Abstract
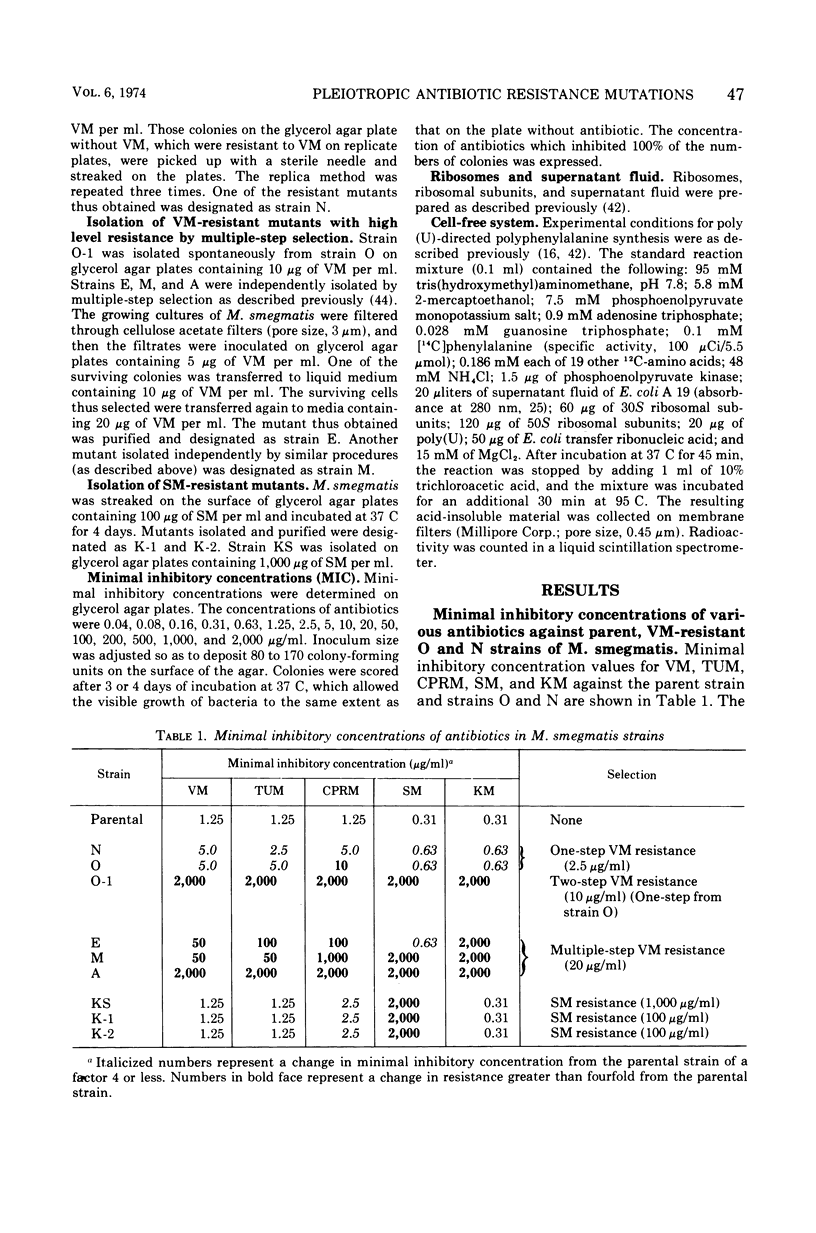
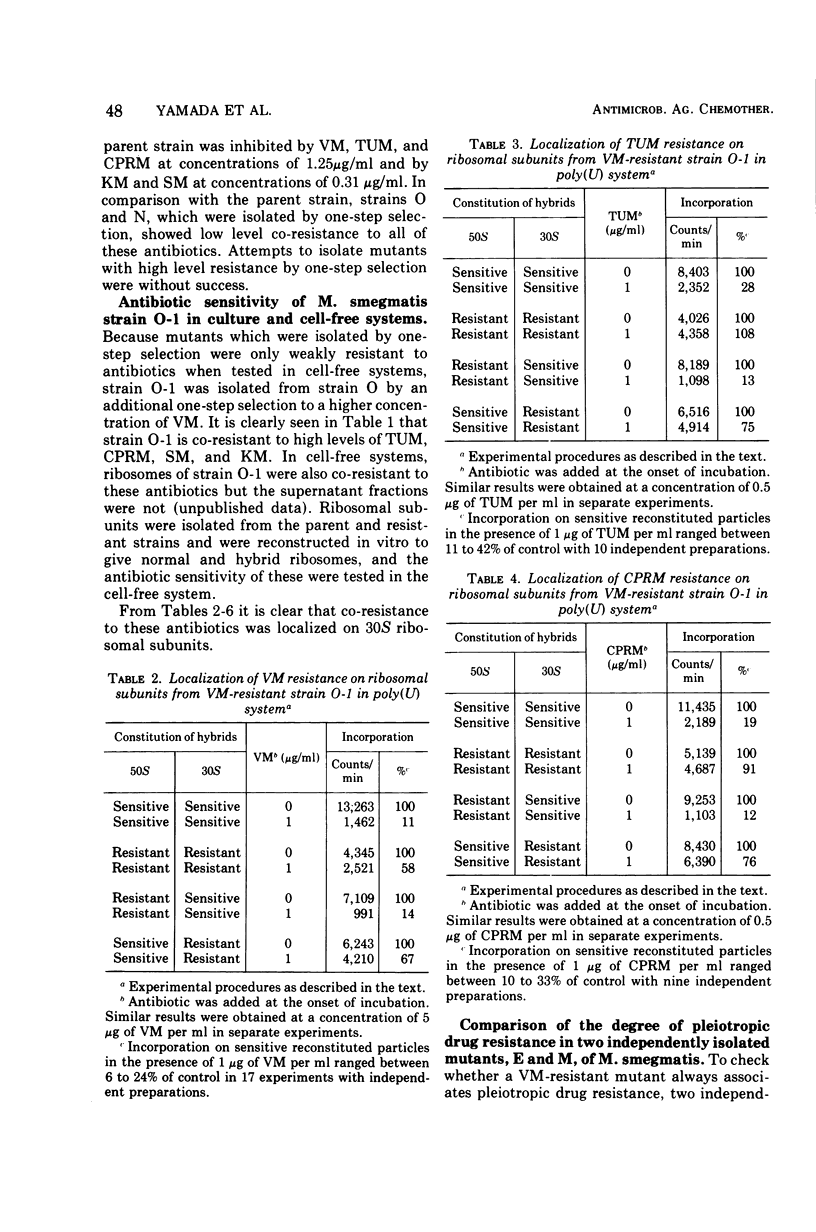
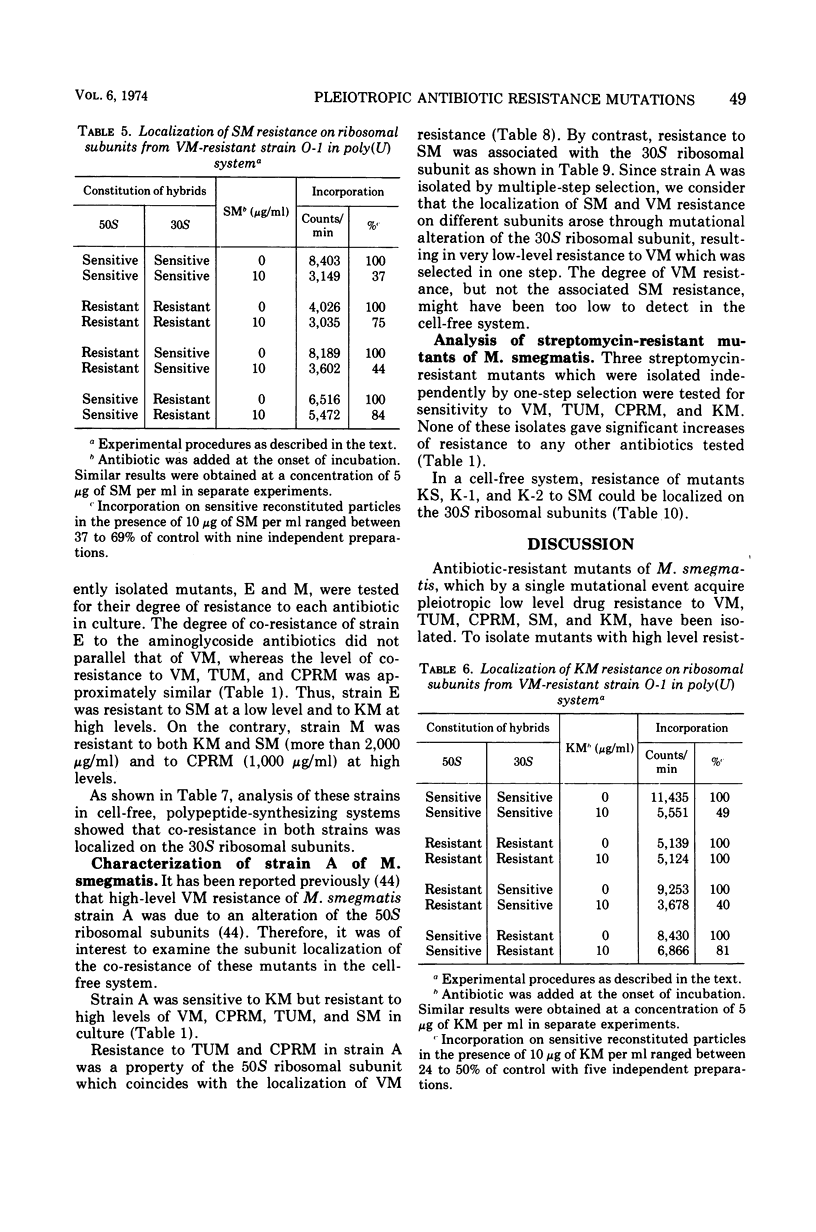
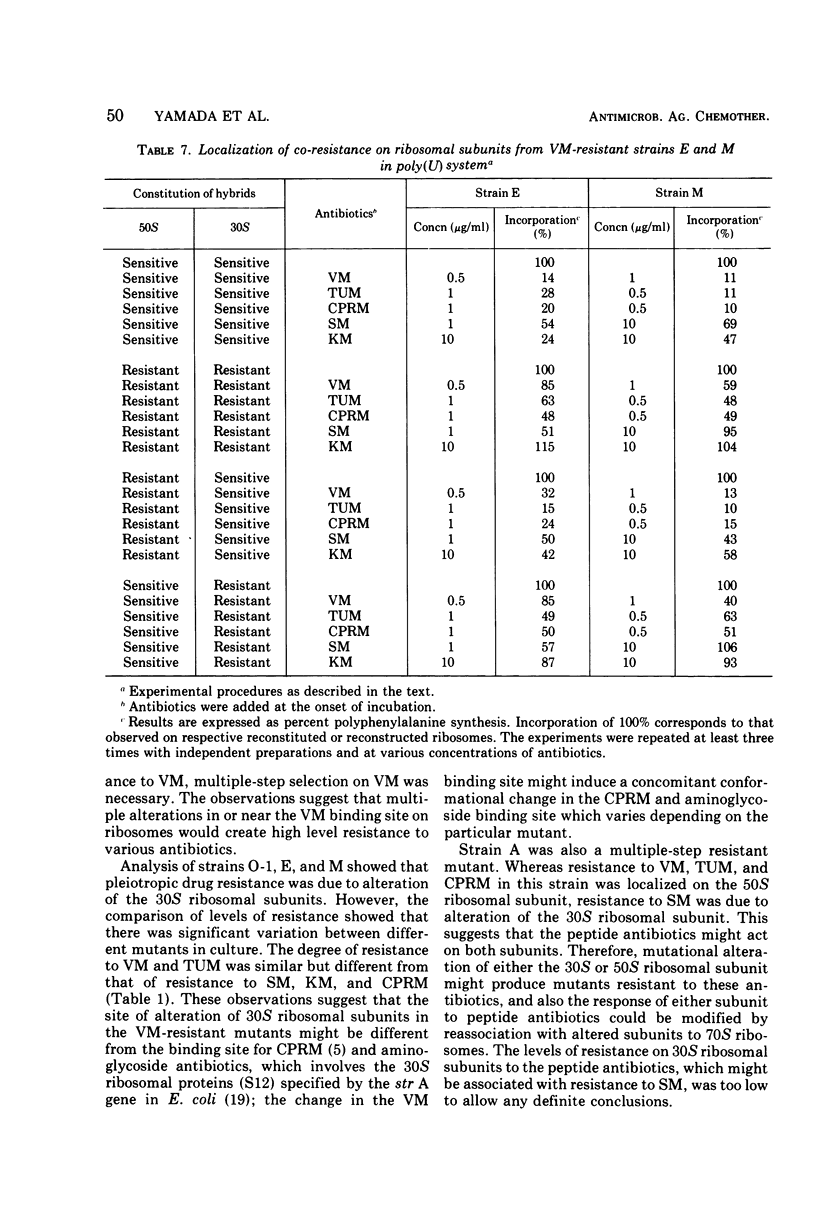
Viomycin-resistant strains isolated from Mycobacterium smegmatis demonstrated pleiotropic resistance to tuberactinomycin-N, capreomycin, streptomycin, and kanamycin as a result of mutational alteration of ribosomes, even though they were selected for resistance to a single antibiotic. The pleiotropic drug resistance of three mutants isolated by stepwise selection for resistance to viomycin was due to alteration of the 30S ribosomal subunit. One mutant, strain A, isolated independently by multiple-step selection to viomycin resistance, was resistant to viomycin, tuberactinomycin-N, and capreomycin through an alteration of the 50S ribosomal subunit, whereas it was sensitive to kanamycin but resistant to streptomycin through an alteration of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Three streptomycin-resistant strains, which were isolated by one-step selection at a high concentration of streptomycin, did not show significant co-resistance to any other antibiotics tested in culture and cell-free systems; streptomycin resistance in these mutants was localized on the 30S ribosomal subunit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Coresistance to neomycin and kanamycin by mutations in an Escherichia coli locus that affects ribosomes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):768–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.768-776.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Yamada T., Davies J. Enzymatic Adenylylation of Streptomycin and Spectinomycin by R-Factor-Resistant Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):109–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.109-119.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. L., Lewandowski L. J. A mutation suppressing streptomycin dependence. I. An effect on ribosome function. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bycroft B. W., Cameron D., Croft L. R., Hassanali-Walji A., Johnson A. W., Webb T. Total structure of capreomycin IB, a tuberculostatic peptide antibiotic. Nature. 1971 Jun 4;231(5301):301–302. doi: 10.1038/231301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLETSOS P. J., ORIOT E. ACTION DE LA CAPR'EOMYCINE SUR MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS EN MILIEUX DE CULTURE LIQUIDES, SEULE OU ASSOCI'EE 'A LA STREPTOMYCINE, A L'INH ET AU PAS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Aug;107:215–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Gorini L., Davis B. D. Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;1(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Smith I., Marmur J. Gene conservation in Bacillus species. II. The location of genes concerned with the synthesis of ribosomal components and soluble RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):724–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo K., Takahashi M., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. [Isolation of tubercle bacilli resistant to kanamycin or viomycine from tuberculous patients]. J Antibiot B. 1967 Aug;20(4):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite C., Smith I. Physiological characterization of antibiotic resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):190–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01788888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford N., Sueoka N. Chromosomal location of antibiotic resistance markers in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):267–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSEKI Y., OKAMOTO S. STUDIES ON CROSS-RESISTANCE BETWEEN CAPREOMYCIN AND CERTAIN OTHER ANTI-MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTS. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1963 Feb;16:31–38. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.16.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEDA T. [Studies on the resistance of tubercle bacilli to kanamycin. 3. In vitro experiments on the cross resistance of tubercle bacilli to kanamycin, fradiomycin and viomycin]. Kekkaku. 1960 Mar;35:159–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse W. C., Sproat E. F., Arrington C. W., Hawkins J. A. M. tuberculosis in vitro susceptibility and serum level experiences with capreomycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Apr 20;135(2):983–988. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb45539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata A., Mase M., Yamamoto M., Nakamura H. [Effects of streptomycin-resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on induction rate of resistance to kanamycin, viomycin and capreomycin and on cross-resistance among these drugs]. Kekkaku. 1969 Jun;44(6):173–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto S., Suzuki Y. Chloramphenicol-, dihydrostreptomycin-, and kanamycin-inactivating enzymes from multiple drug-resistant Escherichia coli carrying episome 'R'. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1301–1303. doi: 10.1038/2081301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinick N. L., Wilhelm J. M., Corcoran J. W. Nonidentity of the site of action of erythromycin A and chloramphenicol on Bacillus subtilis ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 29;155(1):290–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90358-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Benveniste R., Tipper D., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics: inactivation by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli carrying R factors. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1144–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1144-1146.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. M., Reeve E. C. Two mutations giving low-level streptomycin resistance in Escherichia coli K 12. Genet Res. 1970 Dec;16(3):359–365. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON K. E., DEMEREC M. THE LINKAGE MAP OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Genetics. 1965 Jun;51:897–913. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEENKEN W., Jr, MONTALBINE V., THURSTON J. R. The antituberculous activity of kanamycin in vitro and in the experimental animal (guinea pig). Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Jan;79(1):66–71. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Goldthwaite C., Dubnau D. The genetics of ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:85–89. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. B., Gordee R. S., Wick W. E., Stanfield L. In vitro and in vivo laboratory studies on the antituberculous activity of capreomycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Apr 20;135(2):947–959. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb45536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORII F., YAMAMOTO M., HAYASHI M., NODA Y., TSUKAMURA M. Studies on the kanamycin-resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. II. Kanamycin-sensitivity of various drug-resistant strains. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 May;12(3):103–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUKAMURA M., NODA Y., YAMAMOTO M. Studies on the kanamycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. V. Sensitivity of kanamycin-resistant mutants to various antituberculous drugs and mutation frequency to various drug resistance in kanamycin-resistant mutants. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Nov;12:323–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Tamaki M., Takata R., Osawa S. Low affinity for chloramphenicol of erythromycin resistant Escherichia coli ribosomes having an altered protein component. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 24;46(6):1979–1983. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90747-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Igusa S. Effects of viomycin and polymyxin B on protein synthesis in vitro. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):239–240. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H. Reversal of the inhibitory action of chloramphenicol on the ribosomal peptidyl transfer reaction by erythromycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):535–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teraoka H., Tanaka K., Tamaki M. The comparative study on the effects of chloramphenicol, erythromycin and lincomycin on polylysine synthesis in an Escherichia coli cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;174(2):776–778. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamura M., Toyama H., Mizuno S., Tsukamura S. [Cross-resistance relationship among capreomycin, kanamycin, viomycin and streptomycin resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis]. Kekkaku. 1967 Oct;42(10):399–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takasawa S., Okanishi M., Utahara R. Adenylylstreptomycin, a product of streptomycin inactivated by E. coli carrying R factor. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jan;21(1):81–82. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERBIST L., GYSELEN A. CAPREOMYCIN SUSCEPTIBILITY OF STRAINS RESISTANT TO STREPTOMYCIN AND/OR VIOMYCIN. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Oct;90:640–641. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.4.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Binding of chloramphenicol to ribosomes. The effect of a number of antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELCH H., WRIGHT W. W., WEINSTEIN H. I., STAFFA A. W. In vitro and pharmacological studies with kanamycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Sep 30;76(2):66–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb54693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE A. D., HAHN F. E. MODE OF ACTION OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. IX. EFFECTS OF CHLORAMPHENICOL UPON A RIBOSOMAL AMINO ACID POLYMERIZATION SYSTEM AND ITS BINDING TO BACTERIAL RIBOSOME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:146–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Davies J. A genetic and biochemical study of streptomycin- and spectinomycin-resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(3):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00337833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Kawaguchi K., Masuda K., Shoji K., Hori M. Inhibition of polyphenylalanine synthesis on ribosomes of mycobacteria by tuberactinomycin-N. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Nov;106(5):769–771. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.5.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Masuda K., Shoji K., Hori M. Analysis of ribosomes from viomycin-sensitive and -resistant strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.1-6.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Tipper D., Davies J. Enzymatic inactivation of streptomycin by R factor-resistant Escherichia coli. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):288–291. doi: 10.1038/219288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



