Abstract
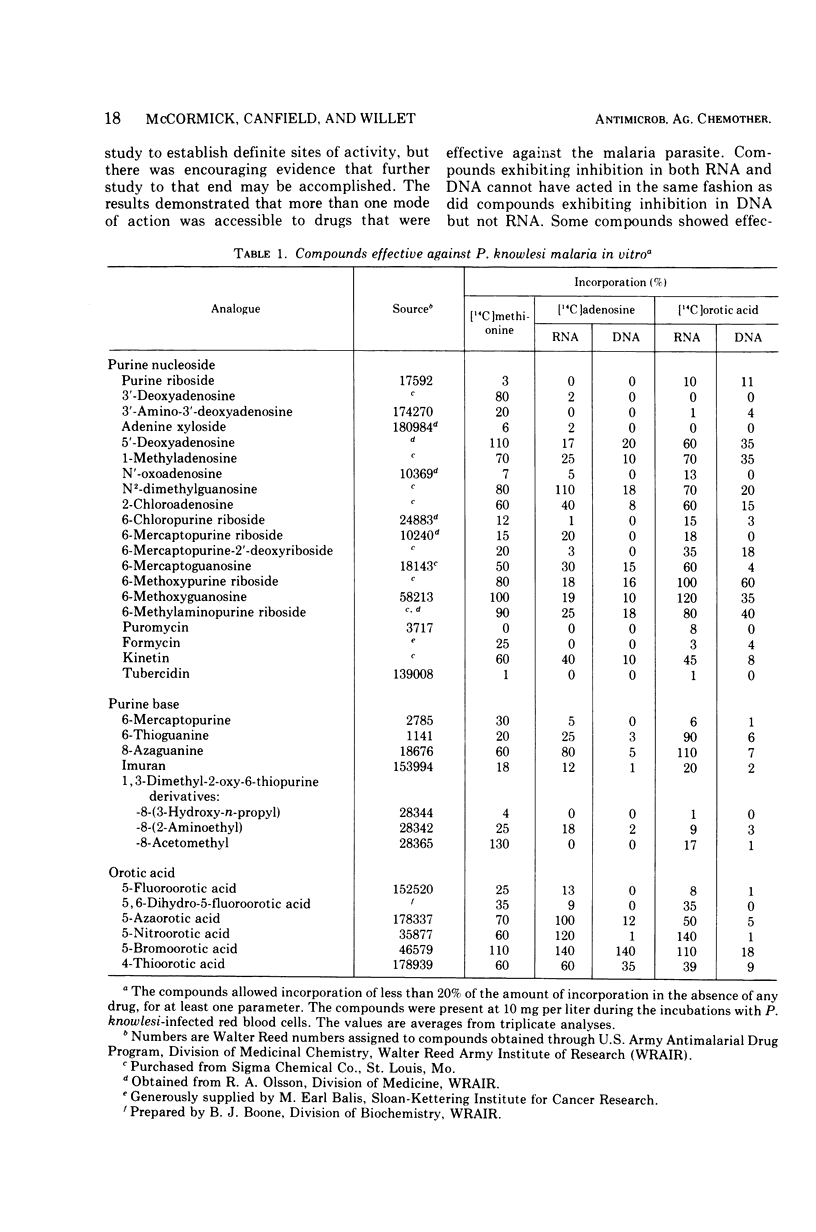
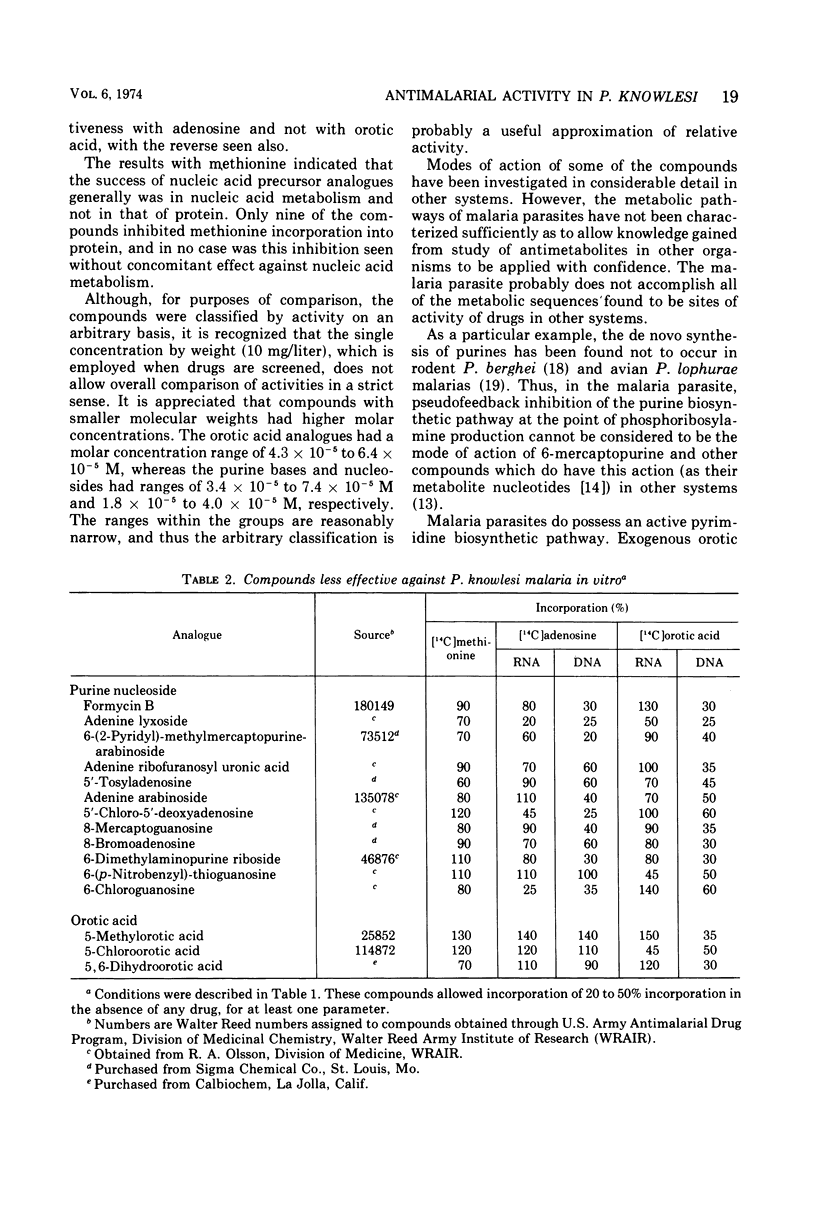
Analogues of nucleic acid precursors were screened for antimalarial activity in Plasmodium knowlesi by using an in vitro culture system. Activity was assessed by the degree of inhibition of incorporation of l-[methyl-14C]methionine into protein and of [8-14C]adenosine and [6-14C]orotic acid into ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid. The incorporation of adenosine or orotic acid was effectively inhibited by many of the compounds, including 3′ analogues of purine nucleosides, many of the 6-position analogues of purine bases and nucleosides, and 5-position analogues of orotic acid. Only a few compounds inhibited methionine incorporation into protein, and in each instance adenosine or orotic acid incorporation also was inhibited. Some compounds inhibited adenosine or orotic acid incorporation into both ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic, whereas other analogues inhibited incorporation into one nucleic acid only. The qualitative and quantitative differences suggest that this experimental system may be appropriate for investigation of metabolic pathways of the malaria parasite, as well as for demonstration of antimalarial activity of candidate antimalaria drugs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOSCH L., HARBERS E., HEIDELBERGER C. Studies on fluorinated pyrimidines. V. Effects on nucleic acid metabolism in vitro. Cancer Res. 1958 Apr;18(3):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield C. J., Altstatt L. B., Elliot V. B. An in vitro system for screening potential antimalarial drugs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Nov;19(6):905–909. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. T., Aikawa M., Rock R. C., Little W., Sprinz H. The isolation and fractionation of Plasmodium knowlesi. Mil Med. 1969 Sep;134(10):866–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. B., LePage G. A. Some inhibitory effects of 9-beta-D-xylofuranosyladenine, an adenosine analog, on nucleotide metabolism in ascites tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Nov;1(3):231–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Tokuyasu K., Ilan J. Phosphorylation of D-Arabinosyl adenine by Plasmodium berghei and its partial protection of mice against malaria. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1300–1301. doi: 10.1038/2281300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick G. J., Canfield C. J., Willet G. P. Plasmodium knowlesi: in vitro evaluation of antimalarial activity of folic acid inhibitors. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Aug;30(1):88–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVERGAARD-HANSEN K. THE INHIBITION OF 5-PHOSPHORIBOSYL-1-PYROPHOSPHATE FORMATION BY CORDYCEPIN TRIPHOSPHATE IN EXTRACTS OF EHRLICH ASCITES TUMOR CELLS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 23;80:504–507. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Barr C. F. DNA, RNA , and protein synthesis in erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium knowlesi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Sep;17(5):672–679. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior R. B., Kreier J. P. Plasmodium berghei freed from host erythrocytes by a continuous-flow ultrasonic system. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Oct;32(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt L. H. Chemotherapy of the drug-resistant malarias. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:427–454. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siev M., Weinberg R., Penman S. The selective interruption of nucleolar RNA synthesis in HeLa cells by cordycepin. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):510–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tay B. S., Lilley R. M., Murray A. W., Atkinson M. R. Inhibition of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase from Ehrlich ascites-tumour cells by thiopurine nucleotides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Apr;18(4):936–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trigg P. I., Gutteridge W. E., Williamson J. The effects of cordycepin on malaria parasites. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(4):514–520. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(71)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrsted G., Sartorelli A. C. Inhibition of the synthesis of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate by 3'-deoxy-adenosine and structurally related nucleoside analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke K., Tremblay G. C., Lantz C. H., Szustkiewicz C. The source of purines and pyrimidines in Plasmodium berghei. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Mar;19(2):202–208. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. J., Sherman I. W. Purine and pyrimidine synthesis by the avian malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae. J Protozool. 1968 Nov;15(4):763–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


