Abstract
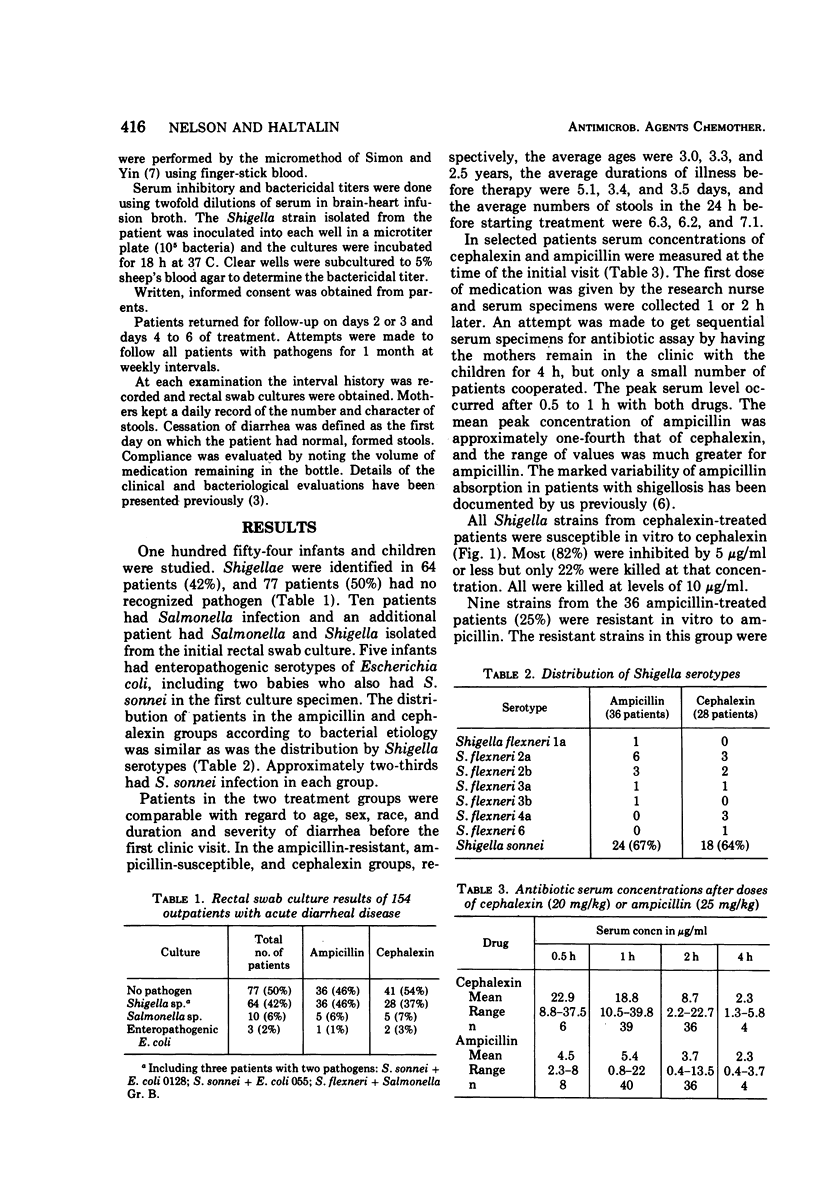
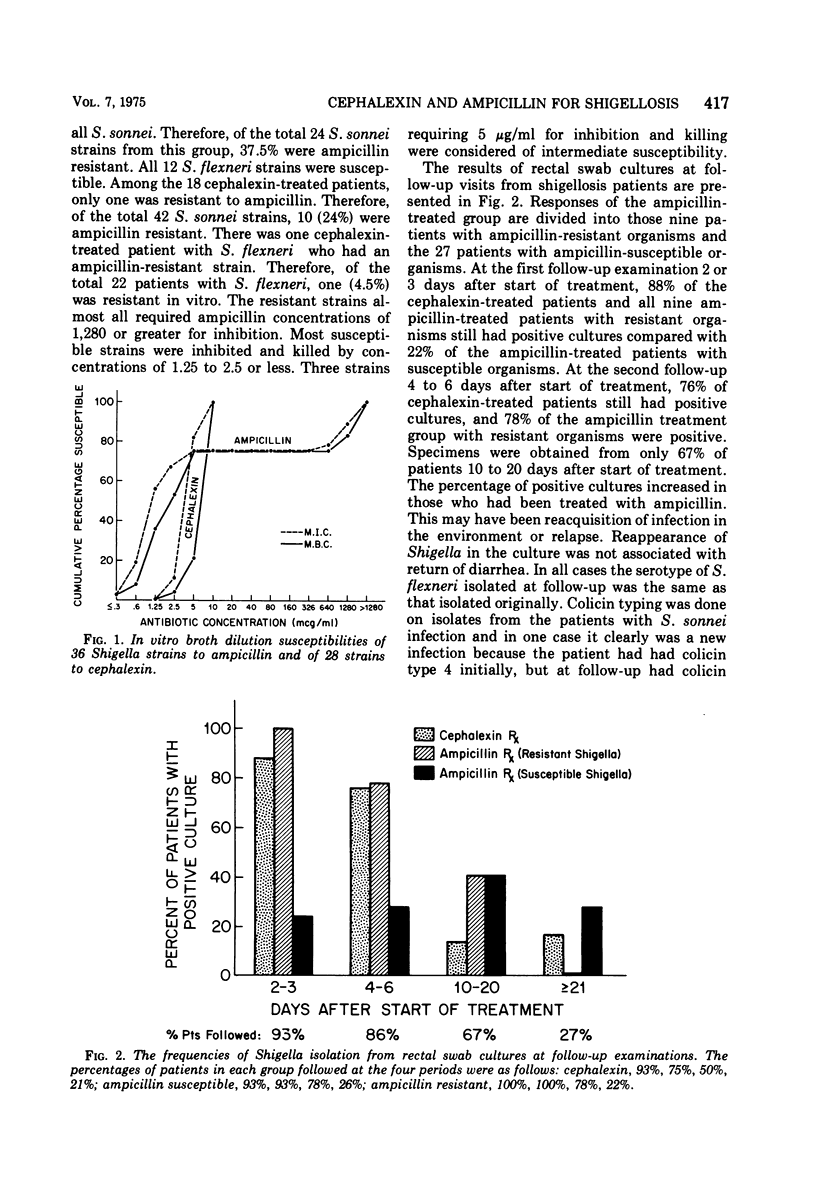
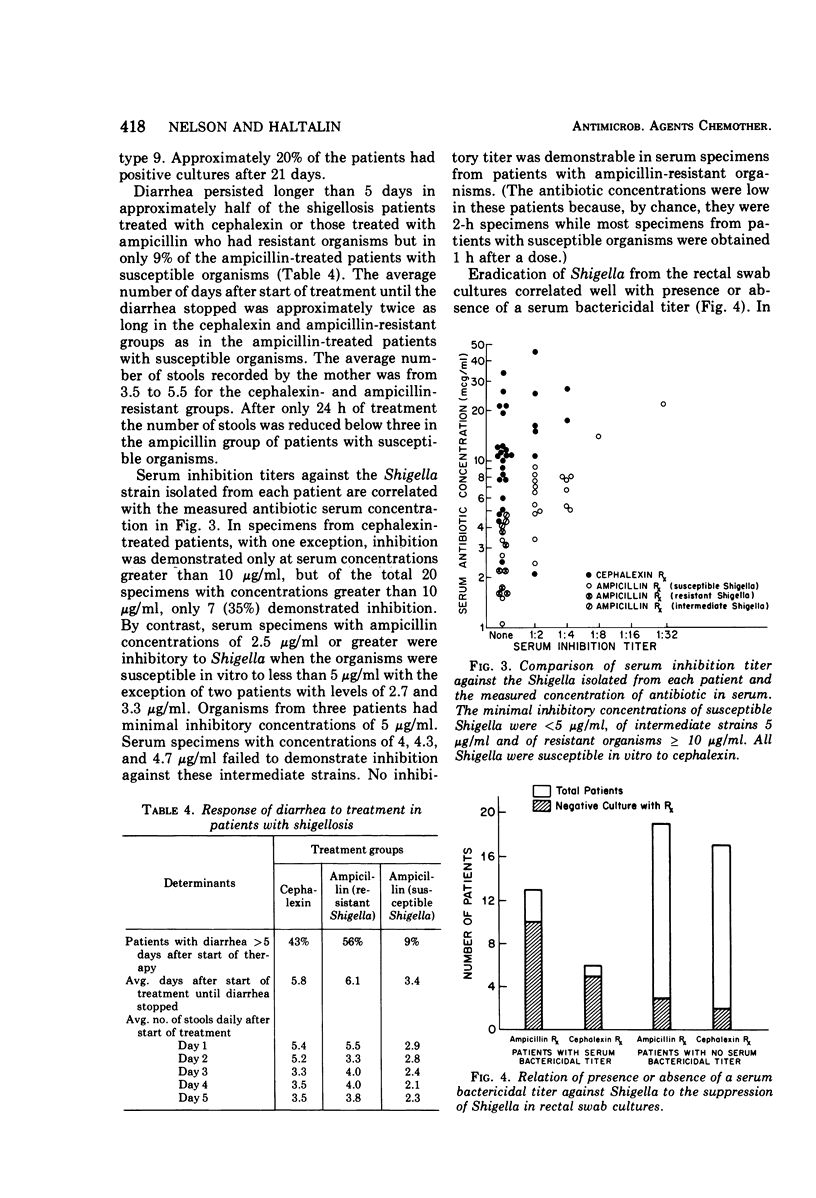
Most ampicillin-resistant Shigella are susceptible to cephalexin. Randomized treatment with cephalexin or ampicillin was given to 154 infants and children with acute diarrhea. Rectal swab cultures revealed Shigella in 42%, Salmonella in 6%, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in 2%, and no pathogen in 50%. Cephalexin failed to eradicate Shigella after 5 days of treatment in 76% of patients as contrasted with 28% of ampicillin-treated patients with susceptible organisms. Shigella persisted in 78% of ampicillin-treated patients with resistant organisms. Diarrhea lasted more than 5 days in 43% of cephalexin-treated patients, in 56% of the ampicillin group with resistant organisms, but in only 9% of ampicillin-treated patients with susceptible organisms. The failure of cephalexin was due to the relatively high minimal inhibitory concentrations and minimal bacterial concentrations of 5 or 10 μg/ml and, although serum concentrations were twice the minimal bacterial concentration, they were not sufficient to demonstrate killing by the serum dilution method. In vitro susceptibility or resistance of Shigella to ampicillin correlated with clinical success or failure. Cephalexin is not a suitable drug for treatment of shigellosis in patients with ampicillin-resistant organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Haltalin K. C. Ampicillin and shigellosis. Am J Dis Child. 1973 Mar;125(3):458–458. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160030108023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Kusmiesz H. T., Hinton L. V., Nelson J. D. Treatment of acute diarrhea in outpatients. Double-blind study comparing ampicillin and placebo. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Oct;124(4):554–561. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110160092010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltalin K. C., Nelson J. D., Kusmiesz H. T. Comparative efficacy of nalidixic acid and ampicillin for severe shigellosis. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Apr;48(4):305–312. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.4.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. D., Shelton S., Kusmiesz H. T., Haltalin K. C. Absorption of ampicillin and nalidixic acid by infants and children with acute shigellosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Nov-Dec;13(6):879–886. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972136879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



