Abstract
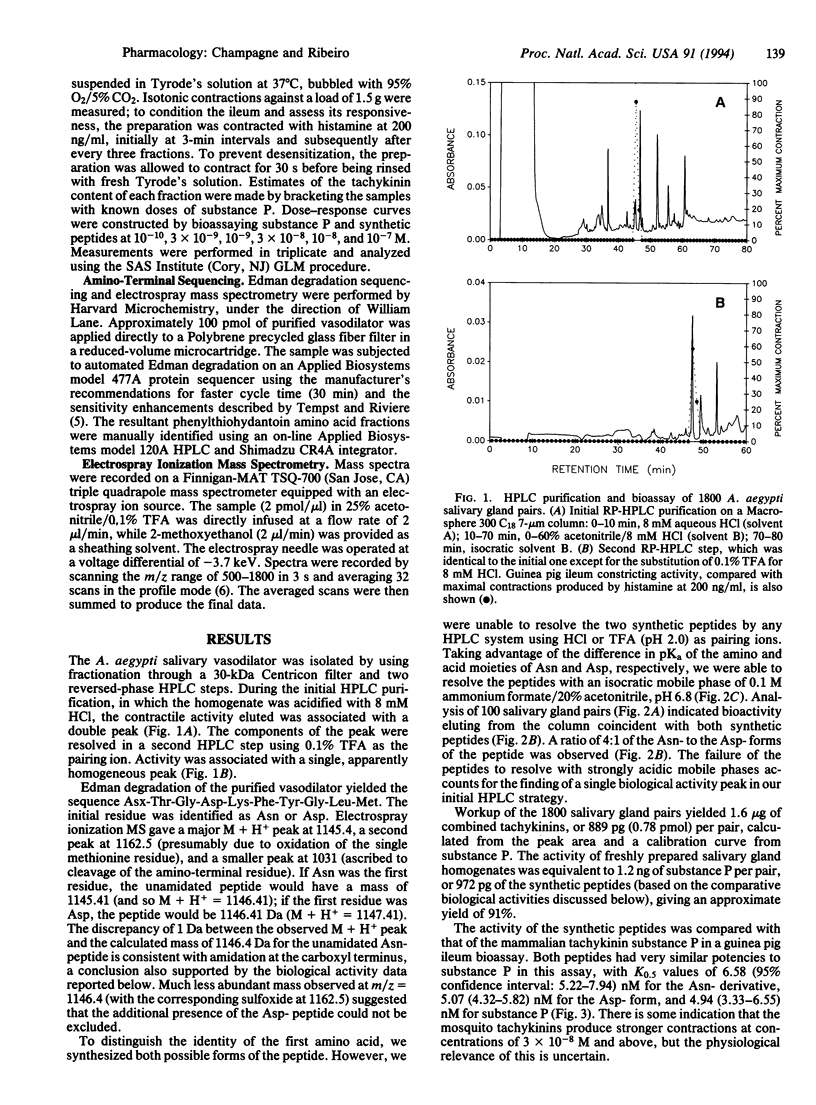
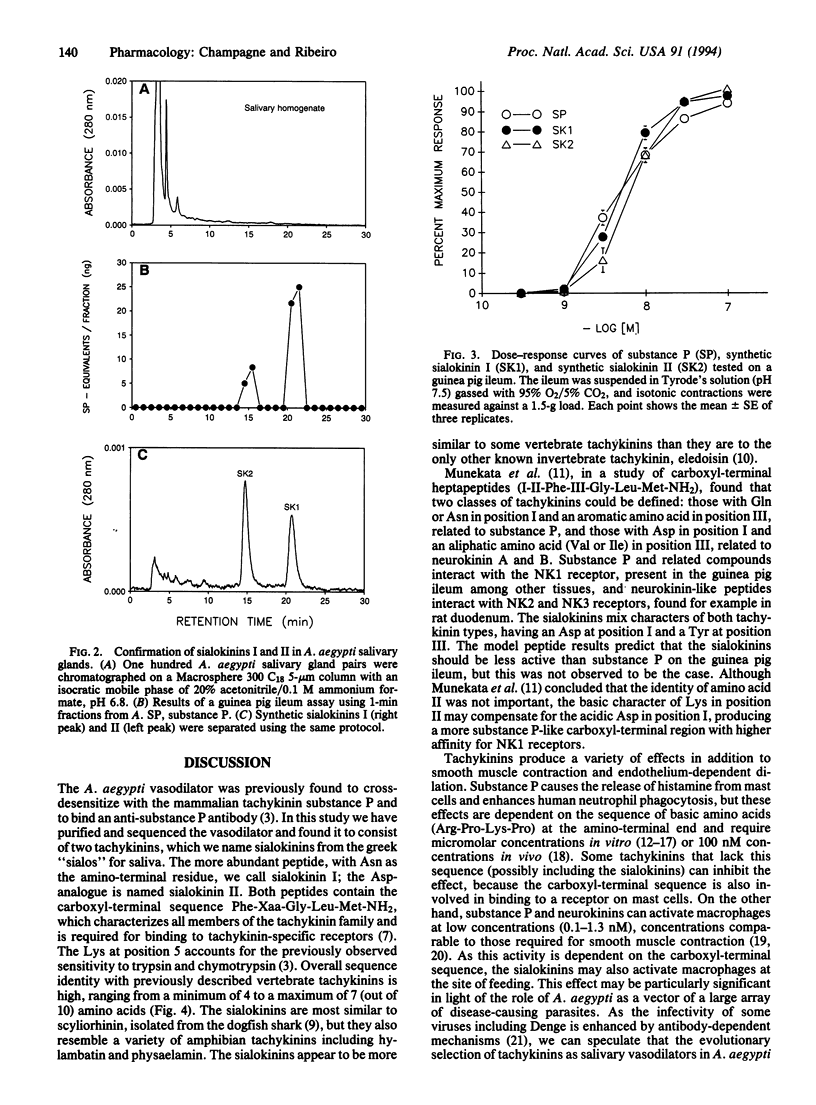
The saliva of the mosquito Aedes aegypti has previously been reported to contain a 1400-Da peptide with pharmacological properties typical of a tachykinin. In the present study this vasodilator has been purified to homogeneity and found to consist of two peptides: sialokinin I, with the sequence Asn-Thr-Gly-Asp-Lys-Phe-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, and sialokinin II, identical to sialokinin I except for an Asp in position 1. These peptides are present in amounts of 0.62 and 0.16 pmol (711 and 178 ng), respectively, per salivary gland pair. When assayed on the guinea pig ileum, both peptides are as active as the mammalian tachykinin substance P, with K0.5 values of 5.07, 6.58, and 4.94 nM for sialokinin I, sialokinin II, and substance P, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANASTASI A., ERSPAMER V. The isolation and amino acid sequence of eledoisin, the active endecapeptide of the posterior salivary glands of Eledone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:56–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Goldman R., Stabinsky Y., Gottlieb P., Fridkin M., Teichberg V. I., Blumberg S. Enhancement of phagocytosis - a newly found activity of substance P residing in its N-terminal tetrapeptide sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1445–1451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedeczky I., Kiss J. Z., Somogyi P. Light and electron microscopic localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the cerebral ganglion of locust with a monoclonal antibody. Histochemistry. 1982;75(1):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00492539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelleschi S., Vanni L., Ledda F., Giotti A., Maggi C. A., Fantozzi R. Tachykinins activate guinea-pig alveolar macrophages: involvement of NK2 and NK1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):417–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M., Deacon C. F., O'Toole L., Thim L. Scyliorhinin I and II: two novel tachykinins from dogfish gut. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Loof A., Schoofs L. Homologies between the amino acid sequences of some vertebrate peptide hormones and peptides isolated from invertebrate sources. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;95(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90003-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Salhy M., Abou-el-Ela R., Falkmer S., Grimelius L., Wilander E. Immunohistochemical evidence of gastro-entero-pancreatic neurohormonal peptides of vertebrate type in the nervous system of the larva of a dipteran insect, the hoverfly, Eristalis aeneus. Regul Pept. 1980 Dec;1(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(80)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Salhy M., Falkmer S., Kramer K. J., Speirs R. D. Immunohistochemical investigations of neuropeptides in the brain, corpora cardiaca, and corpora allata of an adult lepidopteran insect, Manduca sexta (L). Cell Tissue Res. 1983;232(2):295–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00213788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C. M., Foreman J. C., Jordan C. C., Oehme P., Renner H., Stewart J. M. The effects of substance P on histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine release in the rat. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:393–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J., Jordan C. Histamine release and vascular changes induced by neuropeptides. Agents Actions. 1983 Apr;13(2-3):105–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01967311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D., Nusbaum M. P., Marder E. Substance P-like immunoreactivity in the stomatogastric nervous systems of the crab Cancer borealis and the lobsters Panulirus interruptus and Homarus americanus. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Jun;252(3):515–522. doi: 10.1007/BF00216638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelikhuijzen C. J., Balfe A., Emson P. C., Powell D., Sundler F. Substance P-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of hydra. Histochemistry. 1981;71(3):325–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00495879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen B. L., Hansen G. N., Scharrer B. Immunoreactive material resembling vertebrate neuropeptides in the corpus cardiacum and corpus allatum of the insect Leucophaea maderae. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;225(2):319–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00214685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Toyka K. V. Activation of macrophages by substance P: induction of oxidative burst and thromboxane release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 6;89(3-4):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helke C. J., Krause J. E., Mantyh P. W., Couture R., Bannon M. J. Diversity in mammalian tachykinin peptidergic neurons: multiple peptides, receptors, and regulatory mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1606–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law J. H., Ribeiro J. M., Wells M. A. Biochemical insights derived from insect diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Shoemaker C. B. Maxadilan. Cloning and functional expression of the gene encoding this potent vasodilator peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1062–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. J., Wolfgang W., Wu Y. N., North R. A., Forte M. Cloning, heterologous expression and developmental regulation of a Drosophila receptor for tachykinin-like peptides. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3221–3229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist T., Nässel D. R. Substance P-, FMRFamide-, and gastrin/cholecystokinin-like immunoreactive neurons in the thoraco-abdominal ganglia of the flies Drosophila and Calliphora. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):161–178. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek N., Pecht I., Teichberg V. I., Blumberg S. The role of the N-terminal tetrapeptide in the histamine releasing action of substance P. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Nov;20(11):1025–1027. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier D., Colas J. F., Rosay P., Hen R., Borrelli E., Maroteaux L. NKD, a developmentally regulated tachykinin receptor in Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1298–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munekata E., Kubo K., Tanaka H., Osakada F. Structure-activity studies of heptapeptide derivatives related to substance P, neurokinin A, B and other tachykinins on smooth muscles. Peptides. 1987 Jan-Feb;8(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nässel D. R., Lundquist T., Hög A., Grimelius L. Substance P-like immunoreactive neurons in the nervous system of Drosophila. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 22;507(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90276-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repke H., Bienert M. Mast cell activation--a receptor-independent mode of substance P action? FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80932-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M. Characterization of a vasodilator from the salivary glands of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. J Exp Biol. 1992 Apr;165:61–71. doi: 10.1242/jeb.165.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Evans P. M., MacSwain J. L., Sauer J. Amblyomma americanum: characterization of salivary prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha by RP-HPLC/bioassay and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Feb;74(1):112–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90145-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Hazzard J. M., Nussenzveig R. H., Champagne D. E., Walker F. A. Reversible binding of nitric oxide by a salivary heme protein from a bloodsucking insect. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):539–541. doi: 10.1126/science.8386393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Marinotti O., Gonzales R. A salivary vasodilator in the blood-sucking bug, Rhodnius prolixus. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):932–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Nussenzveig R. H. The salivary catechol oxidase/peroxidase activities of the mosquito Anopheles albimanus. J Exp Biol. 1993 Jun;179:273–287. doi: 10.1242/jeb.179.1.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M. Role of saliva in blood-feeding by arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol. 1987;32:463–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.32.010187.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs L., Holman G. M., Hayes T. K., Kochansky J. P., Nachman R. J., De Loof A. Locustatachykinin III and IV: two additional insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. Regul Pept. 1990 Dec 10;31(3):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90006-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs L., Holman G. M., Hayes T. K., Nachman R. J., De Loof A. Locustatachykinin I and II, two novel insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):397–401. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80601-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata H., Mio M., Tasaka K. Analysis of the mechanism of histamine release induced by substance P. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 30;846(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taban C. H., Cathieni M. Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in Hydra. Experientia. 1979 Jun 15;35(6):811–812. doi: 10.1007/BF01968266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Riviere L. Examination of automated polypeptide sequencing using standard phenyl isothiocyanate reagent and subpicomole high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaert P., De Loof A. Substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the blattarian insect Periplaneta americana L. revealed by a monoclonal antibody. Histochemistry. 1985;83(6):501–507. doi: 10.1007/BF00492451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano H., Wershil B. K., Arizono N., Galli S. J. Substance P-induced augmentation of cutaneous vascular permeability and granulocyte infiltration in mice is mast cell dependent. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1276–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI114295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. M., Wheat T. E. Optimization of high-performance liquid chromatographic peptide separations with alternative mobile and stationary phases. J Chromatogr. 1990 Jul 20;512:273–281. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)89494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



