Abstract
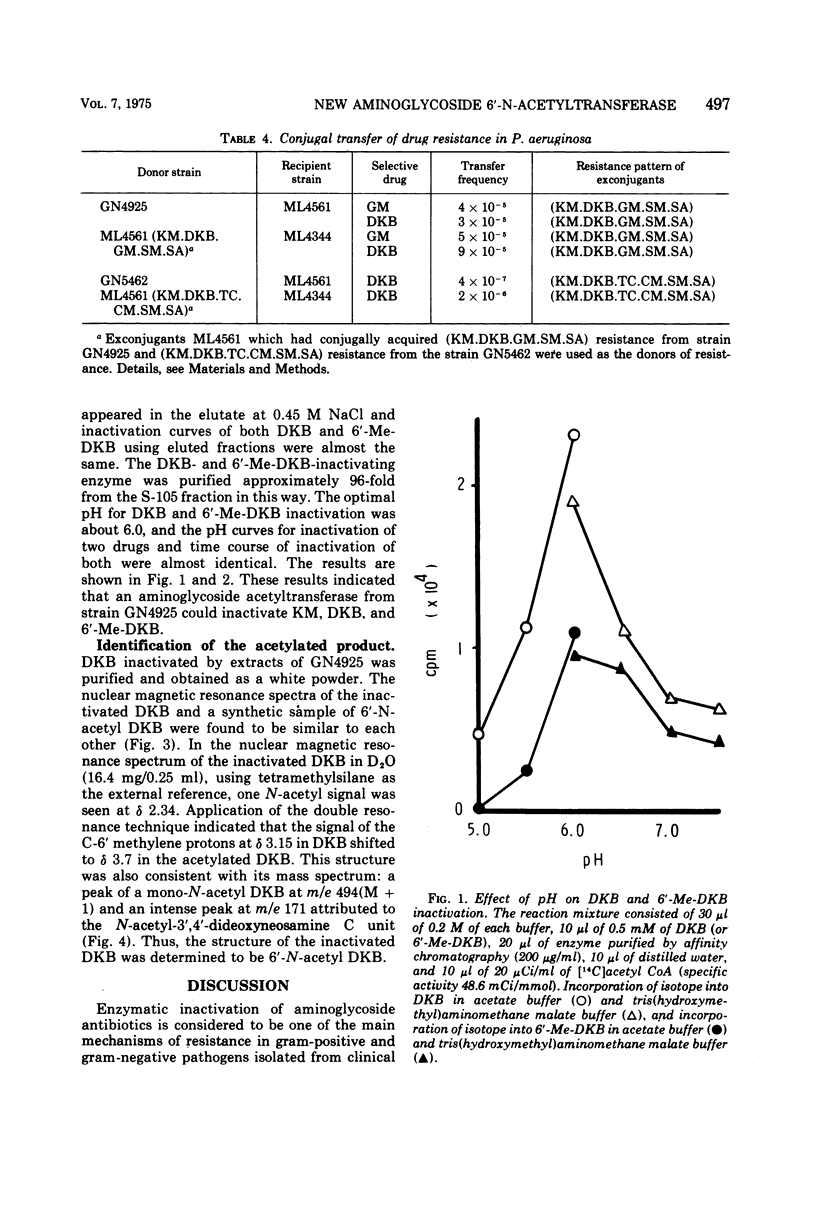
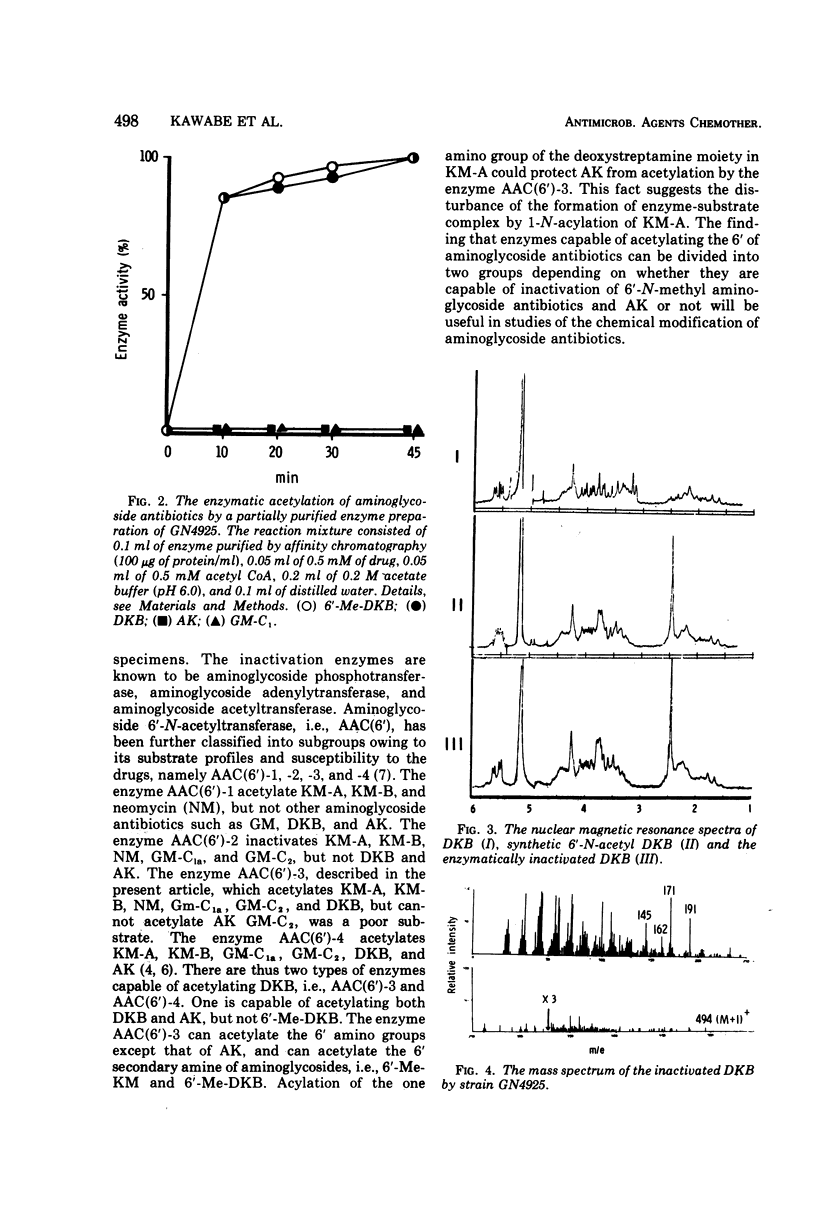
The newly introduced semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotics, i.e., 3′,4′-dideoxykanamycin B (DKB), 6′-N-methyl DKB (6′-Me-DKB) and amikacin (AK) have been found to be effective against gram-negative pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are resistant to the known aminoglycoside antibiotics. We have demonstrated in our stock cultures two types of P. aeruginosa strains resistant to DKB, i.e., (DKBr.AKr.6′-Me-DKBs) and (DKBr.AKs.6′-Me-DKBr) (where r = resistant; s = sensitive). Both groups of strains inactivate the drugs by acetylation. The acetylating enzyme was extracted from GN4925(DKBr.AKs.6′-Me-DKBr) and purified by affinity chromatography. Enzymatic studies of the inactivation reaction and chemical studies of the inactivated products indicated that DKB and 6′-Me-DKB were inactivated by acetylation of the 6′-amino group of the drugs. This enzyme acetylates kanamycin A (KM-A), KM-B, DKB, 6′-Me-DKB, 6′-N-methyl kanamycin B, but not KM-C, AK, and gentamicin C1. The enzyme is named aminoglycoside 6′-N-acetyltransferase 3. Genetic studies of two strains resistant to DKB and 6′-Me-DKB disclosed that the enzyme catalyzing inactivation of both DKB and 6′-Me-DKB was mediated by an R factor, i.e., Rms167 and Rms168, capable of conferring resistance to KM, DKB, and 6′-Me-DKB, in addition to resistance to gentamicin, streptomycin, and sulfanilamide, and resistance to tetracycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin and sulfanilamide respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Inactivation of dihydrostreptomycin and spectinomycin by Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):553–557. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe H., Mitsuhashi S. Acetylation of dideoxykanamycin B by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Microbiol. 1972 Sep;16(5):436–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe H., Naito T., Mitsuhashi S. Acetylation of amikacin, a new semisynthetic antibiotic, by Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying an R factor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi H., Naito T., Nakagawa S., Fujisawa K. I. BB-K 8, a new semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):695–708. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oara K., Kono M., Mitsuhashi S. Letter: Structure of enzymatically acetylated sisomicin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 May;27(5):349–351. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanishi M., Kondo S., Suzuki Y., Okamoto S., Umezawa H. Studies on inactivation of kanamycin and resistances of E. coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jul;20(3):132–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Nishimura Y., Tsuchiya T., Umezawa S. Syntheses of 6'-N-methyl-kanamycin and 3',4'-dideoxy-6'-N-methylkanamycin B active against resistant strains having 6'-N-acetylating enzymes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):743–745. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Okanishi M., Utahara R., Maeda K., Kondo S. Isolation and structure of kanamycin inactivated by a cell free system of kanamycin-resistant E. coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jul;20(3):136–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Umezawa S., Tsuchiya T., Okazaki Y. 3',4'-dideoxy-kanamycin B active against kanamycin-resistant Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jul;24(7):485–487. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagisawa M., Naganawa H., Kondo S., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. 6'-N-acetylation of 3',4'-dideoxykanamycin B by an enzyme in a resistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Aug;25(8):495–496. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Yagisawa M., Naganawa H., Kondo S., Takeuchi T. Kanamycin 6'-acetate and ribostamycin 6'-acetate, enzymatically inactivated products by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Dec;25(12):746–747. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



