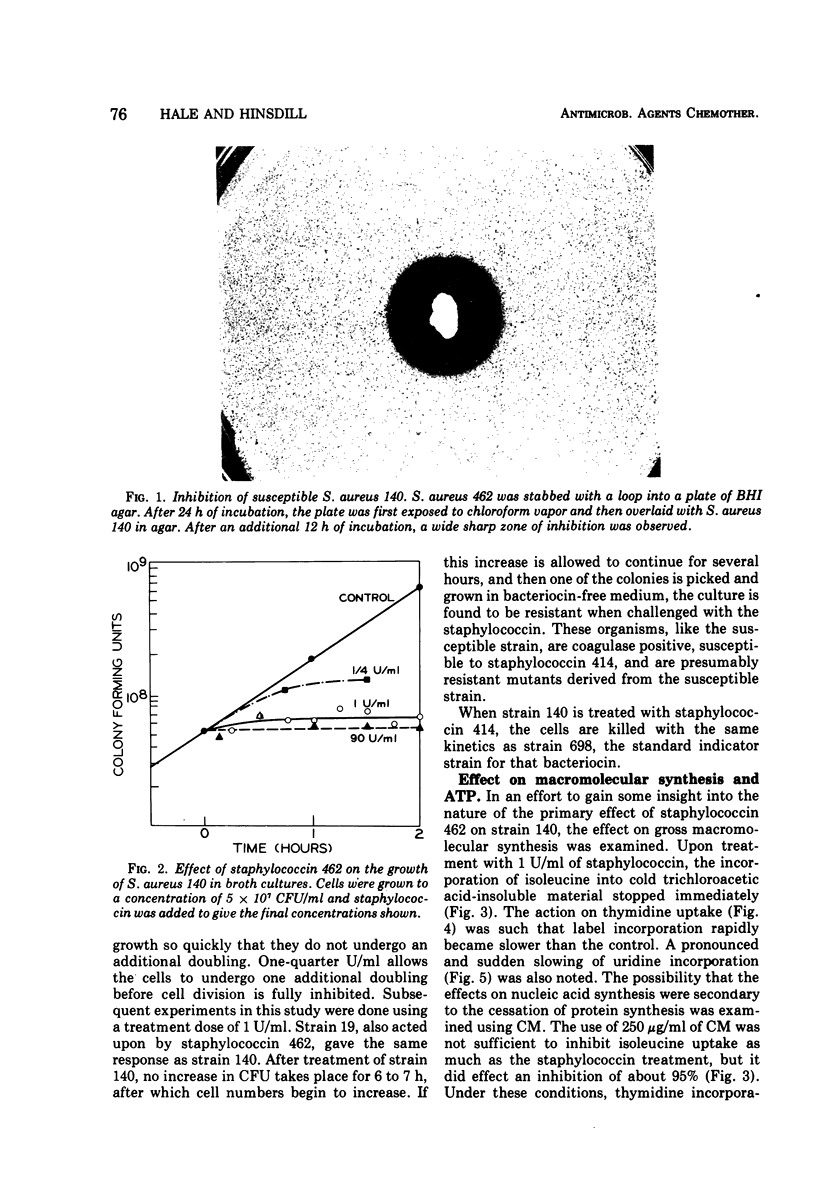
Abstract
Staphylococcin 462 is a proteinaceous inhibitor produced by Staphylococcus aureus strain 462. In broth cultures, susceptible S. aureus strain 140 and 19 respond to treatment with the bacteriocin by stopping growth and cell division. Examination of macromolecular synthesis by measuring the incorporation of radioactive precursors revealed that S. aureus 140 stops synthesizing protein immediately. After exposure to staphylococcin 462, the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid is quickly inhibited also, but not as completely. Treatment of S. aureus 140 with the inhibitor causes a rapid drop in cellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate level to about 60% of control levels. Of the 70 strains of gram-positive bacteria tested for susceptibility to staphylococcin 462, 24 (34%), distributed among 7 genera, were susceptible.
Full text
PDF

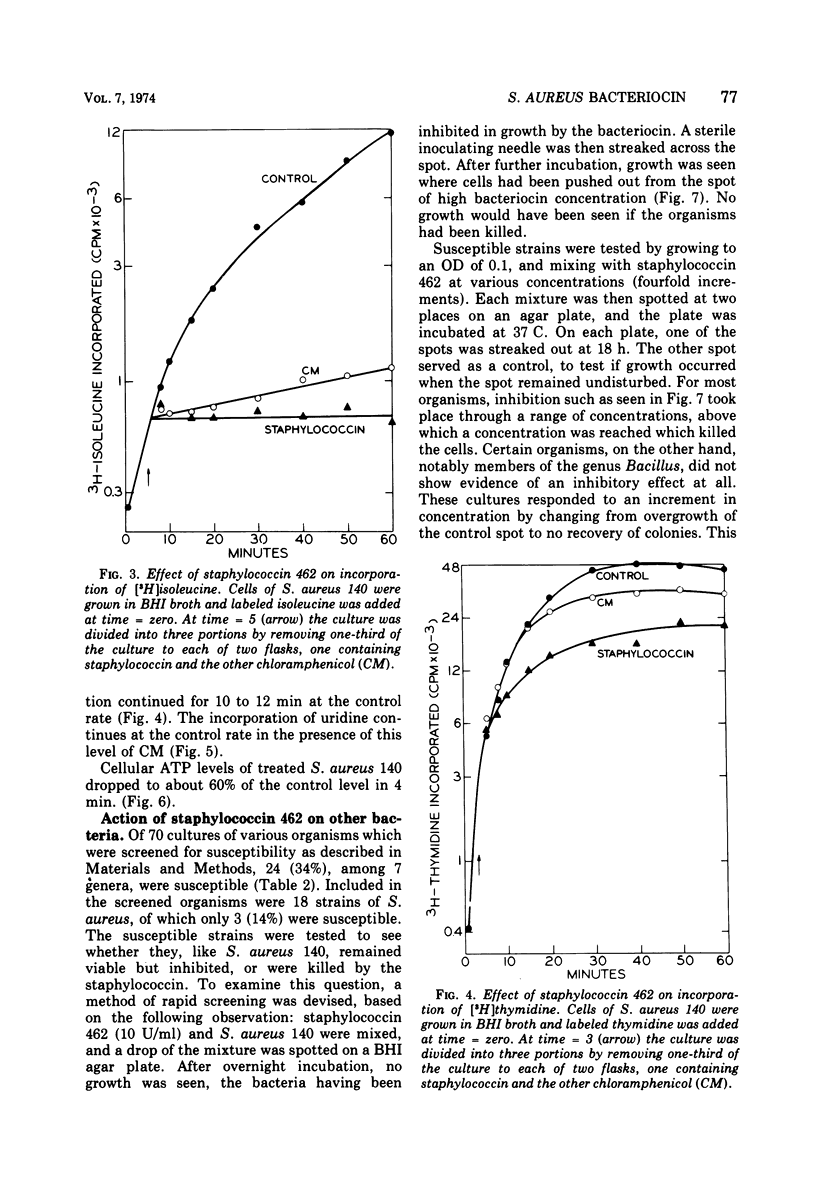
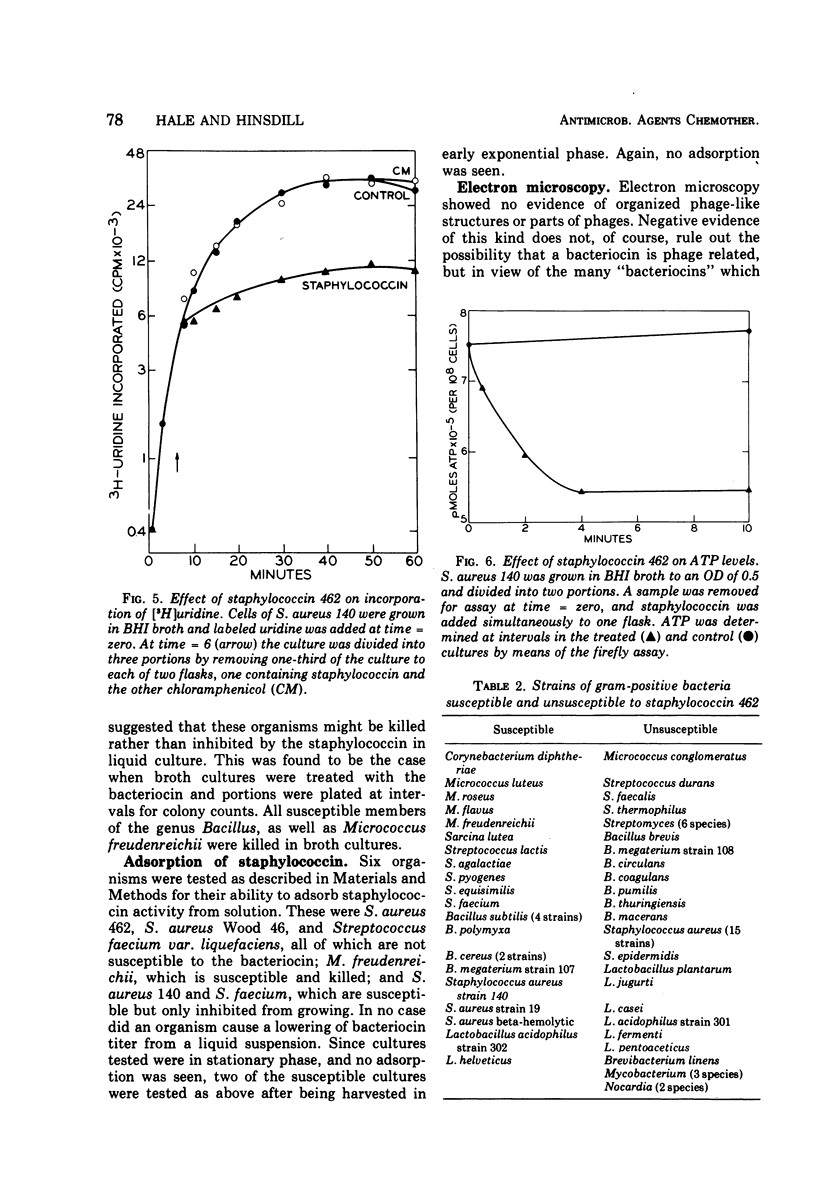


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asheshov E. H. Loss of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus resulting from growth at high temperature. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Mar;42(3):403–410. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson D. E. Biological feedback control at the molecular level. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):851–857. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Taube Z. Plasmid-mediated production of staphylococcin in bacteriophage type 71 Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):594–598. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Kinetic studies on the interaction of bacteriophage type 71 staphylococcal bacteriocin with susceptible bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):738–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.738-742.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on cellular metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):64–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.64-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliano V. J., Hinsdill R. D. Characterization of a Staphylococcus aureus bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):117–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.117-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMON Y., PERON Y. QUELQUES REMARQUES SUR LES BACT'ERIOCINES PRODUITES PAR LES MICROBES GRAM-POSITIFS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 29;257:1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale E. M., Hinsdill R. D. Characterization of a bacteriocin from Staphylococcus aureus strain 462. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):634–640. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH A., WOLLMAN E. Définition de quelques termes relatifs a la lysogénie. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Characterization and extrachromosomal control of bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jul;4(1):49–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Nature and properties of a Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteriocin. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.243-250.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. H., Richmond M. H. The increased rate of loss of penicillinase plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of rifampicin. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):137–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Colicins and related bacteriocins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:257–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVES P. THE BACTERIOCINS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:24–45. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.24-45.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstein S. A., Baldwin J. N. Nature of the elimination of the penicillinase plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus by surface-active agents. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):152–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.152-155.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]