Abstract
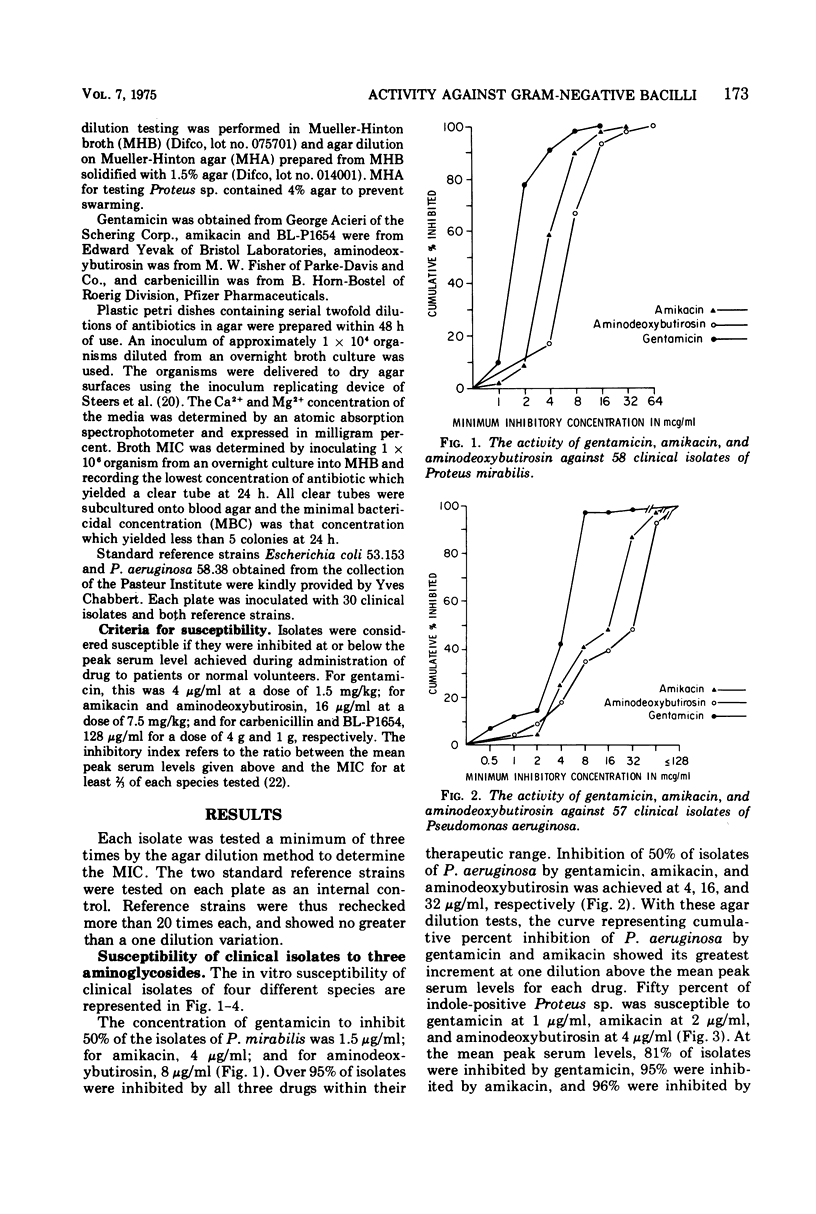
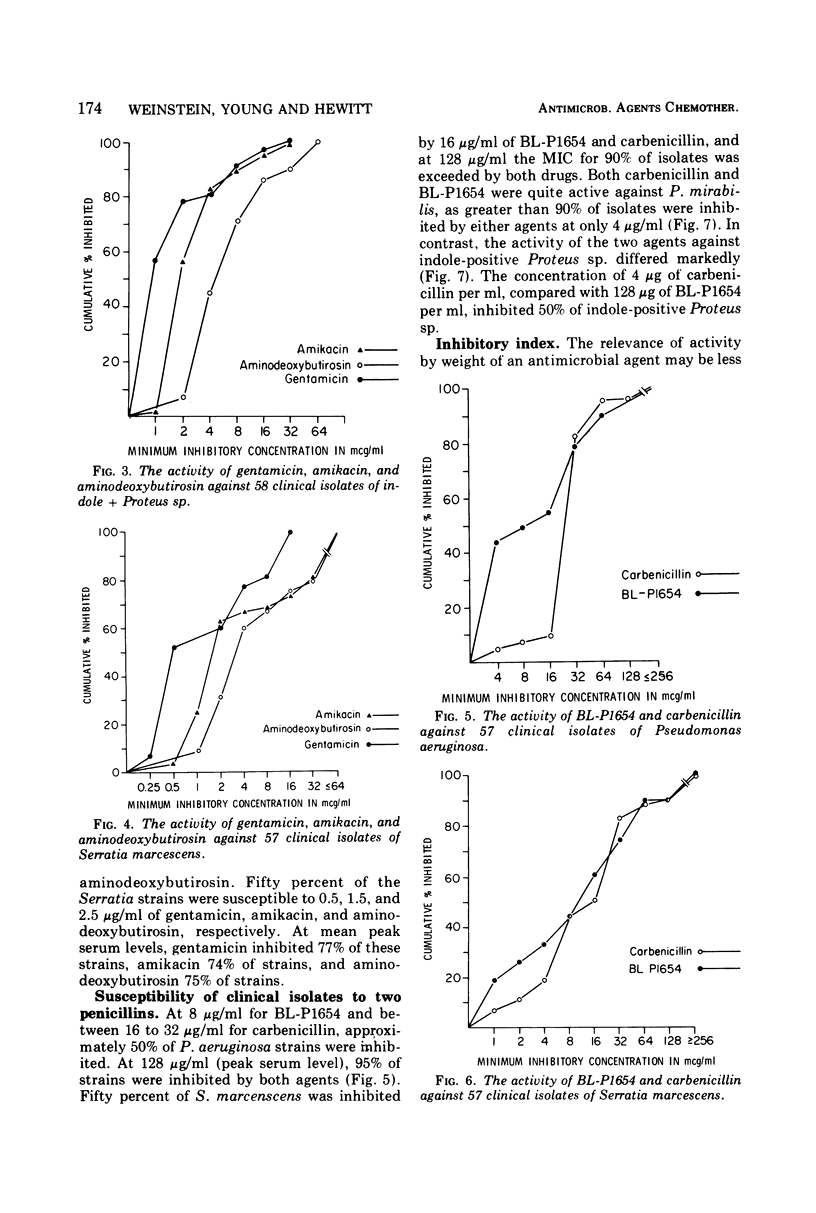
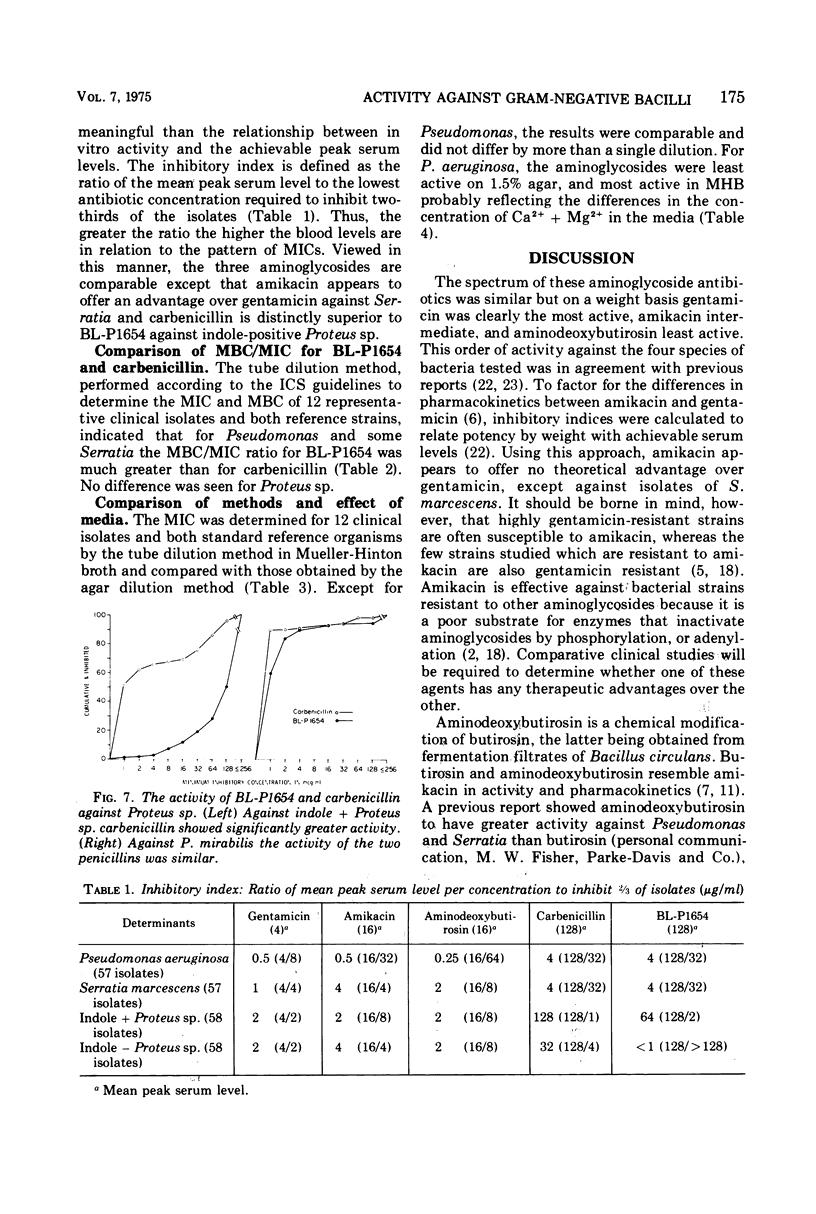
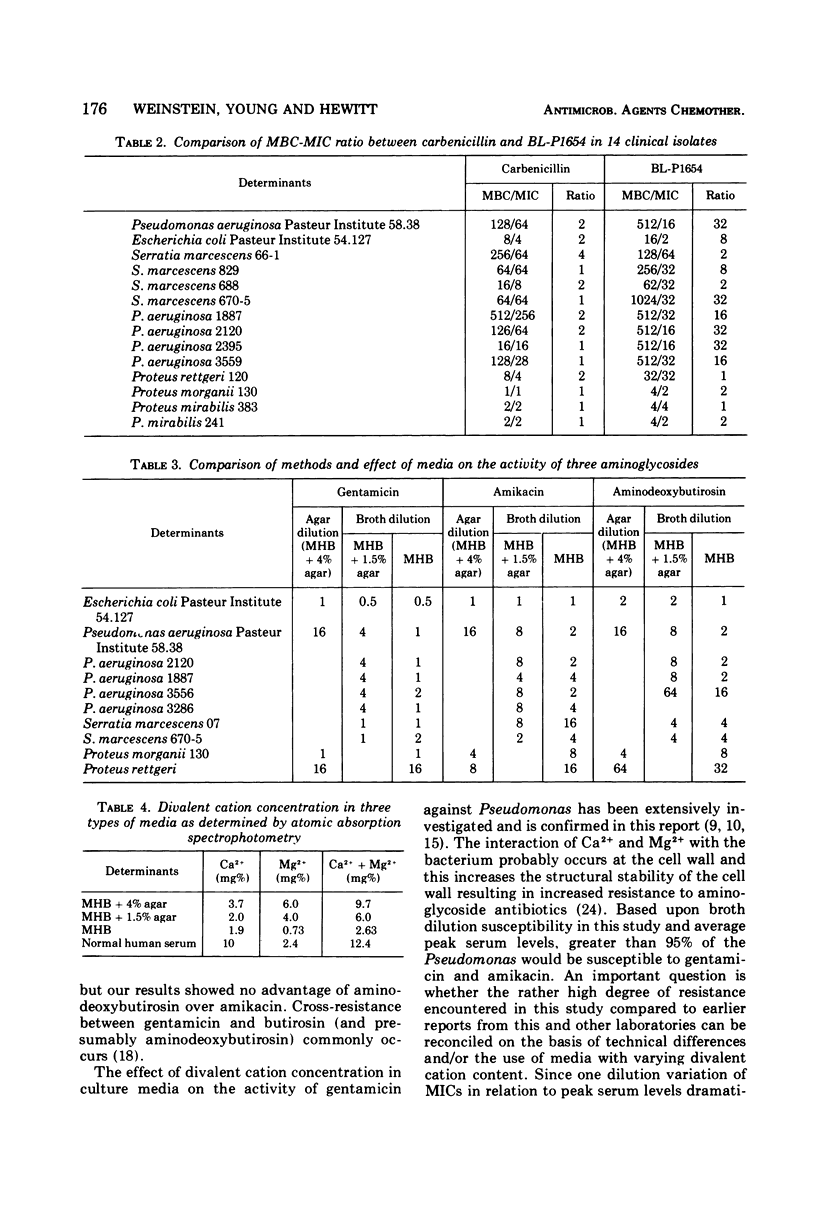
Three aminoglycoside antibiotics and two penicillins were compared for their in vitro activity against 60 isolates of Serratia, Pseudomonas, Proteus mirabilis, and indole-positive Proteus sp. Testing was done by the agar dilution method using Mueller-Hinton broth solidified with 1.5% agar. The activity of amikacin, aminodeoxybutirosin, and gentamicin against Proteus and Pseudomonas, as related to their peak blood levels, showed no significant differences. Amikacin was the most active against Serratia marcescens. Results using Mueller-Hinton media in broth dilution tests correlated with the agar dilution method except for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The minimal inhibitory concentration for aminoglycosides in agar was considerably greater than the minimal inhibitory concentration in Mueller-Hinton broth, and the disparity was related to the higher divalent cation concentration of agar. BL-P1654 and carbenicillin were similar except that carbenicillin was much more active against indole-positive Proteus sp. Additionally, the ratio of bactericidal to bacteriostatic concentrations of BL-P1654 was considerably greater than for carbenicillin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. L., Finland M. Susceptibility of recent isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin, polymyxin, and five penicillins, with observations on the pyocin and immunotypes of the strains. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):870–875. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.870-875.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotic-inactivating enzymes in actinomycetes similar to those present in clinical isolates of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2276–2280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of BB-K8, a new aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Aug;4(2):186–192. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of semisynthetic alpha-(substituted-ureido) penicillins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):710–717. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.710-717.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana B. E., Taggart J. G. Comparative pharmacokinetics of BB-K8 and kanamycin in dogs and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):478–483. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion H. W., Woo P. W., Willmer N. E., Kern D. L., Onaga J., Fusari S. A. Butirosin, a new aminoglycosidic antibiotic complex: isolation and characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Aug;2(2):84–88. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.2.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Effect of medium composition on the apparent sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Kutscher E., Ireland P., Barnett J. A., Sanford J. P. Effect of the concentrations of magnesium and calcium on the in-vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S37–S45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells J. D., Anderson L. E., Coffey G. L., Senos G. D., Underhill M. A., Vogler D. L., Ehrlich J. Butirosin, a new aminoglycosidic antibiotic complex: bacterial origin and some microbiological studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Aug;2(2):79–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.2.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowbury E. J., Lilly H. A., Kidson A., Ayliffe G. A., Jones R. J. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics: emergence of strains highly resistant to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Aug 30;2(7618):448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Eickhoff T. C. Carbenicillin: a clinical and laboratory evaluation. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Aug;73(2):179–187. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. M., Ikari N. S., Zimmerman J., Waitz J. A. A virulent nosocomial Klebsiella with a transferable R factor for gentamicin: emergence and suppression. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S24–S29. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F., Wacker W. E., Yulug N. F. Effect of salt concentration on the apparent in-vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli to gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S59–S64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Pursiano T. A., DeFuria M. D. Activity of BB-K8 (amikacin) against clinical isolates resistant to one or more aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):143–152. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pursiano T. A., Misiek M., Leitner F., Price K. E. Effect of assay medium on the antibacterial activity of certain penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snelling C. F., Ronald A. R., Cates C. Y., Forsythe W. C. Resistance of gram-negative bacilli to gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S264–S270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of five aminoglycoside antibiotics in vitro against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):617–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparative in vitro activity of three aminoglycosidic antibiotics: BB-K8, kanamycin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Aug;4(2):133–139. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics aganst Pseudomonas aeruginosa: specificity and site of calcium and magnesium antagonism. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):663–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



