Abstract
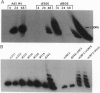
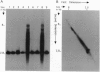
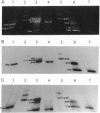
Two mutants containing large deletions in the E4 region of the adenovirus genome H5dl366 (91.9-98.3 map units) and H2dl808 (93.0-97.1 map units) were used to investigate the role of E4 genes in adenovirus DNA synthesis. Infection of KB human epidermoid carcinoma cells with either mutant resulted in production of large concatemers of viral DNA. Only monomer viral genome forms were produced, however, when mutants infected W162 cells, a monkey kidney cell line transformed with and expressing the E4 genes. Diffusible E4 gene products, therefore, complement the E4 mutant phenotype. The viral DNA concatemers produced in dl366- and dl808-infected KB cells did not have any specific orientation of monomer joining: the junctions consisted of head-to-head, head-to-tail, and tail-to-tail joints. The junctions were covalently linked molecules, but molecules were not precisely joined, and restriction enzyme maps revealed a heterogeneous size distribution of junction fragments. A series of mutants that disrupted single E4 open reading frames (ORFs) was also studied: none showed phenotypes similar to that of dl366 or dl808. Mutants containing defects in both ORF3 and ORF6, however, manifested the concatemer phenotype, indicating redundancy in genes preventing concatemer formation. These data suggest that the E4 ORFs 3 and 6 express functions critical for regulation of viral DNA replication and that concatemer intermediates may exist during adenovirus DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahern K. G., Wang K., Xu F. Y., Mathews C. Z., Pearson G. D. Strands hybridize in postreplicative adenovirus overlap recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J. A., Porter J. M., Challberg M. D. Template requirements for in vivo replication of adenovirus DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2115–2124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Desiderio S. V., Kelly T. J., Jr Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: characterization of a protein covalently linked to nascent DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5105–5109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E. Genome structure of incomplete particles of adenovirus. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):685–708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.685-708.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Cutt J. R., Shenk T. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes functions required for efficient DNA replication, late gene expression, and host cell shutoff. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.250-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Stow N. D., McDougall I. M. Replication of adenovirus mini-chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):493–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90181-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T. The origin of adenovirus DNA replication: minimal DNA sequence requirement in vivo. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):421–426. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemström C., Virtanen A., Bridge E., Ketner G., Pettersson U. Adenovirus E4-dependent activation of the early E2 promoter is insufficient to promote the early-to-late-phase transition. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1440–1449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1440-1449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes two gene products with redundant effects in lytic infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2605–2615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2605-2615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda J. E., Enomoto T., Hurwitz J. Replication of adenovirus DNA-protein complex with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):884–888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Wold M. S., Li J. Initiation of viral DNA replication. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:1–42. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Balogh L. A., Hurwitz J. Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. I. Mechanism of action of a host protein required for replication of adenovirus DNA templates devoid of the terminal protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9801–9808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner R. L., Kelly T. J., Jr The structure of replicating adenovirus 2 DNA molecules. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1007–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., Verrijzer C. P., van der Vliet P. C. Transcription factors NFI and NFIII/oct-1 function independently, employing different mechanisms to enhance adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5510–5518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5510-5518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: synthesis of full-length DNA with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4266–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. J., Younghusband H. B., Bellett A. J. A circula DNA-protein complex from adenoviruses. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):54–69. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: a protein linked to the 5' end of nascent DNA strands. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.139-147.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R., Borst P. Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei analyzed by electrophoretic separation of chromosome-sized DNA molecules. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiden M., Osheim Y. N., Beyer A. L., Van der Ploeg L. H. Chromosome structure: DNA nucleotide sequence elements of a subset of the minichromosomes of the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3823–3834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Ketner G. Adenoviral early region 4 is required for efficient viral DNA replication and for late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.833-838.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]