Abstract
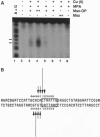
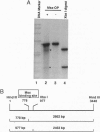
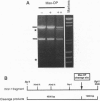
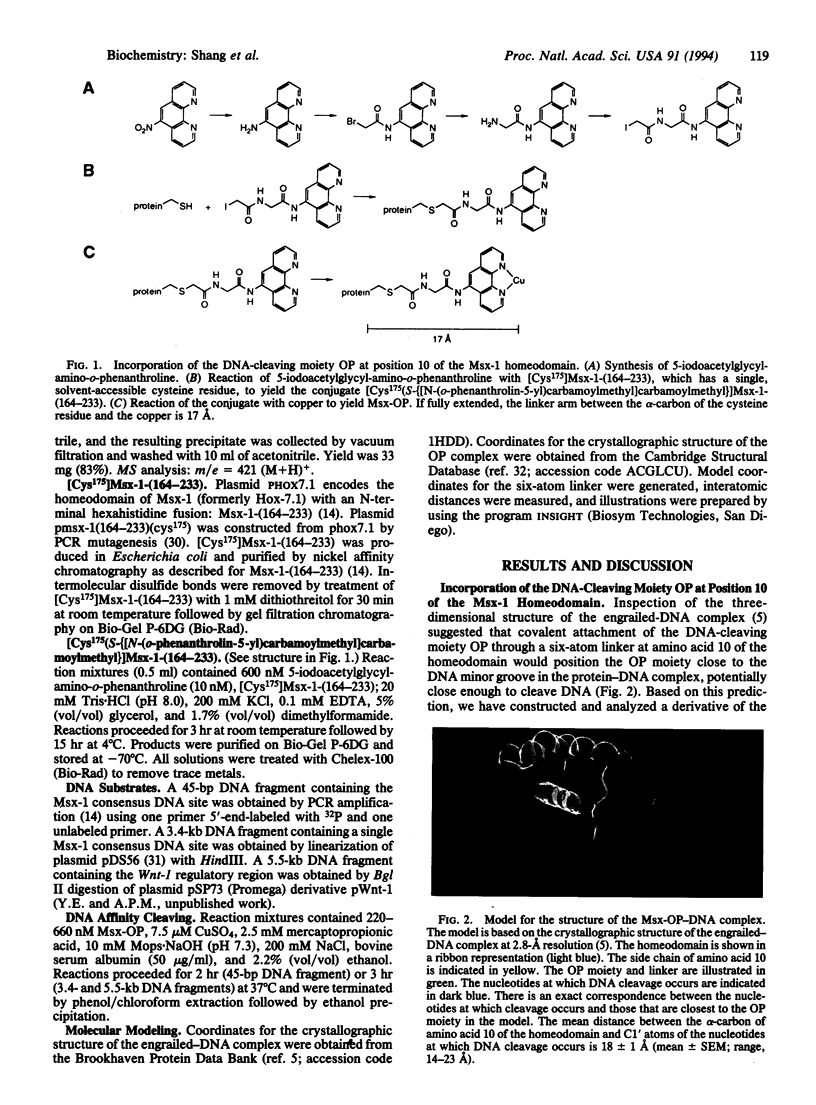
We have incorporated the DNA-cleaving moiety o-phenanthroline-copper at amino acid 10 of the Msx-1 homeodomain, and we have analyzed site-specific DNA cleavage by the resulting Msx-1 derivative. We show that amino acid 10 of the Msx-1 homeodomain is close to the 5' end of the consensus DNA site 5'-(C/G)TAATTG-3' in the Msx-1-DNA complex. Our results indicate that the orientation of the Msx-1 homeodomain relative to DNA is analogous to the orientation of the engrailed and Antennapedia homeodomains. We show further that DNA affinity cleaving permits identification of consensus DNA sites for Msx-1 in kilobase DNA substrates. The specificity of the approach enabled us to identify an Msx-1 consensus DNA site within the transcriptional control region of the developmental regulatory gene Wnt-1. We propose that incorporation of o-phenanthroline-copper at amino acid 10 of a homeodomain may provide a generalizable strategy to determine the orientation of a homeodomain relative to DNA and to identify homeodomain consensus DNA sites in genomic DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bujard H., Gentz R., Lanzer M., Stueber D., Mueller M., Ibrahimi I., Haeuptle M. T., Dobberstein B. A T5 promoter-based transcription-translation system for the analysis of proteins in vitro and in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:416–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catron K. M., Iler N., Abate C. Nucleotides flanking a conserved TAAT core dictate the DNA binding specificity of three murine homeodomain proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2354–2365. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Sigman D. S. Chemical conversion of a DNA-binding protein into a site-specific nuclease. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1197–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.2820056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervan P. B. Characterization of protein-DNA complexes by affinity cleaving. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:497–515. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08026-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessain S., Gross C. T., Kuziora M. A., McGinnis W. Antp-type homeodomains have distinct DNA binding specificities that correlate with their different regulatory functions in embryos. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):991–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Pendergrast P. S., Gunasekera A. Conversion of a helix-turn-helix motif sequence-specific DNA binding protein into a site-specific DNA cleavage agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2882–2886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright Y. W., Chen Y., Ludescher R. D., Ebright R. H. N-(iodoacetyl)-p-phenylenediamine-EDTA: a reagent for high-efficiency incorporation of an EDTA-metal complex at a rationally selected site within a protein. Bioconjug Chem. 1993 May-Jun;4(3):219–225. doi: 10.1021/bc00021a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright Y. W., Chen Y., Pendergrast P. S., Ebright R. H. Incorporation of an EDTA-metal complex at a rationally selected site within a protein: application to EDTA-iron DNA affinity cleaving with catabolite gene activator protein (CAP) and Cro. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10664–10670. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham K. S., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the DNA binding domain of gamma delta-resolvase characterized by affinity cleaving. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16534–16540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Jones P. F., Rees A. R., Sime C. M., Justice M. J., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Graham E., Davidson D. R. A new family of mouse homeo box-containing genes: molecular structure, chromosomal location, and developmental expression of Hox-7.1. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):26–37. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A. DNA binding specificity of homeodomains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 3;30(48):11357–11367. doi: 10.1021/bi00112a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. P., Sluka J. P., Shin J. A., Griffin J. H., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Orientation of the putative recognition helix in the DNA-binding domain of Hin recombinase complexed with the hix site. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6561–6567. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarelli J. M., Ermácora M. R., Fox R. O., Grindley N. D. Mapping interactions between the catalytic domain of resolvase and its DNA substrate using cysteine-coupled EDTA-iron. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):2979–2986. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Joyner A. L., Bradley A., McMahon J. A. The midbrain-hindbrain phenotype of Wnt-1-/Wnt-1- mice results from stepwise deletion of engrailed-expressing cells by 9.5 days postcoitum. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):581–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley M. G., Dervan P. B. Structural motif of the GCN4 DNA binding domain characterized by affinity cleaving. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.2111578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Müller M., Affolter M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Protein--DNA contacts in the structure of a homeodomain--DNA complex determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in solution. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Sassoon D., Jacq B., Gehring W., Buckingham M. Hox-7, a mouse homeobox gene with a novel pattern of expression during embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):91–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P. Vertebrate homeobox gene nomenclature. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin J. A., Ebright R. H., Dervan P. B. Orientation of the Lac repressor DNA binding domain in complex with the left lac operator half site characterized by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5233–5236. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S., Chen C. H. Chemical nucleases: new reagents in molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:207–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton C. L., Mazumder A., Chen C. H., Sigman D. S. Transforming the Escherichia coli Trp repressor into a site-specific nuclease. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4225–4230. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Gönczy P., Vashishtha M., Harris E., Desplan C. A single amino acid can determine the DNA binding specificity of homeodomain proteins. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):553–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]