Abstract
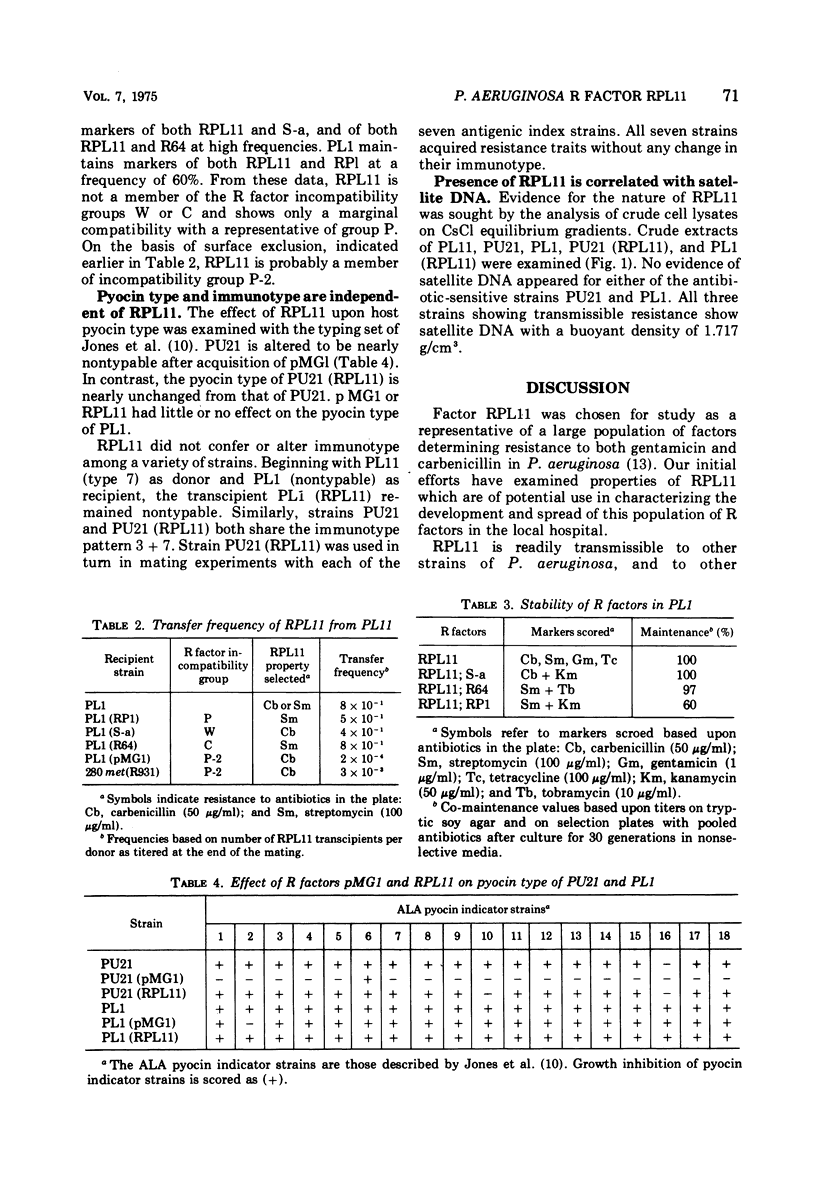
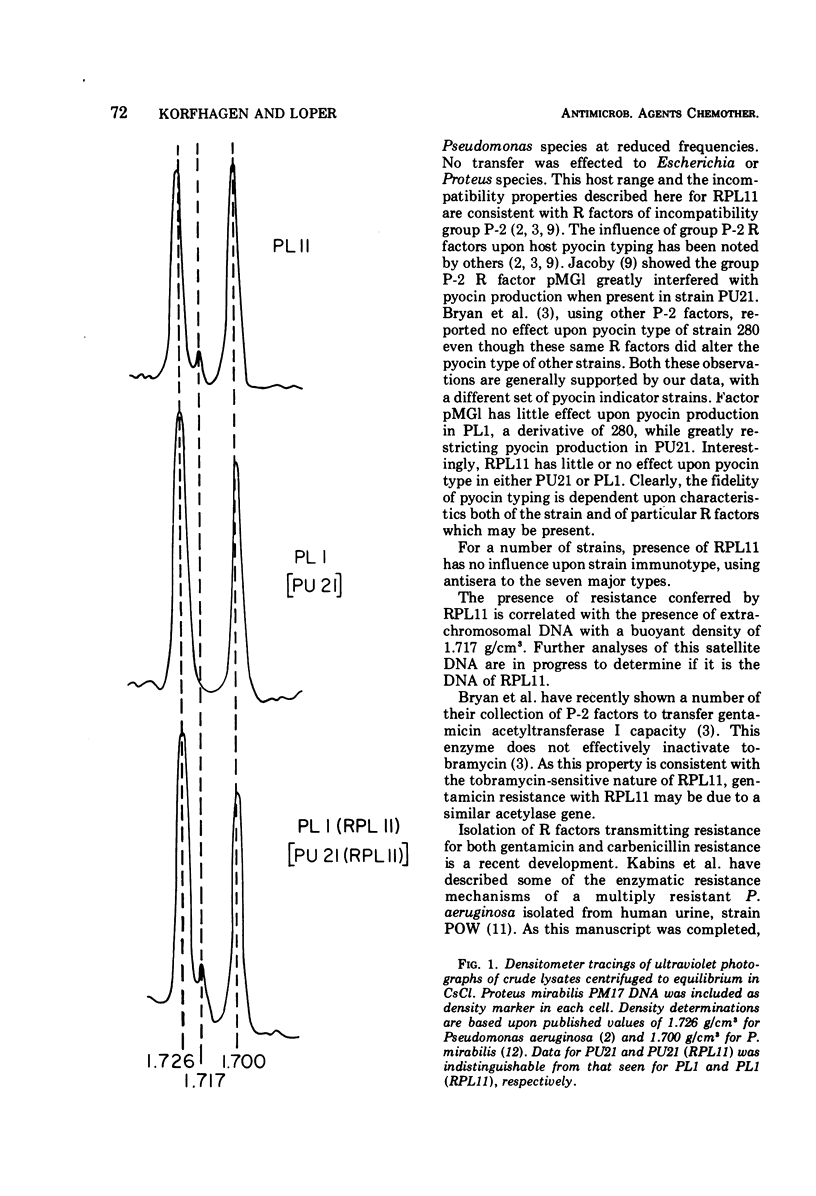
R factor RPL11 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa determines multiple drug resistance including resistance to gentamicin and carbenicillin. The host range and incompatibility properties of RPL11 are those of incompatibility group P-2. Strains harboring the factor are not altered with respect to the major immunotypes 1 through 7 of Parke-Davis, or with respect to pyocin type by using the 18 indicators of Jones and co-workers. Analytical ultracentrifugation of crude extracts of R factor-containing strains shows a band of satellite DNA with a buoyant density of 1.717 g/cm3.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Semaka S. D., Van den Elzen H. M., Kinnear J. E., Whitehouse R. L. Characteristics of R931 and other Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):625–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Shahrabadi M. S., van den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: R-factor-mediated resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):191–199. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M., Tseng J. T. Transferable drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):22–29. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Dissociation of a degradative plasmid aggregate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):815–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.815-820.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. B. Susceptibility of 1,500 isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin, carbenicillin, colistin, and polymyxin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullbrook P. D., Elson S. W., Slocombe B. R-factor mediated beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nature. 1970 Jun 13;226(5250):1054–1056. doi: 10.1038/2261054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A. Properties of R plasmids determining gentamicin resistance by acetylation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):239–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. F., Zakanycz J. P., Thomas E. T., Farmer J. J., 3rd Pyocin typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a simplified method. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):400–406. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.400-406.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabins S., Nathan C., Cohen S. Gentamicin-adenylyltransferase activity as a cause of gentamicin resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):565–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Rownd R. Replication of R-factors in Proteus mirabilis: replication under relaxed control. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):473–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Krcméry V., Sietzen W., Borst J. Transfer of gentamicin resistance from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains highly resistant to gentamicin and carbenicillin. Chemotherapy. 1973;18(4):229–234. doi: 10.1159/000221266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Intergeneric transfer of a beta-lactamase gene between Ps. aeruginosa and E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 6;226(5249):952–954. doi: 10.1038/226952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witchitz J. L., Chabbert Y. A. Résistance transférable à la gentamicine I. Expression du caractère de résistance. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Dec;121(6):733–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg A. J. Transferable resistance to carbenicillin and gentamicin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. S Afr Med J. 1974 Jun 12;48(28):1185–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



