Abstract
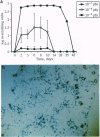
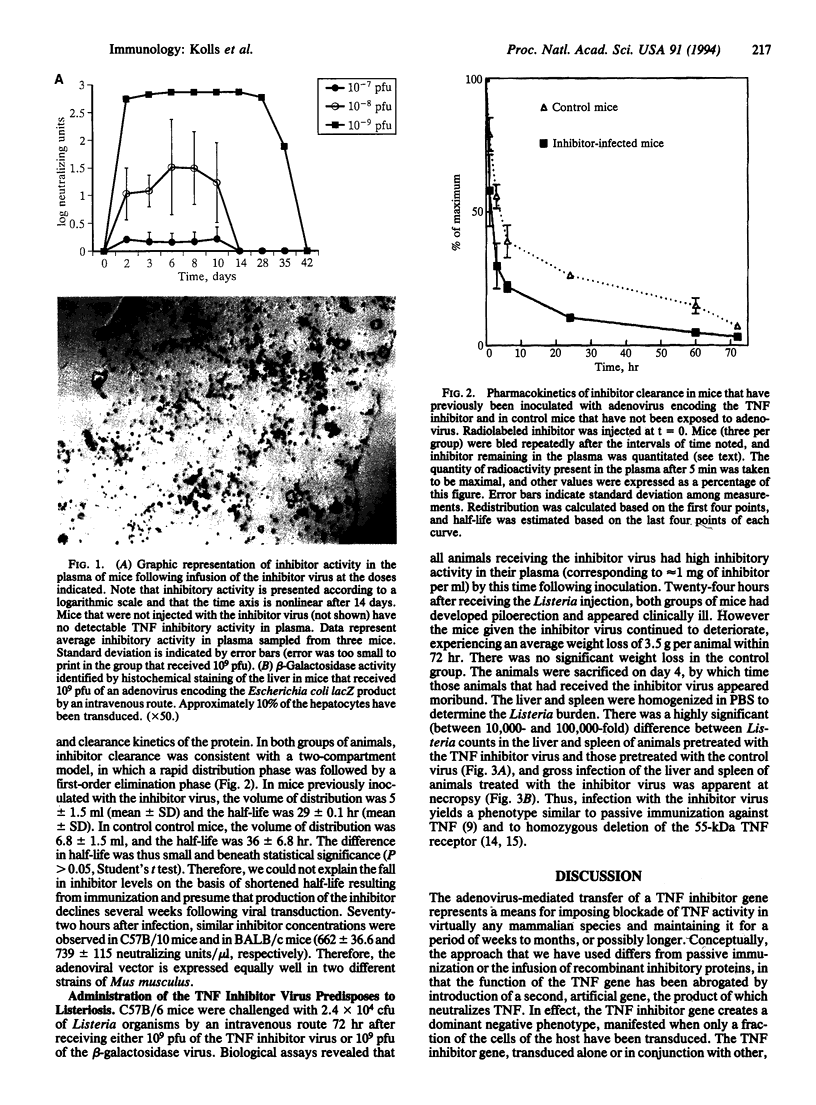
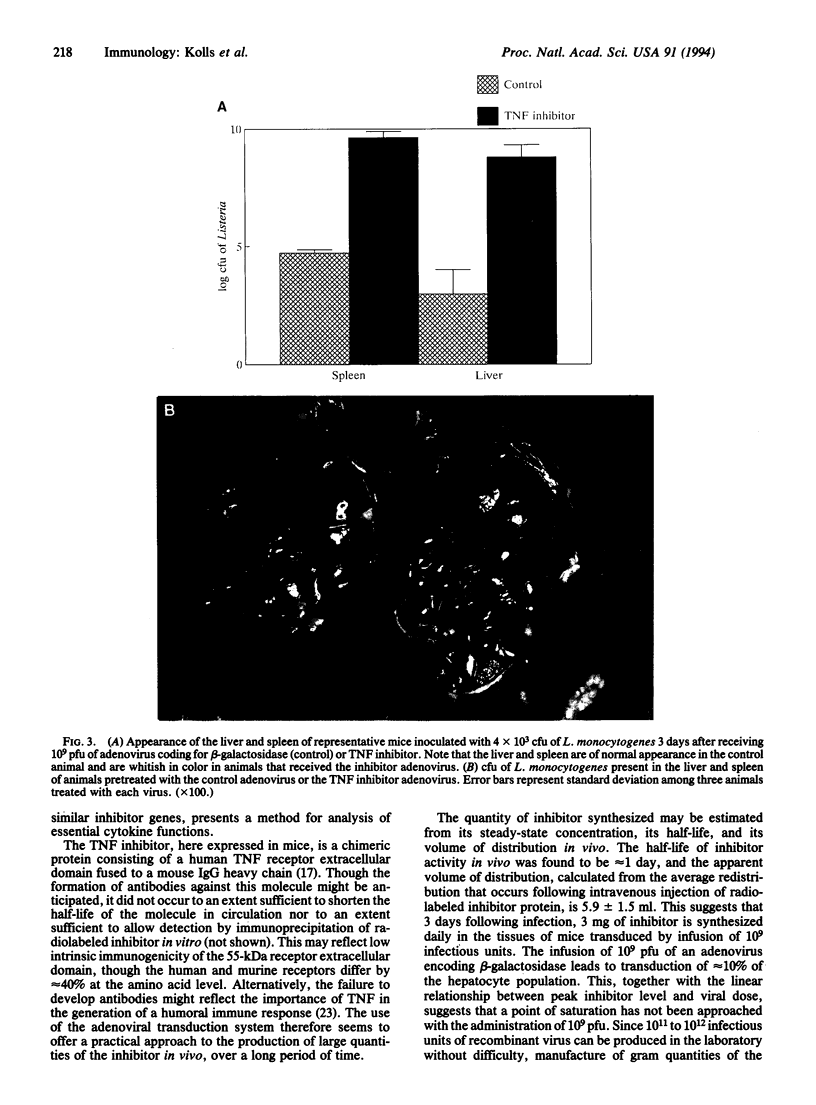
A chimeric protein capable of binding and neutralizing tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and lymphotoxin was expressed in mice transduced with a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector into which a TNF inhibitor gene had been engineered. Within 3 days following the injection of 10(9) infectious particles, the TNF inhibitor concentration exceeded 1 mg/ml of plasma; this level of expression was maintained for at least 4 weeks, and detectable TNF inhibitory activity was measured 6 weeks after injection of the recombinant virus. Introduction of the artificial gene produced a phenotypic effect comparable to homozygous deletion of the 55-kDa TNF receptor, in that animals were rendered highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes, whereas control animals receiving a replication-incompetent virus coding for beta-galactosidase were capable of resisting Listeria challenge. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a gene encoding a TNF inhibitor offers a practical means of imposing effective, long-term blockade of TNF activity in vivo for investigational and therapeutic purposes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins H. L., Bancroft G. J. Cytokine enhancement of complement-dependent phagocytosis by macrophages: synergy of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1447–1454. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Evidence that tumor necrosis factor has an important role in antibacterial resistance. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Aiso S., Michie S. A., McDevitt H. O., Acha-Orbea H. Prevention of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by tumor necrosis factor (TNF): similarities between TNF-alpha and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Fronek Z., Lewis G. D., Koo M., Hansen J. A., McDevitt H. O. Heritable major histocompatibility complex class II-associated differences in production of tumor necrosis factor alpha: relevance to genetic predisposition to systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1233–1237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., McDevitt H. O. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha in murine autoimmune 'lupus' nephritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):356–358. doi: 10.1038/331356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight J. G., Adams D. D. Three genes for lupus nephritis in NZB x NZW mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1653–1660. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Palmer E. The contribution of NZW genes to lupus-like disease in (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1237–1251. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Gentz R., Zulauf M., Lustig A., Tabuchi H., Schlaeger E. J., Brockhaus M., Gallati H., Manneberg M., Lesslauer W. Recombinant 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Stoichiometry of binding to TNF alpha and TNF beta and inhibition of TNF activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18324–18329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Mogg A. E., Burke J. F., Caskey C. T. Histochemical staining of clonal mammalian cell lines expressing E. coli beta galactosidase indicates heterogeneous expression of the bacterial gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):253–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01535207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsters S. A., Frutkin A. D., Simpson N. J., Fendly B. M., Ashkenazi A. Identification of cysteine-rich domains of the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor involved in ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5747–5750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal S. K., McDermott M. R., Johnson D. C., Prevec L., Graham F. L. Monitoring foreign gene expression by a human adenovirus-based vector using the firefly luciferase gene as a reporter. Virus Res. 1993 Apr;28(1):67–90. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90090-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai M., Saigusa T., Shimada Y., Inagawa H., Oshima H., Iriki M. Antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) reduces endotoxin fever. Experientia. 1988 Jul 15;44(7):606–607. doi: 10.1007/BF01953311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Yi H., Rosenblatt H. M., Filipovich A. H., Adelstein S., Modi W. S., McBride O. W., Leonard W. J. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90167-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S. M., Cross A. S., Kelly N. M., Sadoff J. C., Bodmer M. W., Palardy J. E., Victor G. H. Efficacy of a monoclonal antibody directed against tumor necrosis factor in protecting neutropenic rats from lethal infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1148–1152. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppel K., Crawford D., Beutler B. A tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-IgG heavy chain chimeric protein as a bivalent antagonist of TNF activity. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1483–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Matsuyama T., Kündig T. M., Wakeham A., Kishihara K., Shahinian A., Wiegmann K., Ohashi P. S., Krönke M., Mak T. W. Mice deficient for the 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez C., Roldán E., Navas G., Brieva J. A. Essential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the differentiation of human tonsil in vivo induced B cells capable of spontaneous and high-rate immunoglobulin secretion. Eur J Immunol. 1993 May;23(5):1160–1164. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe J., Lesslauer W., Lötscher H., Lang Y., Koebel P., Köntgen F., Althage A., Zinkernagel R., Steinmetz M., Bluethmann H. Mice lacking the tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 are resistant to TNF-mediated toxicity but highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):798–802. doi: 10.1038/364798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorle H., Holtschke T., Hünig T., Schimpl A., Horak I. Development and function of T cells in mice rendered interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):621–624. doi: 10.1038/352621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Ruddle N. H., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of hamster monoclonal antibodies that neutralize murine tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3884–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B. A., Gelin J., Fong Y., Marano M., Wei H., Cerami A., Lowry S. F., Lundholm K. G., Moldawer L. L. Anticachectin/tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibodies attenuate development of cachexia in tumor models. FASEB J. 1989 Jun;3(8):1956–1962. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.8.2721856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Makeh I., Perricaudet M., Briand P. Widespread long-term gene transfer to mouse skeletal muscles and heart. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):626–630. doi: 10.1172/JCI115902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]