Abstract
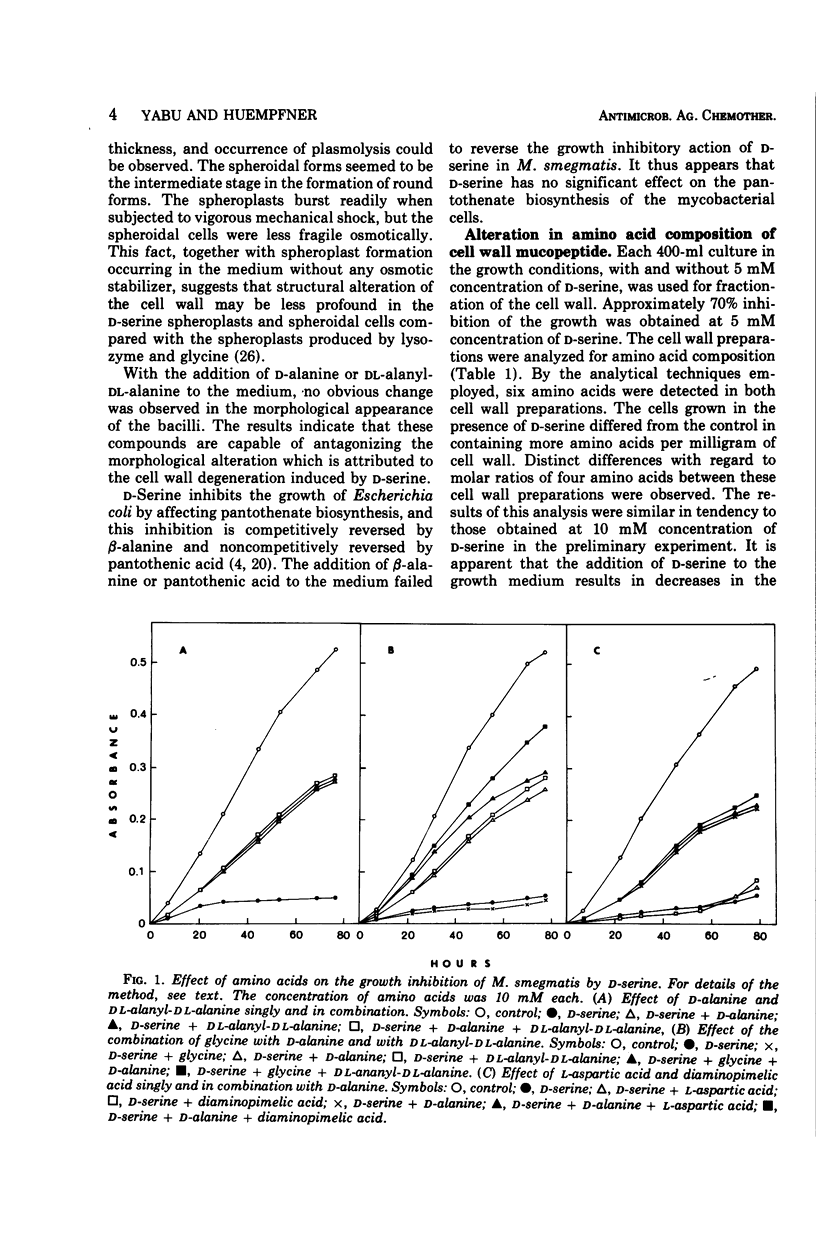
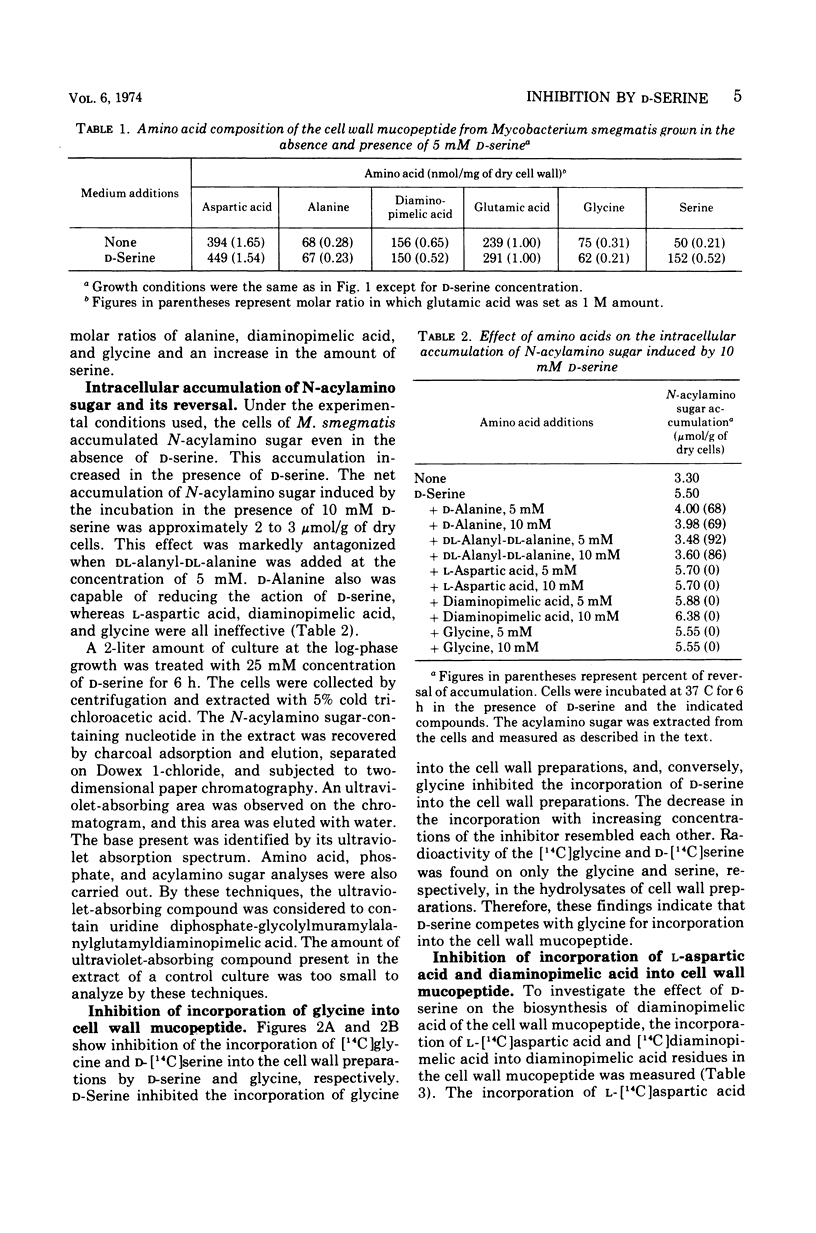
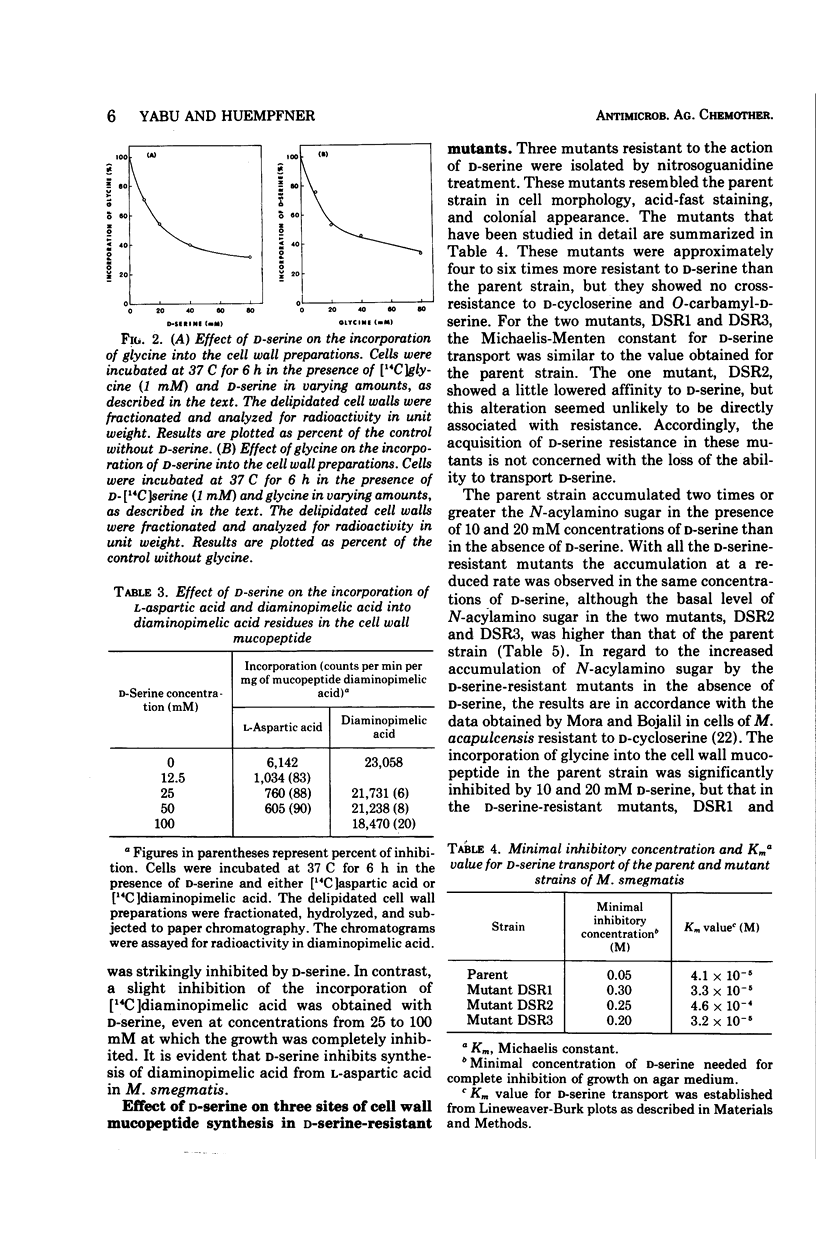
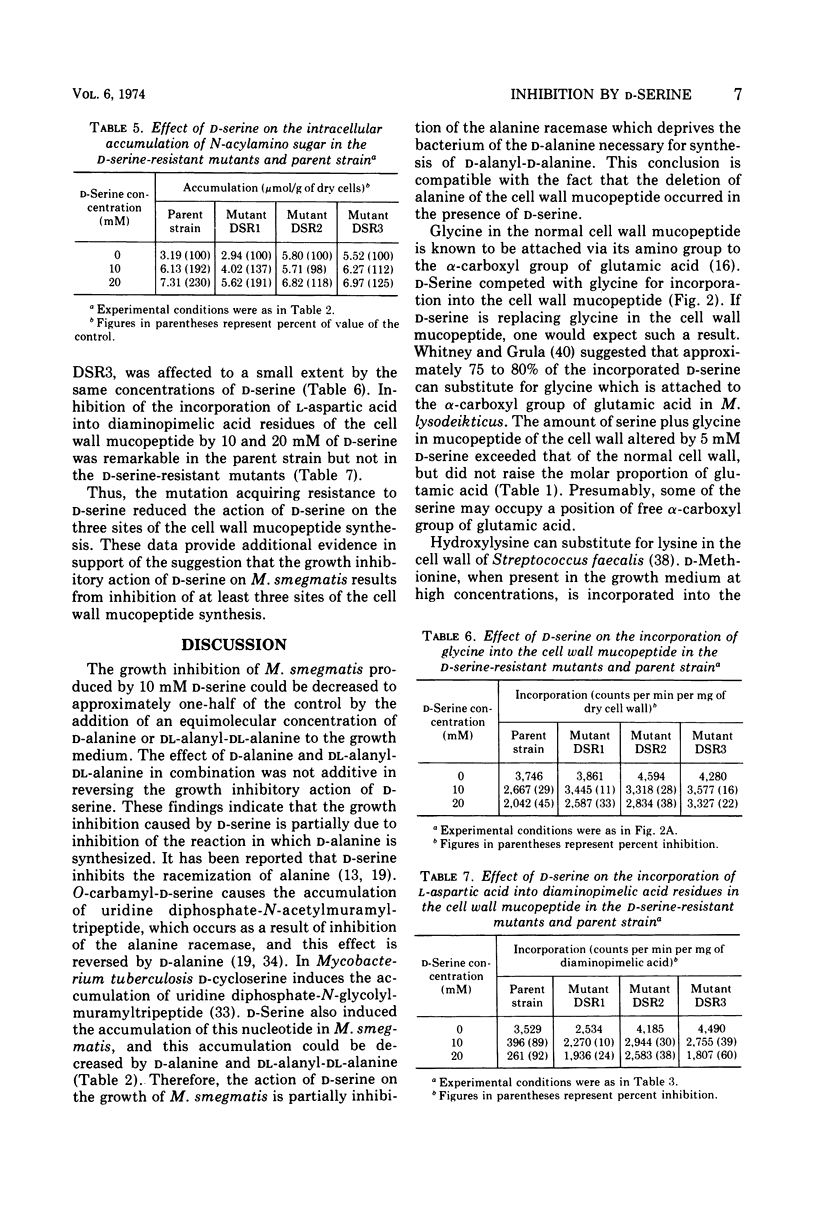
d-Serine inhibited the growth of Mycobacterium smegmatis and induced the morphological alteration of the bacilli. The growth inhibitory action of d-serine was partially reduced by an equimolecular concentration of d-alanine. The combination of glycine with d-alanine reversed the growth inhibition produced by d-serine more than did d-alanine alone. In cells cultured in the presence of d-serine, the amounts of alanine, diaminopimelic acid, and glycine inserted into the cell wall mucopeptide were reduced, and serine was increased. The intracellular accumulation of a precursor of cell wall mucopeptide was increased by d-serine, and this accumulation was reduced by d-alanine. d-Serine competed with glycine for incorporation into the cell wall mucopeptide. The incorporation of l-aspartic acid into diaminopimelic acid residues in the cell wall mucopeptide was markedly inhibited by d-serine. Three mutants resistant to d-serine were isolated by nitrosoguanidine treatment. In these mutants the effects of d-serine on the sites of cell wall mucopeptide synthesis were all reduced. Thus, d-serine inhibition of the growth is due to replacement of glycine residues of the cell wall mucopeptide with d-serine and inhibition of the cell wall synthesis by blocking the formation of d-alanine and diaminopimelic acid.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTIA M., HOARE D. S., WORK E. The stereoisomers of alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid. III. Properties and distribution of diaminopimelic acid racemase, an enzyme causing interconversion of the LL and meso isomers. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):448–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0650448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam A., Petit J. F., Wietzerbin-Falszpan J., Sinay P., Thomas D. W., Lederer E. L'acide N-glycolyl-muramique, constituant des parois de Mycobacterium smegmatis: Identification par spectrometrie de masse. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D. D-serine transport system in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):679–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.679-684.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., McFall E. Metabolism of D-serine in Escherichia coli K-12: mechanism of growth inhibition. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):685–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.685-694.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWIJS H., JOLLES P. CELL WALLS OF THREE STRAINS OF MYCOBACTERIA (MYCOBACTERIUM PHLEI, MYCOBACTERIUM FORTUITUM AND MYCOBACTERIUM KANSASII). PREPARATION, ANALYSIS AND DIGESTION BY LYSOZYMES OF DIFFERENT ORIGINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 1;83:326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILVARG C. The enzymatic synthesis of diaminopimelic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1501–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRULA E. A. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. I. Inhibition of division by D-amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80:375–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.375-385.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Bricas E., Lache M., Leyh-Bouille M. Structure of the cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. 3. Isolation of a new peptide dimer, N-alpha-[L-alanyl-gamma-(alpha-D-glutamylglycine)]-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-N-alpha-[L-alanyl-gamma-(alpha-D-glutamylglycine)]-L-lysyl-D-alanine. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1450–1460. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grula E. A., King R. D. Inhibition of cell division in Micrococcus lysodeikticus dis-II. Can J Microbiol. 1970 May;16(5):317–324. doi: 10.1139/m70-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grula E. A., Smith G. L., Grula M. M. Cell division in a species of Erwinia. X. Morphology of the nuclear body in filaments produced by growth in the presence of D-serine. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):293–298. doi: 10.1139/m68-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. M., Diven W. F. Studies on amino acid racemases. I. Partial purification and properties of the alanine racemase from Lactobacillus fermenti. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5414–5420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. STABILITY OF ALPHA-HYDROGEN OF AMINO ACIDS DURING ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:561–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Yanagida I., Kato K., Matsuda T. Studies on peptides, glycopeptides and antigenic polysaccharide-glycopeptide complexes isolated from an L-11 enzyme lysate of the cell walls of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv. Biken J. 1970 Dec;13(4):249–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARK C., BRADLEY D., LARK K. G. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE INCORPORATION OF D-METHIONINE INTO THE BACTERIAL CELL WALL; ITS INCORPORATION INTO THE R-LAYER AND THE STRUCTURAL CONSEQUENCES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 29;78:278–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91638-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARK C., LARK K. G. The effects of D-amino acids on Alcaligenes fecalis. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Aug;5:369–379. doi: 10.1139/m59-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. L., Neuhaus F. C. On the mechanism of action of the antibiotic O-carbamyld-serine in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):449–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.449-460.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K., DAVIS B. D. Pantothenate studies. I. Interference by D-serine and L-aspartic acid with pantothenate synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):733–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.733-745.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORA J., BOJALIL L. F. ANTAGONISM OF THE D-ALANINE REVERSAL OF D-CYCLOSERINE ACTION BY L-ALANINE IN MYCOBACTERIUM ACAPULCENSIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:49–52. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misaki A., Yukawa S., Tsuchiya K., Yamasaki T. Studies on cell walls of Mycobacteria. I. Chemical and biological properties of the cell walls and the mucopeptide of BCG. J Biochem. 1966 Apr;59(4):388–396. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani T., Araki Y., Ito E. Preparation and characterization of uridinediphosphate-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-meso-2,6-diaminopimelic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):210–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. F., Adam A., Wietzerbin-Falszpan J., Lederer E., Ghuysen J. M. Chemical structure of the cell wall of Mycobacterium smegmatis. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the peptidoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., MAAS W. K., SIMON E. J. An impaired concentrating mechanism for amino acids in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to L-canavanine and D-serine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:582–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90650-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D. Reversal of cycloserine inhibition by D-alanine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:693–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. L., HIGUCHI K. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. V. Inhibition of growth by D-serine and its reversal by various compounds. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:539–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.539-543.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., BIRGE C. H. NUCLEOTIDE ACCUMULATION INDUCED IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY GLYCINE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1124–1127. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1124-1127.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L. Microbial uridine-5'-pyrophosphate N-acetylamino sugar compounds. I. Biology of the penicillin-induced accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):509–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Diena B. B., Greenberg L. The production of spheroplasts by rapid-growing non-virulent mycobacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Oct;11(5):807–810. doi: 10.1139/m65-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA N. Mechanism of action of O-carbamyl-D-serine, a new member of cell wall synthesis inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 10;12:68–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEAS H. J. Mutants of Bacillus subtilis that require threonine or threonine plus methionine. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jan;59(1):93–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.1.93-104.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEERI A. E. Effect of D-amino acids on growth of lactobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):686–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.686-688.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUNG C. M., SMITH W. G., LEACH F. R., HENDERSON L. M. Hydroxylysine metabolism in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1194–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., David H. L., Wang L., Goldman D. S. Isolation and characterization of uridine diphosphate-N-glycolylmuramyl-L-alanyl-gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-alpha,alpha'-diaminopimelic acid from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90749-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Katz W., Strominger J. L., Ghuysen J. M. Substituents on the alpha-carboxyl group of D-glutamic acid in the peptidoglycan of several bacterial cell walls. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):921–929. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. G., Grula E. A. A major attachment site for D-serine in the cell wall mucopeptide of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 16;158(1):124–129. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. G., Grula E. A. Incorporation of D-serine into the cell wall mucopeptide of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:375–381. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabu K. Reversal of the growth inhibitory action of glycine and glycylglycine by alanylalanine in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 30;184(2):460–463. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


