± 0.0158 | 0.0304 ± 0.0067 | 0.0320 ± 0.0044 | 0.0340 ± 0.0064 |
| Brain | 0.0101 ± 0.0026 | 0.0062 ± 0.0015 | 0.0065 ± 0.0016 | 0.0071 ± 0.0016 |
| Bone | 0.0677 ± 0.0299 | 0.0390 ± 0.0050 | 0.0423 ± 0.0126 | 0.0256 ± 0.0024 |
Presented as %ID per gram ± SD (n = 4).
Fig. 14.
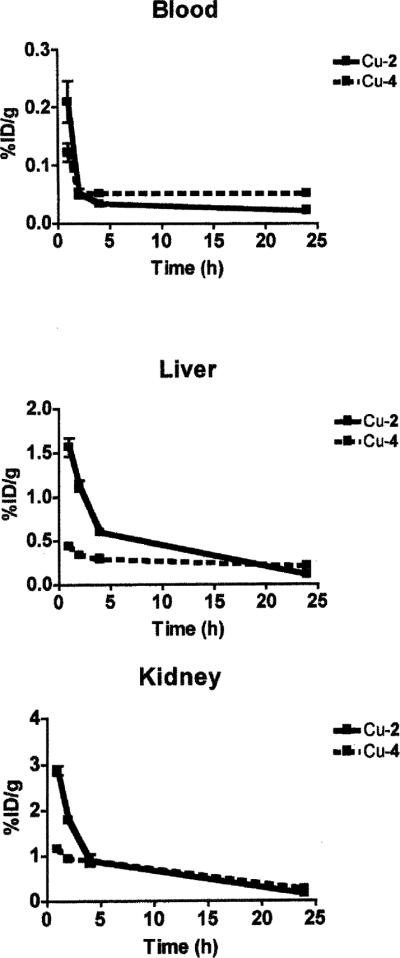
Clearance behavior of 64Cu–2 and 64Cu–4 from the blood, liver and kidney.
Conclusions
Lengthening the N-carboxymethyl pendant arms of cross-bridged ligands 1 and 3 to carboxyethyl arms in 2 and 4 respectively maintained the exceptional kinetic inertness of the cyclam-based copper(II) complexes to acid-decomplexation with the order: Cu–1 ~ Cu–2 > > Cu–4 > Cu–3. While both cyclam-derived Cu–1 and Cu–2 exhibited quasi-reversible electrochemical reductions, the latter is substantially less resistant to reduction by 400 mV making it possibly susceptible to physiological reductants and subsequent Cu(I) loss. Biodistribution studies of 64Cu-labeled analogues of these complexes indeed revealed poorer clearance of both longer-armed ligand complexes relative to their carboxylmethyl-armed homologs, suggesting that a sufficiently low Cu(II) reduction potential may be an essential prerequisite for optimal in vivo performance of Cu(II)-chelator-based radiopharmaceuticals.
Experimental
Methods and materials
CAUTION! Although we did not experience any difficulties, metal perchlorate salts with organic ligands and in organic solvents are potentially explosive and should be prepared and handled only in small quantities with great care.
Proton and 13C{1H} NMR spectra were run at 400 and 100.5 MHz respectively on a Varian Mercury or at 500 and 125.7 MHz respectively on a Varian Inova spectrometer. Spectra were referenced against internal Me4Si unless otherwise indicated. Coupling constants are reported in Hz. IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet MX-1 or a Thermo Nicolet Avatar 360 FT-IR spectrophotometer. UV-Vis data were collected using a Cary 50 Bio UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Elemental analyses were performed at Atlantic Microlab, Inc., Norcross, GA. Ligand synthesis and complexation reactions were run under a nitrogen atmosphere with magnetic stirring in standard Schlenk glassware. Bulk solvent removal was by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure (water aspirator) while trace volatile removal was by a mechanical vacuum pump.
Solvents were used as purchased or dried according to standard procedures. Copper salts were obtained commercially and used without further purification.
Acid-decomplexation studies were performed under pseudo first-order conditions using sample concentrations of between 1– 3 mmol in 1 M, 5 M or 12 M HCl. Changes in the absorption maxima with time were monitored using a Cary 50 Bio UVVis spectrophotometer in thermostated cells. Half-lives were calculated from the slopes of linear ln(absorbance) vs. time plots. All complexes studied except Cu–2 gave well-behaved linear plots.
Cyclic voltammograms were obtained using a Bioanalytical Systems 100B electrochemical system using BAS software. A three-electrode cell under argon was used with a glassy carbon disk working electrode, platinum auxiliary electrode, and silver/silver chloride reference electrode. Samples (~1–3 mM) were run in 0.1 sodium acetate aqueous solutions adjusted to pH 7 with glacial acetic acid at a typical scan rate of 200 mV s−1.
Ligand synthesis
1,4,8,11-Tetraazabicyclo[6.6.2]hexadecane (cross-bridged cyclam)10 and 1,4,7,10-tetraazabicyclo[5.5.2]tetradecane (cross-bridged cyclen)18 were synthesized as described previously.
5,12-Bis-(2-carbo-tert-butoxyethyl)-1,4,8,11-tetraazabicyclo-[6.6.2]hexadecane 5
1,4,8,11-Tetraazabicyclo[6.6.2]hexadecane (2.05 g, 9.06 mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (50 cm3) under nitrogen. tert-Butyl acrylate (11 cm3, 9.8 g, 76 mmol) was added to the stirred solution in one portion and the reaction mixture was stirred for 90 h at room temperature. After the reaction mixture was initially concentrated, excess tert-butyl acrylate was removed by sequential addition of Et2O (50 cm3) and rotary evaporation (10 times). After overnight pumping, pure 5 was obtained as an oil (4.11 g, 97%). IR: νmax(film)/cm−1 1732 (C=O). 1H NMR (500 MHz, C6D6; Me4Si): δH 1.21–1.30 (2 H, m), 1.41 (18 H, s, C(CH3)3), 1.53–1.62 (2H, m), 2.15–2.41 (16 H, m), 2.41–2.49 (2 H, XX′ of AA′ XX′, cross-bridge NCHHCHHN), 2.70 (2 H, ddd, J 13.7 and 11.7 and 3.8), 2.84 (2 H, td, J 12.7 and 4.0), 2.91–3.00 (2 H, m), 3.17–3.26 (2 H, AA′ of AA′ XX′, cross-bridge NCHHCHHN), 3.67 (2 H, td, J 12.1 and 3.8). 13C{1H} NMR (125.7 MHz; C6D6; Me4Si) δC 28.1 (C(CH3)3), 28.4 (CH2CH2CH2), 34.9 (CH2CH2CO2R), 50.7, 51.3, 54.95, 57.5 (cross-bridge NCH2CH2N), 57.9, 59.4, 79.4 (C(CH3)3), 171.8 (C=O). HRMS: m/z (FAB+) 483.3932 ((M + H)+. C26H51N4O4 requires 483.3910 (error 4.5 ppm)).
5,12-Bis-(2-carboxyethyl)-1,4,8,11-tetraazabicyclo[6.6.2]hexadecane H22·4TFA·H2O
5,12-Bis-(2-carbo-tert-butoxyethyl)-1,4,8,11-tetraazabicyclo[6.6.2]-hexadecane (5) (0.24 g, 0.50 mmol) was dissolved in trifluoroacetic acid (19 cm3) and stirred for 10 h at room temperature. The solution was concentrated by rotary evaporation to give an oil which was twice triturated with Et2O (60 cm3) followed by rotary evaporation to give the product as an off-white solid (0.43 g, quantitative). IR: νmax(solid, ATR)/cm−1 1737(br). 1H NMR (400 MHz; D2O; CH3CN secondary ref. set at 2.06 ppm): δH 1.75–1.87 (2 H, dm, J 16.8), 2.34–2.50 (2 H, m), 2.50–2.67 (4 H, br m), 2.80–3.06 (m, 8H), 3.06–3.14 (2 H, dm, J 14.8), 3.22–3.35 (6 H, m), 3.41 (2 H, td, J 14.0 and 3.1), 3.61 (2 H, td, J 12.9 and 3.9), 3.76 (2 H, m(~td)), 3.93 (2 H, ~dt, J 14 and 7). 13C{1H} NMR (100.5 MHz; D2O; CH3CN secondary ref. set at 1.47 ppm): δC 19.6 (CH2CH2CH2), 27.7, 49.10 (br), 49.14, 49.7, 54.3, 54.55 (br), 57.6, 116.8 (q, 1JCF 291.3, CF3C=O), 163.2 (q, 2JCF 36.0, CF3C=O), 175.0 (C=O); 19F (376 MHz; (CD3)2CO; C6H5CF3 secondary ref. set at −63.83 ppm): δF −76.70 (4.2 equiv. of TFA by 19F NMR integration against added C6H5CF3; consistent with the formulation C18H34N4O4·4TFA·H2O). HRMS: m/z (FAB+) 371.2648 ((M + H)+. C18H35O4N4 requires 371.2658 (error −2.8 ppm)).
4,10-Bis-(2-carbo-tert-butoxyethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazabicyclo-[5.5.2]tetradecane 6
1,4,7,10-Tetraazabicyclo[5.5.2]tetradecane (0.50 g, 2.5 mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (25 cm3). tert-Butyl acrylate (3.6 cm3, 3.2 g, 24 mmol) was added to the stirred solution in one portion and the reaction mixture was stirred for 48 h at room temperature. Solvent and excess tert-butyl acrylate were removed by rotary evaporation and on a vacuum line overnight to yield 6 as an oil (1.10 g, 97%). IR: νmax(film)/cm−1 1727 (C=O). 1H NMR (500 MHz; C6D6; Me4Si): δH1.45 (18 H, s, C(CH3)3), 2.26 (4 H, t, J 6.8, NCH2CH2CO2R), 2.45 (4 H, ~dt (ddd), J 13.7 and 2.9), 2.56–2.69 (m, 8H), 2.77 (4 H, ddd, J 13.8, 9.7 and 2.9), 2.82 (4 H, t, J 6.8, NCH2CH2CO2R), 3.03 (4 H, s, NCH2CH2N cross-bridge). 13C{1H} NMR (125.7 MHz; C6D6; central peak of C6D6 secondary ref. set at 128.02): δC 28.25 (C(CH3)3), 35.9 (CH2CH2CO2R), 54.6, 56.9, 58.2, 59.2, 79.5 (C(CH3)3), 171.7 (C=O). HRMS: ν/z (FAB+) 455.3069 ((M + H)+. C24H47N4O4 requires 455.3597 (error 2.6 ppm)). 1H and 13C {1H} NMR showed the only measurable impurity to be <1% by weight of tert-butyl acrylate.
4,10-Bis-(2-carboxyethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazabicyclo[5.5.2]tetra decane H24·4.5TFA
4,10-Bis-(2-carbo-tert-butoxyethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazabicyclo[5.5.2]tetradecane (6) (1.10 g, 2.42 mmol) was dissolved in dry CF3CO2H (TFA, 20 cm3, freshly distilled from trifluoroacetic anhydride). The solution was stirred at room temperature for 17 h. Most TFA was then removed by rotary evaporation and residual TFA was subsequently removed under high vacuum over two weeks to give the product (1.93 g, 93%) as a brown oily solid. Elemental analysis: Found: C, 35.3; H, 4.0; N, 6.3. Calc. for C16H30N4O4·4.5(C2HF3O2): C, 35.1; H, 4.1; N, 6.55%. IR: νmax(solid, ATR)/cm−1 1717, 1664. 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, CH3CN secondary ref. set at 2.06 ppm): δH 2.94 (4 H, s, NCH2CH2N cross-bridge), 2.99 (8 H, XX′ of AA′ XX′ (apparent t), Japp 7.0), 3.00–3.20 (8 H, m), 3.56 (8 H, ddd, J 15.6 and 12.5 and 5.5), 3.63 (4 H, AA′ of AA′ XX′ (apparent t), Japp 7.0), 3.72 (4 H, ddd, J 14.8 and 5.5 and 1.6). 13C {1H} NMR (100.5 MHz, D2O, CH3CN secondary ref. set at 1.47 ppm): δC 29.2, 47.0, 52.8, 53.6, 58.1, 116.8 (q, 1JCF 290.8, CF3C=O), 163.2 (q, 2JCF 36.1, CF3C=O), 175.8 (C=O). 19F NMR (376 MHz, (CD3)2CO, C6H5CF3 secondary ref. set at −63.83 ppm): ΔF 76.87 (3.8 equiv of TFA by 19F NMR integration against added−C6H5CF3). The quantitative 19F NMR experiment is most consistent with the formulation C16H30N4O4·4TFA·H2O, which corresponds to a yield of 98%.
Complex synthesis and characterization
Cu–2
The tert-butyl ester of ligand 2 (307 mg, 0.833 mmol) was dissolved in 5 mL of trifluoroacetic acid and stirred overnight at room temperature. After evaporation of all volatiles using a mechanical vacuum pump, the oily residue was taken up in 10 mL of 95% ethanol and one equivalent of Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O (309 mg, 0.833 mmol) was then added. The pH of the resulting solution was adjusted to approximately 9 using 1 M aq. NaOH. The dark blue solution was then refluxed under nitrogen for 24 h. After cooling to room temperature and centrifugation to remove a small amount of yellow-green precipitate, the blue supernatant was evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude solid residue was redissolved in a minimum amount of 95% ethanol, centrifuged to remove a small amount of insoluble matter, and placed in test tubes in an ether chamber. A light-blue powder deposited and was collected after 2 to 3 d. After drying, the desired complex was obtained (139 mg, 26%). Elemental analysis: Found: C 36.97, H 5.62, N 9.15, Cl 6.38%. Calc. for CuC18H32N4O4·1.1NaClO4·1.3H2O: C, 36.64; H, 5.91; N, 9.49; Cl, 6.61%. IR: νmax/cm−1 3450–3600 (OH), 2870–3000 (CH), 1596s (COO), 1559s (COO), 1096vs (ClO4). Electronic spectrum: λmax(H2O)/nm 629 (e/dm3 mol−1 cm−1 40.2); λmax(5 M HCl)/nm 650 (36.9). Dark-blue X-ray quality crystals were obtained after repeated recrystallizations of the complex from methanol–diethyl ether.
Cu–H2
The monoprotonated complex was obtained by recrystallization of the parent complex from methanol containing a few drops of 0.1 M HClO4 by diethyl ether diffusion. Dark-blue crystals were harvested. IR: νmax/cm−1 3380–3450br (OH), 2880– 2980 (CH), 1730s (COOH), 1558s (COO), 1089vs (ClO4).
Cu–H22
A small amount (20 mg) of Cu–H2 was dissolved in about 1 mL of 0.1 M HClO4. Slow evaporation in air overnight yielded dark-blue crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction studies. Elemental analysis: Found: C 33.30, H 5.33, N 8.48, Cl 11.23%. Calc. for CuCl2C18H34N4O12·H2O: C, 33.21; H, 5.57; N, 8.61; Cl, 10.89%. IR: νmax/cm−1 3200–3300 br (OH), 2880–2980 (CH), 1713s (COOH), 1659s (COOH), 1092 (ClO4).
Cu–4
An amount of the tert-butyl ester of 4 (264 mg, 0.580 mmol) was stirred in 5 mL of CF3CO2H overnight. The resulting solution was evaporated to dryness. A volume of 10 mL of 95% ethanol was added to the deprotected ligand. This solution was then added to a solution of Cu(ClO4)2·6H2O (215 mg, 0.581 mmol) in 10 mL of 95% ethanol. After adjustment of the pH to around 8 using 1 M NaOH, the reaction mixture was refluxed for 1.5 h and then cooled to room temperature. A small amount of yellow-brown precipitate was removed by centrifugation and the blue supernatant subjected to diethyl ether diffusion. The blue oily deposit was redissolved in 5 mL 95% ethanol and again diethyl ether diffused. Dark-blue feathery crystals were obtained (79 mg, 39%). Elemental analysis: Found: C 32.47, H 5.38, N 9.41, Cl 7.60%. Calc. for Cu(C16H28N4O4)·1.25NaClO4·2H2O: C 32.40, H 5.44, N 9.45, Cl 7.47%. IR: νmax/cm−1 3400–3500 (OH), 2880– 2980 (CH), 1600s (COO), 1555s (COO), 1091vs (ClO4). Electronic spectrum: λmax(H2O)/nm 644 (e/dm3 mol−1 cm−1 114); X-ray quality crystals of Cu–4 were obtained by a third recrystallization of the microcrystalline product from 95% ethanol–diethyl ether.
X-Ray data collection and refinement details
Crystallographic data are summarized in Table 6. All data were collected on Bruker diffractometers equipped with APEX CCD detectors. The crystals were affixed to nylon loops with mineral oil. The space group for [Cu–H22] was assigned from systematic absences. For [Cu–4] the centrosymmetric alternative was shown to be correct by the results of refinement, and for both [Cu–2]2 and [Cu–H2] the non-centrosymmetric alternative was preferred because of the lack of appropriate mirror plane symmetry. For the former structure, it was found to be a racemic twin with a BASF of 0.336, and for the latter the Flack parameter was 0.040(9). During refinement all non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically and hydrogen atoms were treated as isotropic, idealized contributions. All software was contained in the SMART, SAINT and SHELXTL libraries distributed by Bruker-AXS (Madison, WI).
Table 6.
X-Ray data collection and refinement details
| Complex | [Cu–2]2·3NaClO4·CH3OH | [Cu–H2]ClO4·CH3OH | [Cu–H22](ClO4)2·2H2O | [Cu–4]·NaClO4·3H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | C37H68Cl3Cu2N8Na3O21 | C19H37ClCuN4O9 | C18H38Cl2CuN4O14 | C16H34ClCuN4NaO11 |
| Formula weight | 1263.41 | 564.52 | 668.96 | 580.45 |
| Temperature/K | 213(2) | 213(2) | 213(2) | 218(2) |
| Wavelength/Å | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic | Orthorhombic | Monoclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | Pna2(1) | Pca2(1) | P2(1)/n | P1 |
| a/ Å | 15.6342(17) | 27.6657(19) | 8.7623(5) | 8.0242(5) |
| b/ Å | 34.587(4) | 7.9539(6) | 17.9633(10) | 9.3141(6) |
| c/ Å | 9.4238(10) | 10.7296(7) | 17.2184(10) | 5.3597(10) |
| α/ ° | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 96.6070(10) |
| β/ ° | 90.00 | 90.00 | 93.2180(10) | 97.3590(10) |
| γ/ ° | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 92.5420(10) |
| Volume/Å3 | 5095.9(10) | 2361.1(3) | 2705.9(3) | 1128.90(13) |
| μ/mm−1 | 1.103 | 1.096 | 1.079 | 1.172 |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Refl. collected | 10941 | 15470 | 18531 | 8321 |
| Ind. refl. [Rint] | 9862 | 4095 | 5315 | 4894 |
| R1,wR2[I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0538, 0.1291 | 0.0246, 0.0605 | 0.0404, 0.1005 | 0.0372, 0.1000 |
| R1,wR2(all data) | 0.0612, 0.1355 | 0.0261, 0.0614 | 0.0521, 0.1075 | 0.0358, 0.1011 |
| Goodness of fit | 1.070 | 1.028 | 1.027 | 1.054 |
CCDC reference numbers 635719–635722.
For crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/b702938a
Radiochemistry
The complexation of 64Cu to the ligands 2 and 4 was achieved using protocols based on literature procedures.6,7 Radio-TLC was conducted on a Bioscan AR 2000 radio-TLC scanner using Winscan v.3 analysis software and 64Cu(OAc)2 as standard control.
The complexation of 64Cu to 4 was achieved by reacting 100 μL of a 10 mM H24 solution in 0.1 M NH4OAc (pH = 6.5) with a 200 μL solution of 0.1 M NH4OAc (pH = 6.5) containing 2 mCi of 64Cu(OAc)2 and heating at 43 °C for 2 h. The reaction progress and purity were analyzed by radio-TLC using silica plates and a 1 : 2 10% NH4OAc–MeOH eluent mixture.
The complexation of 64Cu to 2 required more rigorous conditions. Briefly, 200 μL of a 5 mM H22 solution was heated at 95 °C for 1 h in the presence of excess Cs2CO3. The 64CuCl2 was added to the heterogeneous solution and the new reaction mixture was heated for another 1.5 h. The supernatant was then transferred to a clean tube and the reaction was evaporated to near dryness at which time 200 μL of 0.1 M NH4OAc (pH 6.5) was added. Reaction progress and final purity were monitored by radio-TLC using C-18 plates and an eluent mixture of 3 : 7 10% NH4OAc– MeOH.
Biodistribution
The biodistribution study was conducted as previously described.6 Female Sprague Dawley rats (180–200 g) were injected with either 64Cu–4 or 64Cu–2 (0.15 mCi in 100 μL per rat). Animals were sacrificed at selected time points post-injection (p.i.), organs of interest were removed, weighed, and counted on a Beckman Gamma Counter 8000. The percent injected dose per gram (%ID per gram) and percent injected dose per organ (%ID per organ) were calculated by comparison to a weighed, counted standard.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NCI grant R01 CA93375. T.J.W. was supported by NCI NRSA grant F32 CA115148. The production of 64Cu at Washington University School of Medicine was supported by an NCI grant R24 CA86307. We also acknowledge two SURF grants at the University of New Hampshire supporting summer undergraduate research scholars (K.J.H and K.S.W.). The authors thank Daniel C. Hill for exploratory ligand synthetic studies.
References
- 1.Blower PJ, Lewis JS, Zweit J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1996;23:957. doi: 10.1016/s0969-8051(96)00130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wadas TJ, Wong EH, Weisman GR, Anderson CJ. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007;13:3. doi: 10.2174/138161207779313768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anderson CJ, Welch MJ. Chem. Rev. 1999;99:2219. doi: 10.1021/cr980451q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith SV. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004;98:1874. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bass LA, Wang M, Welch MJ, Anderson CJ. Bioconjugate Chem. 2000;11:527. doi: 10.1021/bc990167l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sun X, Wuest M, Weisman GR, Wong EH, Reed DP, Boswell CA, Motekaitis RJ, Martell AE, Welch MJ, Anderson CJ. J. Med. Chem. 2002;45:469. doi: 10.1021/jm0103817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boswell CA, Sun X, Niu W, Weisman GR, Wong EH, Rheingold AL, Anderson CJ. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47:1465. doi: 10.1021/jm030383m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sprague JE, Peng Y, Sun X, Weisman GR, Wong EH, Achilefu S, Anderson CJ. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004;10:8674. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Woodin KS, Heroux KJ, Boswell CA, Wong EH, Weisman GR, Niu W, Tomellini SA, Anderson CJ, Zakharov LN, Rheingold AL. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005:4829. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wong EH, Weisman GR, Hill DC, Reed DP, Rogers ME, Condon JP, Fagan MA, Calabrese JC, Lam K-C, Guzei IA, Rheingold AL. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:10561. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Anda C, Bencini A, Berni E, Ciattini S, Chuburu F, Danesi A, Giorgi C, Handel H, Baccon ML, Paoletti P, Tripier R, Turcry V, Valtancoli B. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005:2044. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kang S-G, Ryu K-S, Nam K, Kim J. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2005;358:2224. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Keire DA, Jang YH, Li L, Dasgupta S, Goddard WA, III, Shively JE. Inorg. Chem. 2001;40:4310. doi: 10.1021/ic0010297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tschudin D, Basak A, Kaden TA. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1988;71:100. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lecomte C, Dahouri-Gindrey V, Chollet H, Gros C, Mishra AK, Barbette F, Pullumbi P, Guilard R. Inorg. Chem. 1997;36:3827. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Siegfried L, Kaden TA. Dalton Trans. 2005:3079. doi: 10.1039/b505866j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schatz M, Becker M, Thaler F, Hampel F, Schindler S, Jacobson RR, Tuekar Z, Murthy NN, Ghosh P, Chen Q, Zubieta J, Karlin KD. Inorg. Chem. 2001;40:2312. doi: 10.1021/ic000924n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Niu W, Wong EH, Weisman GR, Hill DC, Tranchemontagne DJ, Lam K-C, Sommer RD, Zakharov LN, Rheingold AL. Dalton Trans. 2004:3536. doi: 10.1039/b410738a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gros C, Chollet H, Mishra AK, Guilard R. Synth. Commun. 1996;26:35. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Morrow JR, Amin S, Lake CH, Churchill MR. Inorg. Chem. 1993;32:4566. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Moi MK, Yanuck M, Desphpande SV, Hope H, DeNardo SJ, Meares CF. Inorg. Chem. 1987;26:3458. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aneetha H, Lai Y-H, Lin S-C, Panneerselvam K, Lu T-H, Chung C-S. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1999:2885. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bernhardt PV, Sharpe PC. Inorg. Chem. 2000;39:2020. doi: 10.1021/ic9906353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Riesen A, Zehnder M, Kaden TA. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1986;69:2067. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chapman J, Ferguson G, Gallagher JF, Jennings MC, Parker D. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1992:345. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen L, Thompson LK, Bridson JN, Xu J, Ni S, Guo R. Can. J. Chem. 1993;71:1805. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kang S-G, Kim S-J, Jeong JH. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2003;340:187. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Belsky VK, Streltsova NR, Kumina EN, Nazarenko AY. Polyhedron. 1993;12:831. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nakamoto K. Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds. John Wiley and Sons; New York: 1963. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nakamoto K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds. John Wiley and Sons; New York: 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brucher E. Top. Curr. Chem. 2002;221:103. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Addison AW, Rao TN, Reedijk J, Van J, Rijn, Verschoor GC. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1984:1349. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gazo J, Bersuker IB, Garaj J, Kabesova M, Kohout J, Langfelderova H, Melnik M, Serator M, Valach F. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1976;19:253. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Burton VJ, Deeth RJ, Kemp CM, Gilbert PJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:8407. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brown ID. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci. 1992;48:553. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Thorp HH. Inorg. Chem. 1992;31:1585. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shields GP, Raithby PR, Allen FH, Motherwell WD, Samuel WD. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. B: Struct. Sci. 2000;56:455. doi: 10.1107/s0108768199015086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cambridge Structural Database ID codes of structures of copper(II) bis-carboxylate complexes of cyclam and cyclen-based ligands: BASNAL, BIMSOG, DAPTAP, DESQAT, FEKVAS, FORMOO, GEWCEQ, IXOKIP, JECDEB, JECDIF, LEWCOF, LIZTET, MEMYUY, MITGAX, OMECEO, PARQIJ, PIMFEW, RAJMIZ, RAZGOP, ULOLUW, VIQKEL, VOPSAU, VUYSOX, WEQJEH, ZIWJEU.
- 39.Cambridge Structural Database ID codes for structures of copper(II) bis-carboxylate complexes of acyclic amines: BIBTUB, ELAHOO, GAWHAN, KULNIO, MEVJEC, NEGYON, NEGYUT, NEGZAA, OBIYED, PABKAE, PACBZC, PACUBB, PACUIB, PANBCU, PAPMBC, PCUBBZ, PCUFBZ, PDCUNB, PRACUB01, PRMBCU, QERRAG, QQQGUA10, TOKKEJ, TOQDOS, WACZOP.
- 40.Weisman GR, Wong EH, Hill DC, Rogers ME, Reed DP, Calabrese JC. Chem. Commun. 1996:947. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kotek J, Lubal P, Hermann P, Cisarova I, Lukes I, Godula T, Svobodova I, Taborsky P, Havel J. Chem.–Eur. J. 2003;9:233. doi: 10.1002/chem.200390017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Broge L, Pretzmann U, Jensen N, Sotofte I, Olsen CE, Springborg J. Inorg. Chem. 2001;40:2323. doi: 10.1021/ic0011157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hay RW, Pujari MP. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 1985;100:L1. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen L-H, Chung C-S. Inorg. Chem. 1988;27:1880. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Balogh E, Tripier R, Ruloff R, Toth E. Dalton Trans. 2005:1058. doi: 10.1039/b418991d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sargeson AM. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986;58:1511. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gustafson L. BS Thesis. University of New Hampshire; 2006. A Comparative Study of Inertness: Cu-DiAmSar vs Cu-CB-TE2A. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Caughey WS, Corwin AH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955;77:1509. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Khelevina OG, Chizhova NV, Berezin BD. Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Khim. Khim. Tekhnol. 1989;32:45. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Khelevina OG, Stuzhin PA, Berezin BD. Zh. Fiz. Khim. 1986;60:1881. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Klueva ME, Suslova EE, Lomova TN. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2003;73:1303. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Klyueva ME, Lomova TN, Suslova EE, Semeikin AS. Theor. Exp. Chem. 2003;39:309. [Google Scholar]
- 53.McMurry TJ, Pippin CG, Wu C, Desal KA, Brechbiel MW, Mirzadeh S, Gansow OA. J. Med. Chem. 1998;41:3546. doi: 10.1021/jm980152t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zubieta J, Karlin KD, Hayes JC. In: Copper Coordination Chemistry: Biochemical and Inorganic Perspectives. Karlin KD, Zubieta J, editors. Adenine Press; Guilderland, N. Y.: 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wei N, Murthy NN, Karlin KD. Inorg. Chem. 1994;33:6093. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rorabacher DB. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:651. doi: 10.1021/cr020630e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Raymond KN, Carrano CJ. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979;12:183. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Abergel RJ, Warner JA, Shuh DK, Raymond KN. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:8920. doi: 10.1021/ja062046j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hubin TJ, Alcock NW, Busch DH. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C: Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2000;56:37. doi: 10.1107/s010827019901255x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jones-Wilson TM, Deal KA, Anderson CJ, McCarthy DW, Kovacs Z, Motekaitis RJ, Sherry AD, Martell AE, Welch MJ. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1998;25:523. doi: 10.1016/s0969-8051(98)00017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]