Abstract
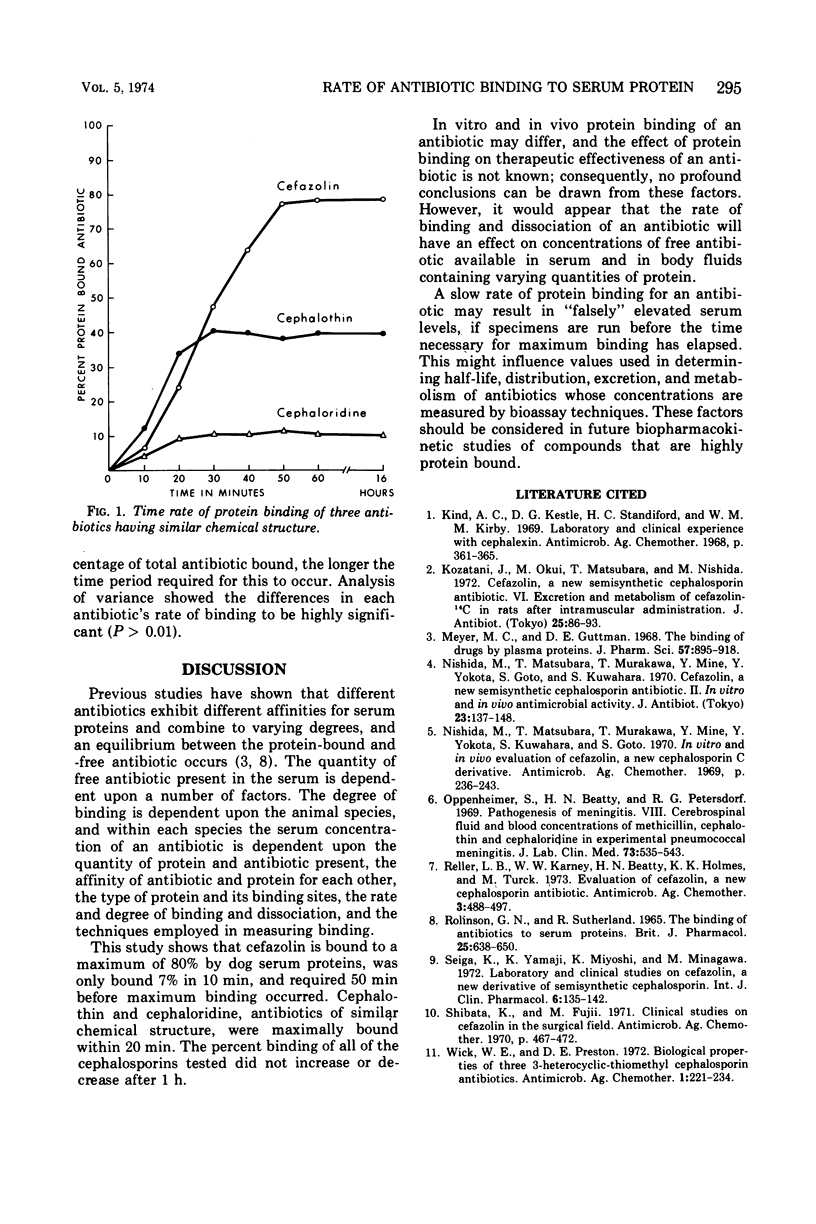
The time rates of binding of three antibiotics of similar chemical structure, each with differing degrees of protein binding, were determined. Cephaloridine, which is 10% bound by serum proteins, was bound at a more rapid rate than cephalothin, which is 40% bound by serum protein. Cefazolin, bound 80%, required for longest time period for maximum binding to occur. The rate of protein binding appears directly related to the total percentage bound. The data from this study indicate that prolonged rates of binding of highly protein-bound drugs may influence pharmacological studies.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kind A. C., Kestle D. G., Standiford H. C., Kirby W. M. Laboratory and clinical experience with cephalexin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:361–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozatani J., Okui M., Matsubara T., Nishida M. Cefazolin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. VI. Excretion and metabolism of cefazolin- 14 C in rats after intramuscular administration. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Feb;25(2):86–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. C., Guttman D. E. The binding of drugs by plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):895–918. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neter E., Olson T. A., Press E., Reese E. M., Roark K. T., Rosenstock I. M., Steele J. H., Mattison B. F., Baker A. G., Bierman P. Committee Reports: Committee on Evaluation and Standards: REPORT OF THE CHAIRMAN, 1967. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1968 Feb;58(2):365–366. doi: 10.2105/ajph.58.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Matsubara T., Murakawa T., Mine Y., Yokota Y. Cefazolin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic. II. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Mar;23(3):137–148. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Matsubara T., Murakawa T., Mine Y., Yokota Y., Kuwahara S., Goto S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin C derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer S., Beaty H. N., Petersdorf R. G. Pathogenesis of meningitis. VIII. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood concentrations of methicillin, cephalothin, and cephaloridine in experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Apr;73(4):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Karney W. W., Beaty H. N., Holmes K. K., Turck M. Evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):488–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiga K., Yamaji K., Miyoshi K., Minagawa M. Laboratory and clinical studies on cefazolin, a new derivative of semisynthetic cephalosporin. Int J Clin Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;6(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Fujii M. Clinical studies of cefazolin in the surgical field. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick W. E., Preston D. A. Biological properties of three 3-heterocyclic-thiomethyl cephalosporin antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Mar;1(3):221–234. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



