Abstract
Robotic surgery has been eagerly adopted by patients and surgeons alike in the field of urology, over the last decade. However, there is a lack of standardization in training curricula and accreditation guidelines to ensure surgeon competence and patient safety. Accordingly, in this review, we aim to highlight ‘who’ needs to learn ‘what’ and ‘how’, to become competent in robotic surgery. We demonstrate that both novice and experienced open surgeons require supervision and mentoring during the initial phases of robotic surgery skill acquisition. The experienced open surgeons possess domain knowledge, however, need to acquire technical knowledge under supervision (either in simulated or clinical environment) to successfully transition to robotic surgery, whereas, novice surgeons need to acquire both domain as well as technical knowledge to become competent in robotic surgery. With regard to training curricula, a variety of training programs such as academic fellowships, mini-fellowships, and mentored skill courses exist, and cater to the needs and expectations of postgraduate surgeons adequately. Fellowships provide the most comprehensive training, however, may not be suitable to all surgeon-learners secondary to the long-term time commitment. For these surgeon-learners short-term courses such as the mini-fellowships or mentored skill courses might be more apt. Lastly, with regards to credentialing uniformity in criteria regarding accreditation is lacking but earnest efforts are underway. Currently, accreditation for competence in robotic surgery is institutional specific.
Keywords: Curriculum, robotics, simulation, surgical learning, training
INTRODUCTION
Minimally-invasive surgery (MIS) began in the year 1987 with laparoscopic cholecystectomy.[1] The advantages and disadvantages of the MIS approach became quickly apparent. The advantages included decreased surgical site infection, blood loss and postoperative pain, shorter hospital stay, and better cosmesis. On the other hand, the disadvantages included loss of haptic feedback and hand-eye coordination.[2] These limitations made delicate dissections and anastomoses difficult if not impossible.[3] Robotic surgery was, thus, developed to overcome these limitations of the MIS and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.[2]
Robotic surgery, over the last decade, has been enthusiastically adopted by patients and surgeons alike in the field of urology, and today, is utilized for oncological,[4,5,6] reconstructive,[7,8] pediatric,[9,10,11] urogynecological,[12] and kidney transplantation procedures.[13,14,15] However, there is a lack of standardization in training curricula and accreditation guidelines to ensure surgeon competence and patient safety. Although, there have been institutional and surgical-societal level efforts at standardization of these processes, so far these efforts have met with limited success and heterogeneity in certification standards persists.[16,17,18] Hence, as adoption of robotic surgery continues to increase, there is an urgent need for unifying the training and credentialing requirements to ensure patient safety. Accordingly, in this review, we aim to highlight ‘who’ needs to learn ‘what’ and ‘how’, to become competent in robotic surgery.
Who Needs to Learn?
Learning is an essential part of skill acquisition and of surgical apprenticeship. During the learning process, however, there is an increased propensity for error, and in the setting of clinical practice this may or may not be acceptable depending on the risk involved. A learning curve can exist in two situations in surgical practice [Figure 1a]:
Figure 1.
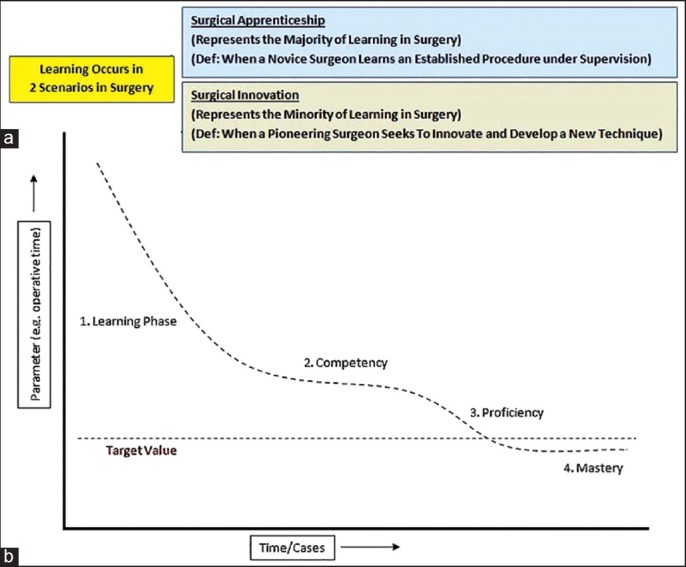
(a) Two types of learning scenarios in surgery; (b) The classic phases of a learning curve – learning phase, competency, proficiency and mastery (non-CUSUM learning curve)
When a novice surgeon learns an established procedure under supervision (surgical apprenticeship).
When a pioneering surgeon seeks to innovate and develop a new technique (surgical innovation).
In both of the aforementioned scenarios, the patient maybe at an increased risk for adverse outcome; however, the former situation represents by far the more common setting, albeit a less risky one. Further, the precautions to counter the increased risk in both these scenarios vary vastly. For example, in the case of surgical innovation the pathway to ensure patient safety is to perform preclinical (animal/cadaveric) feasibility and simulator studies before performing patient surgery.[19,20] While on the other hand, the usual pathway for ensuring uncompromised patient outcomes during training of a novice surgeon includes theoretical learning and mentoring, although occasionally simulator/animal studies maybe utilized. In the current review, we will limit the discussion to the latter learning pathway (surgical apprenticeship), as it is the primary topic of interest to this review.
To address the concern of training a novice surgeon, mentors/credentialing committees have traditionally relied on learning curves[21,22] which help estimate the number of cases a surgeon-learner must perform under supervision to become competent (and avoid compromising patient outcomes). An ideal learning curve is shown in Figure 1b. Each new task a novice surgeon acquires will have an associated learning curve. Depending on the magnitude of difference in the tasks being learnt, the surgeon may or may not need supervision for each new task. For example, if a surgeon has learnt to perform iliac vessel anastomoses, he should presumably be competent to perform anastomoses of other similar-sized blood vessels without supervision. While on the other hand, if a surgeon has learnt to perform iliac vessel anastomoses via open surgery would he be capable of performing the same via robotic surgery without supervision? Does he need to learn anything?
These questions are applicable to the case of experienced open surgeons adopting robotic surgery. The answer to the earlier-given questions lie in distinguishing between domain knowledge and technical knowledge (please see the next section). Many open surgeons hold the notion that secondary to their acclimation with the open surgical technique they will be able to perform the same given task equally well robotically. However, recently, it has been shown that skilled open surgeons adopting robotic surgery have a substantial learning phase that varies with the task being learnt. Specifically, in the study of robotic kidney transplantation (RKT) with regional hypothermia, three surgeon groups were evaluated with varying open and robotic experience/training.[23] Group-1: robotic trained with limited kidney transplantation (KT) experience (patients=7); Group-2: robotic trained and KT experienced (patients=20); and Group-3: KT experienced with limited robotic training (patients=14). It was demonstrated that for surgeons in group 1 and 2, there was a minimal-to-nil learning phase. However, for group 3 there was a significant learning phase. Learning phase lasted until case 9 and 12 for venous and arterial anastomoses, respectively [Figures 2a and b]. Similarly, for the ureterovesical anastomosis, the learning phase continued beyond patient 14 [Figure 2c]* and for re-warming time, competency was achieved after case 11 [Figure 2d]. For graft function, the learning phase was short, and competency and mastery were achieved after case 3 and 13, respectively [Figures 3a and b]. Hence, there is a clear role of mentoring and/or precepting in even the experienced open surgeons during early phases of the adoption of robotic technology to ensure patient safety.[23]
Figure 2.
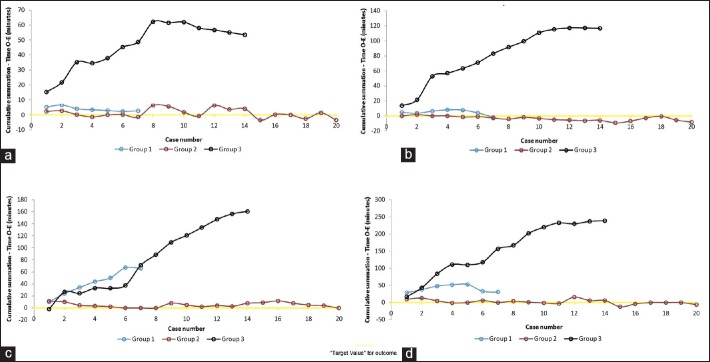
Learning curve assessment using CUSUM method for technical outcomes. (a) for venous anastomosis; (b) for arterial anastomosis; (c) for uretero-vesical anastomosis; (d) for re-warming time (Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Inc., European Urology; 2014 Mar 4; Application of the Statistical Process Control Method for Prospective Patient Safety Monitoring During the Learning Phase: Robotic Kidney Transplantation with Regional Hypothermia [IDEAL Phase 2a-b]; Sood et al.)
Figure 3.
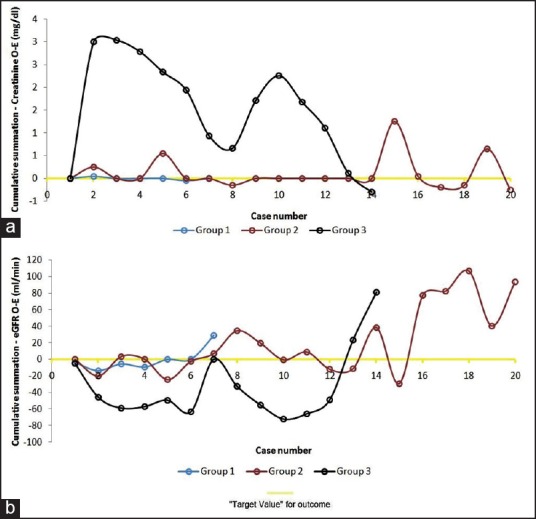
Learning curve assessment using CUSUM method for functional outcomes. (a) for POD 7 serum creatinine; (b) for POD 7 estimated GFR (Reproduced with permission from Elsevier Inc., European Urology; 2014 Mar 4; Application of the Statistical Process Control Method for Prospective Patient Safety Monitoring During the Learning Phase: Robotic Kidney Transplantation with Regional Hypothermia [IDEAL Phase 2a-b]; Sood et al.)
[The graphs are cumulative summation (CUSUM) derived learning curves, for details on methodology and how to interpret them accurately please refer to the original text, but essentially the plateau denotes the end of learning phase].[23]
Lastly, in robotic surgery, in addition to training of the surgeon there is a clear place for learning of the skill by the team as a whole.[24] Thiel et al.[25] in their study of robotic prostatectomy evaluated the role of training bedside assistants — in this study, the participants underwent a three-phase learning course including teaching regarding the basics of robot functionality (phase-1), a step-by-step video showing the optimal role of an assistant during robotic prostatectomy (phase-2), and lastly, a hands-on practice session (phase-3). The authors noted that all 13 participants who underwent the 3-phase learning course recorded improved spatial orientation during surgery and felt that the training made them a better assistant (100% response rate). The module that was most useful was the ‘hands-on’ drill. Hence, while setting up a robotic surgery program, it might be worthwhile to keep in consideration the training of assistants to further improve patient outcomes.
What Needs to be Learned and when?
For successful performance of any task a person needs to have the knowhow of what to do (domain knowledge) and how to do it (technical knowledge; Figure 4), as David Eddy pointed out in his landmark paper.[26] Domain knowledge, also alluded to as functional knowledge sometimes, refers to the understanding of a concept while technical knowledge represents the acquaintance of an individual with the steps in execution of a task. Domain knowledge is primarily acquired from theory whereas technical knowledge is acquired by practice. We briefly alluded to these concepts in the previous section, and using the same example, we highlight that the reason why open surgeons cannot transition into robotic surgery without going through a learning phase is because of lack of technical knowledge. An experienced open surgeon possesses the domain knowledge, but to achieve competency in technical knowledge — the surgeon needs to practice either in a simulated environment or under mentorship in a clinical environment, much akin to training of a novice surgeon. However, a resident/fellow learning a robotic procedure will need to acquire both domain and technical knowledge.
Figure 4.
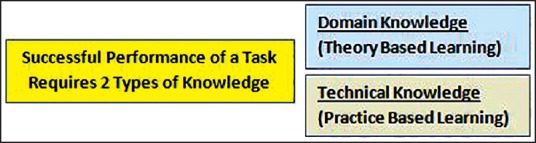
The two types of knowledge required for successful execution of a task
Lastly, the time to learn is also important when acquiring a new technical skill, as prior studies show.[27] We humbly submit that open surgeons should only consider taking robotic training modules when they have the desire and the setup to perform robotic surgery on a regular basis, as many of the courses (detailed in next section) offer short-term training, can be expensive and might not leave a lasting impression unless robotic surgery in continued afterwards.
How can it be Learned? And When Can a New Skill Be Considered Learned?
An ideal curriculum for teaching technical skills (technical knowledge) requires, foremost, setting of clear goals and objectives that can be achieved by trainees with the help of targeted interventions. The next crucial step is designing and incorporating these interventions along with assessment tools that can certify the surgeon-learner's competency.[28] Assessment is a critical part of learning, not only because it ensures surgeon competence but also because it helps learning by the virtue of feedback (operant conditioning).[29]
As stated previously, there have been several institutional and surgical-societal level efforts to develop and standardize the training curriculum and certification requirements in minimally-invasive surgical training. Although, these processes have met with limited success so far, the hospitals, credentialing committees/associations and program directors are increasingly recognizing the need for formal MIS training and credentialing, and the adoption of these processes is increasing.[17,18,30,31] Further, with regards to certification — there has been a tremendous overhaul in the way competency is evaluated. Traditionally, a trainee's competence was measured based on time-based apprentice-type system where time spent within a specialty was the defining factor in skill acquisition. However, in the contemporary system a trainee's progress is determined by instating specific benchmarks for him/her to achieve which lead to more objective and evidence-based credentialing.[28]
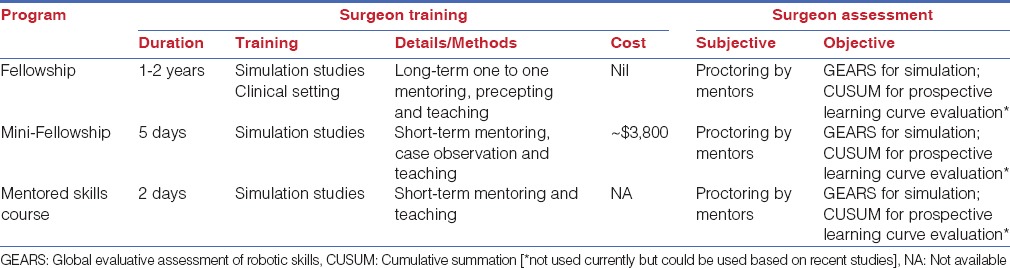
Table 1 details the various training programs that exist for training surgeons in robotic surgery. The current generation of resident surgeons has some degree of robotic experience (at least in the United States). However, mostly the experience is insufficient to warrant independent practice. Hence, the training programs described in the following are applicable to all surgeons with varying degrees of open/laparoscopic/robotic surgical experience. There are primarily three types of training programs (curricula):[32]
Table 1.
Various training curricula for acquiring minimally invasive surgical skills
Fellowships.
Mini-fellowships.
Mentored skills courses.
Depending on the time a surgeon can devote for training and the desired level of learning intended, one of the aforementioned courses might be more suitable. A fellowship is the most comprehensive course which includes one-to-one mentoring, precepting, and teaching in both simulated and clinical environments. The training duration usually ranges between 1 to 2 years. However, a fellowship might not be suitable for most post-graduate surgeons due to time constraints. A mini-fellowship or a mentored skills course maybe more ideal in this situation. A mini-fellowship (developed at the University of California Irvine, USA) is a 5 day teaching and mentor-mentee course during which the mentee's attends didactic sessions, live OR-cases, and hands-on lab sessions.[33,34] Whereas, the mentored skills course combines online learning with a 2-day mentored course.[32,35] Both of these programs have been demonstrated to have excellent content and construct validity; however, the performance predictive validity has not been evaluated.[17,28] Further, despite the short duration of the latter two courses, approximately 70-80% of the trainees successfully transition to robotic surgery, and are regularly practicing it at 3 years post-training.[18,32] Lastly, somewhat related to this topic is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandated basic robot-handling training required for all surgeons performing robot-assisted procedures. The FDA training necessitates the knowhow on how to safely and rapidly remove the device in an emergency, what to do if the system stops responding, and how to respond if the system makes movements that are potentially unsafe to the patient. This training is offered by the Institutive Surgical Inc.[36]
The guidelines on credentialing for robotic competency are more opaque at this time and vary from institution to institution.[18] Currently, most commonly, the surgeon-learner is subjectively assessed by the mentor (proctoring), which might be an acceptable way of evaluation over the long-term mentor-mentee relationship during a fellowship, however, may not represent a valid method of assessment during the short-term courses. Accordingly, there are certain tools such as the global evaluative assessment of robotic skills (GEARS)[37] which permit objective assessment and can be used to grade performance during simulation exercises. However, there is a lack of consensus on what the cutoffs for competency, proficiency and mastery should be (the different phases of a learning curve; Figure 1B). We believe that these cutoffs need to be devised based on consensus-performance of experienced surgeons according to the GEARS tool at a multi-institutional level.
Further, more recently, in the study of RKT with regional hypothermia, referred to previously[23] — the authors described a novel method of assessing competence by evaluating learning curves prospectively, objectively at an individual level utilizing cutoffs based on outcomes from previous kidney transplant series. By setting a target value (for technical [operative/anastomoses times] and functional [graft function] outcomes) prospectively and utilizing the mathematical cumulative summation (CUSUM) method, allowed the authors to evaluate the learning curve for each surgeon-learner continuously, objectively, and prospectively. This in turn permitted competency declaration at an individual level instead of utilizing an arbitrary cutoff of a standard number of cases for each surgeon-learner irrespective of their learning capabilities and training background. This methodology, theoretically speaking, combined with GEARS-cutoffs derived from experienced surgeons (as proposed earlier) can be used to monitor learning curves of surgeon-learners adopting robotic surgery continuously and prospectively during simulation training, and might allow recommendations regarding their learning status to be made in a more objective and individualized manner.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, both novice and experienced open surgeons require supervision and mentoring during the initial phases of robotic surgery skill acquisition. The experienced open surgeons possess domain knowledge, however, need to acquire technical knowledge under supervision (either in simulated or clinical environment) to successfully transition to robotic surgery, whereas, novice surgeons need to acquire both domain as well as technical knowledge to become competent in robotic surgery. A variety of training programs such as academic fellowships, mini-fellowships and mentored skill courses exist, and cater to the needs and expectations of postgraduate surgeons thoroughly and adequately. With regards to credentialing uniformity in criteria regarding accreditation is lacking but earnest efforts are underway. Currently, accreditation for competence in robotic surgery is institutional specific.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Polychronidis A, Laftsidis P, Bounovas A, Simopoulos C. Twenty years of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Philippe Mouret--March 17, 1987. JSLS. 2008;12:109–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sood A, Jeong W, Peabody JO, Hemal AK, Menon M. Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Inching Toward Gold Standard. Urol Clin North Am. 2014;41:473–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2014.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lanfranco AR, Castellanos AE, Desai JP, Meyers WC. Robotic surgery: A current perspective. Ann Surg. 2004;239:14–21. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000103020.19595.7d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hayn MH, Hussain A, Mansour AM, Andrews PE, Carpentier P, Castle E, et al. The learning curve of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Eur Urol. 2010;58:197–202. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.04.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sukumar S, Rogers CG. Robotic partial nephrectomy: Surgical technique. BJU Int. 2011;108(6 Pt 2):942–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Abaza R. Initial series of robotic radical nephrectomy with vena caval tumor thrombectomy. Eur Urol. 2011;59:652–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ghani KR, Rogers CG, Sood A, Kumar R, Ehlert M, Jeong W, et al. Robot-assisted anatrophic nephrolithotomy with renal hypothermia for managing staghorn calculi. J Endourol. 2013;27:1393–8. doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mufarrij PW, Shah OD, Berger AD, Stifelman MD. Robotic reconstruction of the upper urinary tract. J Urol. 2007;178:2002–5. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sammon JD, Zhu G, Sood A, Sukumar S, Kim SP, Sun M, et al. Pediatric nephrectomy: Incidence, indications and use of minimally invasive techniques. J Urol. 2014;191:764–70. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.09.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sukumar S, Roghmann F, Sood A, Abdo A, Menon M, Sammon JD, et al. Correction of Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Children: National Trends and Comparative Effectiveness in Operative Outcomes. J Endourol. 2014;28:592–8. doi: 10.1089/end.2013.0618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peters CA. Robotically assisted surgery in pediatric urology. Urol Clin North Am. 2004;31:743–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2004.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li H, Sammon J, Roghmann F, Sood A, Ehlert M, Sun M, et al. Utilization and perioperative outcomes of robotic vaginal vault suspension compared to abdominal or vaginal approaches for pelvic organ prolapse. Can Urol Assoc J. 2014;8:100–6. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abaza R, Ghani KR, Sood A, Ahlawat R, Kumar RK, Jeong W, et al. Robotic kidney transplantation with intraoperative regional hypothermia. BJU Int. 2014;113:679–81. doi: 10.1111/bju.12572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Menon M, Sood A, Bhandari M, Kher V, Ghosh P, Abaza R, et al. Robotic kidney transplantation with regional hypothermia: A Step-by-step Description of the Vattikuti Urology Institute-Medanta Technique (IDEAL Phase 2a) Eur Urol. 2014;65:991–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Giulianotti P, Gorodner V, Sbrana F, Tzvetanov I, Jeon H, Bianco F, et al. Robotic transabdominal kidney transplantation in a morbidly obese patient. Am J Transplant. 2010;10:1478–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.US Food and Drug Administration, Centers for Devices and Radiological Health; 2013. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 4]. Small Sample Survey-Final report. Topic: da Vinci Surgical System. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/ medicaldevices/productsandmedicalprocedures/surgeryandlifesupport/computerassistedroboticsurgicalsystems/ucm374095.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bahler CD, Sundaram CP. Training in Robotic Surgery: Simulators, Surgery, and Credentialing. Urol Clin North Am. 2014;41:581–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2014.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee JY, Mucksavage P, Sundaram CP, McDougall EM. Best practices for robotic surgery training and credentialing. J Urol. 2011;185:1191–7. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.McCulloch P, Cook JA, Altman DG, Heneghan C, Diener MK. IDEAL Group. IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 1: The idea and development stages. BMJ. 2013;346:f3012. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Menon M, Abaza R, Sood A, Ahlawat R, Ghani KR, Jeong W, et al. Robotic Kidney Transplantation with Regional Hypothermia: Evolution of a Novel Procedure Utilizing the IDEAL Guidelines (IDEAL Phase 0 and 1) Eur Urol. 2014;65:1001–9. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hopper AN, Jamison MH, Lewis WG. Learning curves in surgical practice. Postgrad Med J. 2007;83:777–9. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.2007.057190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Abboudi H, Khan MS, Guru KA, Froghi S, de Win G, Van Poppel H, et al. Learning curves for urological procedures: A systematic review. BJU Int. 2013 doi: 10.1111/bju.12315. [In Press] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sood A, Ghani KR, Ahlawat R, Modi P, Abaza R, Jeong W, et al. Application of the Statistical Process Control Method for Prospective Patient Safety Monitoring During the Learning Phase: Robotic Kidney Transplantation with Regional Hypothermia (IDEAL Phase 2a-b) Eur Urol. 2014;66:371–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.02.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yule S, Rowley D, Flin R, Maran N, Youngson G, Duncan J, et al. Experience matters: Comparing novice and expert ratings of non-technical skills using the NOTSS system. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79:154–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2008.04833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thiel DD, Lannen A, Richie E, Dove J, Gajarawala NM, Igel TC. Simulation-based training for bedside assistants can benefit experienced robotic prostatectomy teams. J Endourol. 2013;27:230–7. doi: 10.1089/end.2012.0382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Eddy DM. Clinical decision making: From theory to practice. Anatomy of a decision. JAMA. 1990;263:441–3. doi: 10.1001/jama.263.3.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lendvay TS, Brand TC, White L, Kowalewski T, Jonnadula S, Mercer LD, et al. Virtual reality robotic surgery warm-up improves task performance in a dry laboratory environment: A prospective randomized controlled study. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216:1181–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shepherd W, Arora KS, Abboudi H, Shamim Khan M, Dasgupta P, Ahmed K. A review of the available urology skills training curricula and their validation. J Surg Educ. 2014;71:289–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2013.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Skinner BF. Are theories of learning necessary? Psychol Rev. 1950;57:193–216. doi: 10.1037/h0054367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Forster JA, Browning AJ, Paul AB, Biyani CS. Surgical simulators in urological training--views of UK Training Programme Directors. BJU Int. 2012;110:776–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Le CQ, Lightner DJ, VanderLei L, Segura JW, Gettman MT. The current role of medical simulation in american urological residency training programs: An assessment by program directors. J Urol. 2007;177:288–91. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.08.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hay D, Khan MS, Van Poppel H, Van Cleynenbreugel B, Peabody J, Guru K, et al. Current Status and Effectiveness of Mentorship Programmes in Urology — A Systematic Review. BJU Int. doi: 10.1111/bju.12713. [In Press] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McDougall EM, Corica FA, Chou DS, Abdelshehid CS, Uribe CA, Stoliar G, et al. Short-term impact of a robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy ‘mini-residency’ experience on postgraduate urologists’ practice patterns. Int J Med Robot. 2006;2:70–4. doi: 10.1002/rcs.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gamboa AJ, Santos RT, Sargent ER, Louie MK, Box GN, Sohn KH, et al. Long-term impact of a robot assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy mini fellowship training program on postgraduate urological practice patterns. J Urol. 2009;181:778–82. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Patel SR, Hedican SP, Bishoff JT, Shichman SJ, Link RE, Wolf JS, Jr, et al. Skill based mentored laparoscopy course participation leads to laparoscopic practice expansion and assists in transition to robotic surgery. J Urol. 2011;186:1997–2000. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Herron DM, Marohn M SAGES-MIRA Robotic Surgery Consensus Group. A consensus document on robotic surgery. Surg Endos. 2008;22:313–25. doi: 10.1007/s00464-007-9727-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Goh AC, Goldfarb DW, Sander JC, Miles BJ, Dunkin BJ. Global evaluative assessment of robotic skills: Validation of a clinical assessment tool to measure robotic surgical skills. J Urol. 2012;187:247–52. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


