Abstract
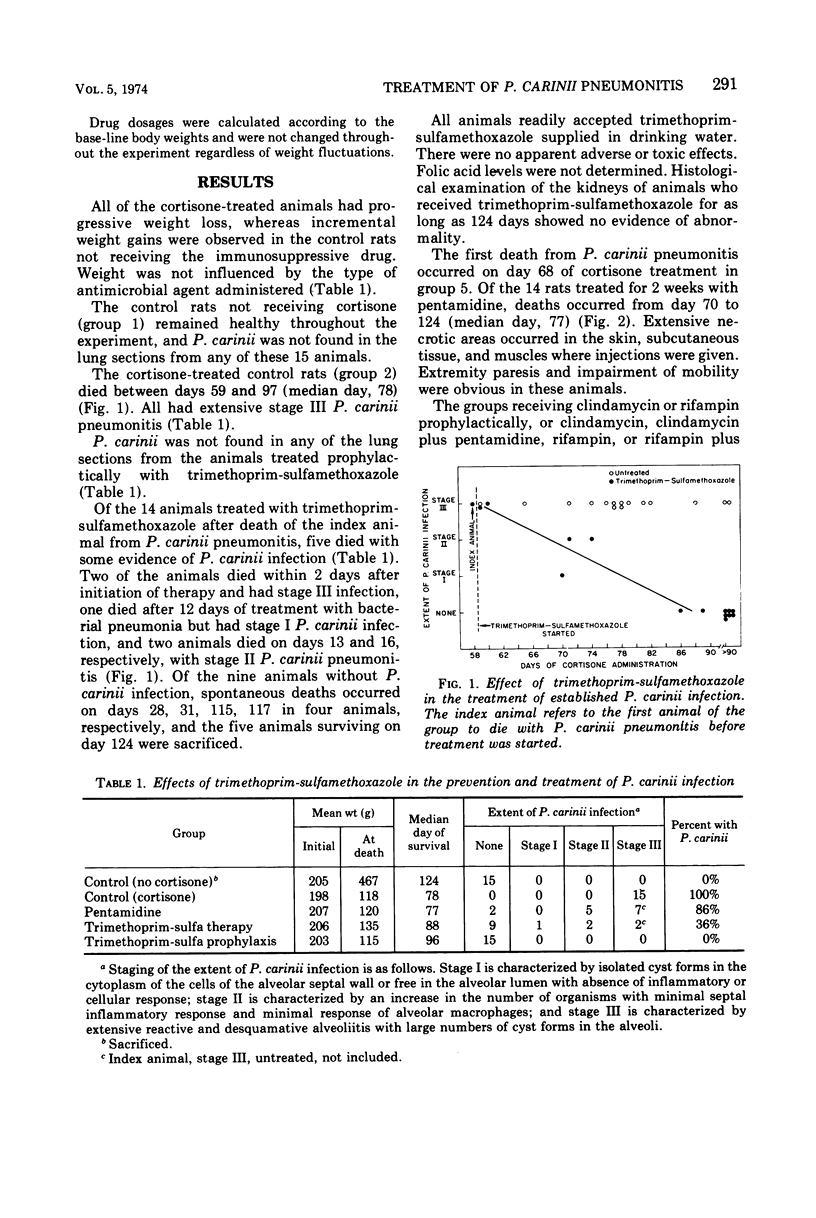
A combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole was effective in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in cortisonetreated rats. Although all of 15 untreated rats died with P. carinii pneumonitis, none of 15 given trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylactically acquired the infection. After P. carinii pneumonitis was established, 9 of 14 rats recovered after treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole compared with only 2 of 14 treated with pentamidine isethionate. Rifampin and clindamycin, separately or in combination with pentamidine, were ineffective in the prevention and treatment of P. carinii infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvilommi H., Vuori M., Salmi A. Immunosuppression by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Sep 23;3(5829):761–762. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5829.761-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvilommi H., Vuori M., Salmi A. Immunosuppression by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Sep 23;3(5829):761–762. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5829.761-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUZIER G., WILLIS T., BARNETT R. N. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in an infant. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Jul;26(7):787–793. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.7.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donno L., Sanguineti V. Therapy of natural falciparum malaria with combinations of antifolic drugs in non-immune subjects. Chemotherapy. 1970;15(2):118–124. doi: 10.1159/000220674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylarde P. M., Sarkany I. Suppression of thymidine uptake of human lymphocytes by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 15;3(5819):144–146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5819.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghilchik M. W., Morris A. S., Reeves D. S. Immunosuppressive powers of the antibacterial agent trimethoprim. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):393–394. doi: 10.1038/227393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Kim H. K., Price R. A., Miller C. Attempts at prophylaxis for murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1973 Aug;15(8):581–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Price R. A., Kim H. K., Coburn T. P., Grigsby D., Feldman S. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in children with malignancies. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNSETH J. H., KIRMSE T. W., PREZYNA A. P., GERTH R. E. Interstitial plasma cell pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1955 Feb;46(2):137–145. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(55)80202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. Antiplasmodial activity of halogenated lincomycin analogues in Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:537–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster P. R., Powers K. G., Finerty J. F., Lunde M. N. The effect of two chlorinated lincomycin analogues against acute toxoplasmosis in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Jan;22(1):14–17. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C., Fakouhi T., Dutz W., Bandarizadeh B., Kohout E. E. Prophylaxis of epidemic infantile pneumocystosis with a 20:1 sulfadoxine+pyrimethamine combination. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1971 May;13(5):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisberg B., Herzog J., Weinstein L. In vitro antibacterial activity of trimethoprim alone and combined with sulfonamides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:424–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Yagura T., Robinson W. S. The effect of rifampin on Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Rieder J. Pharmacokinetics of sulfamethoxazole plus trimethoprim in man and their distribution in the rat. Chemotherapy. 1970;15(6):337–355. doi: 10.1159/000220701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udall V. Toxicology of sulphonamide-trimethoprim combinations. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):42–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Western K. A., Perera D. R., Schultz M. G. Pentamidine isethionate in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):695–702. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



