Abstract
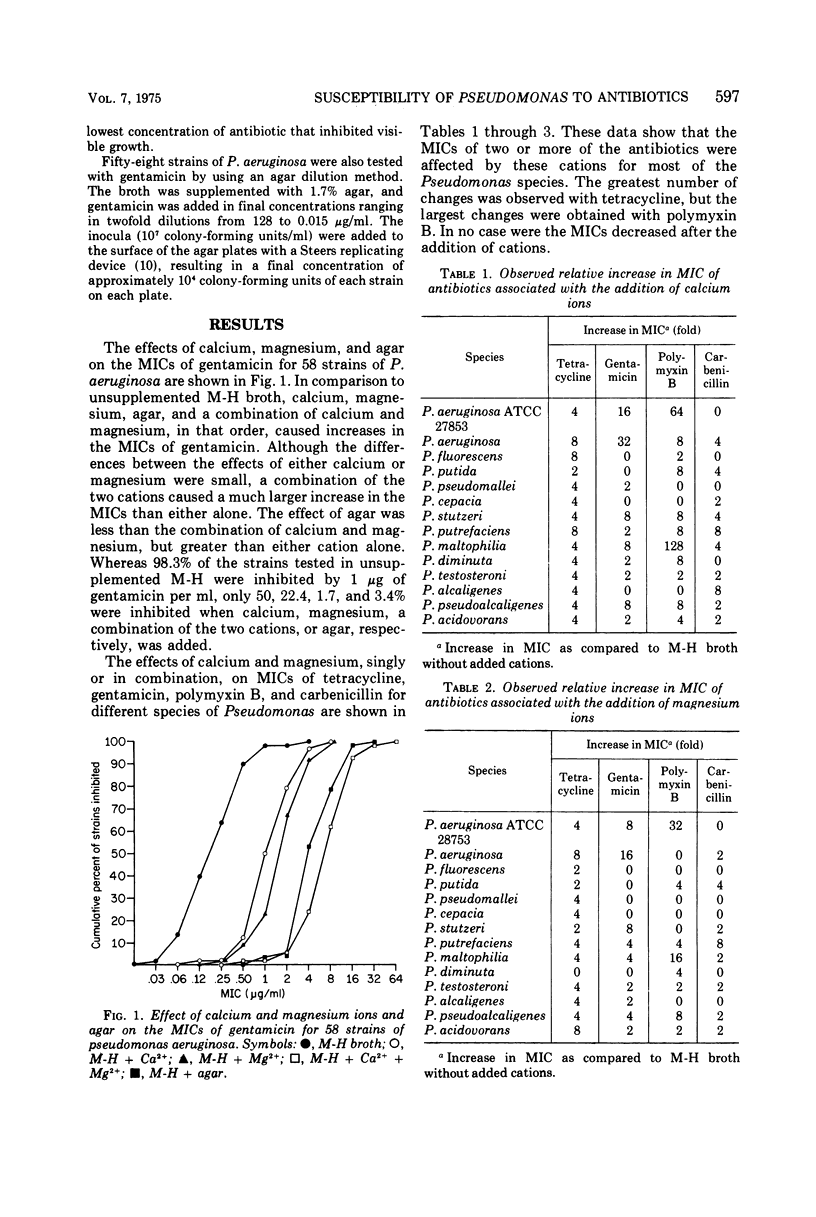
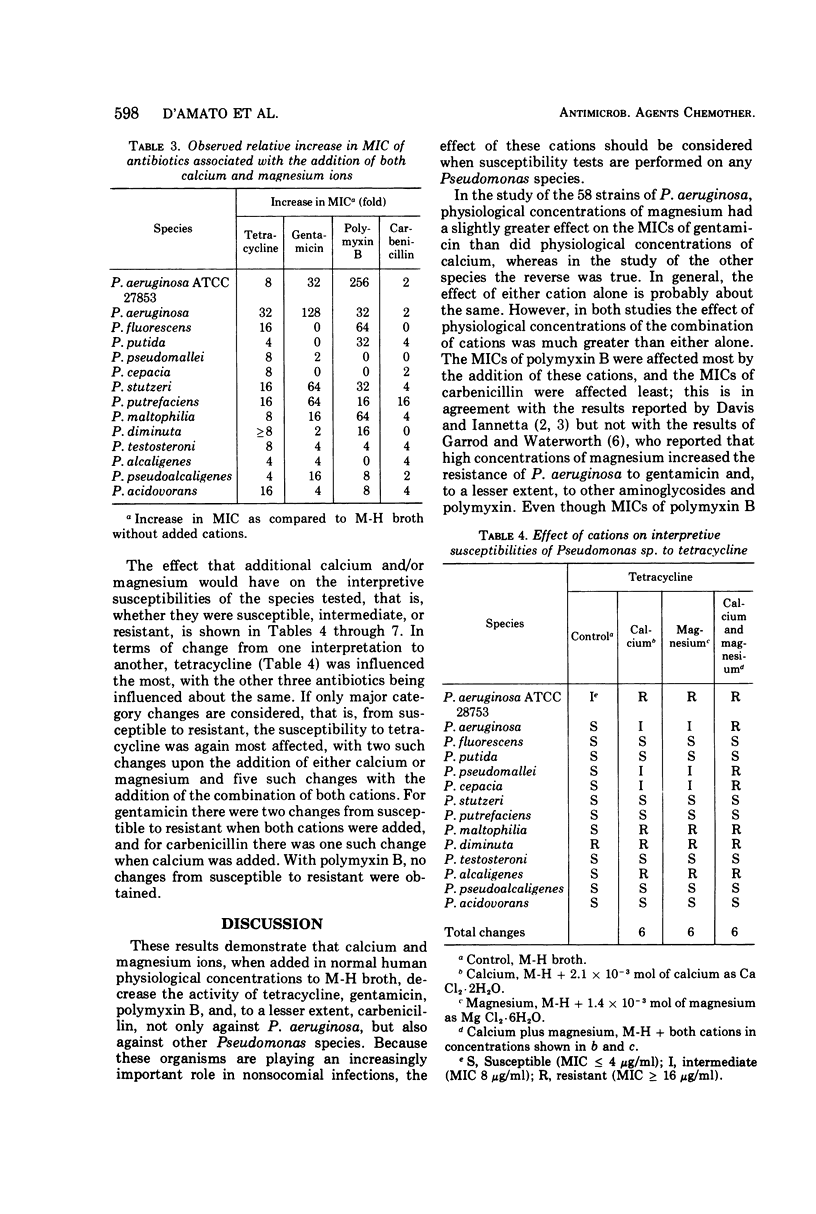
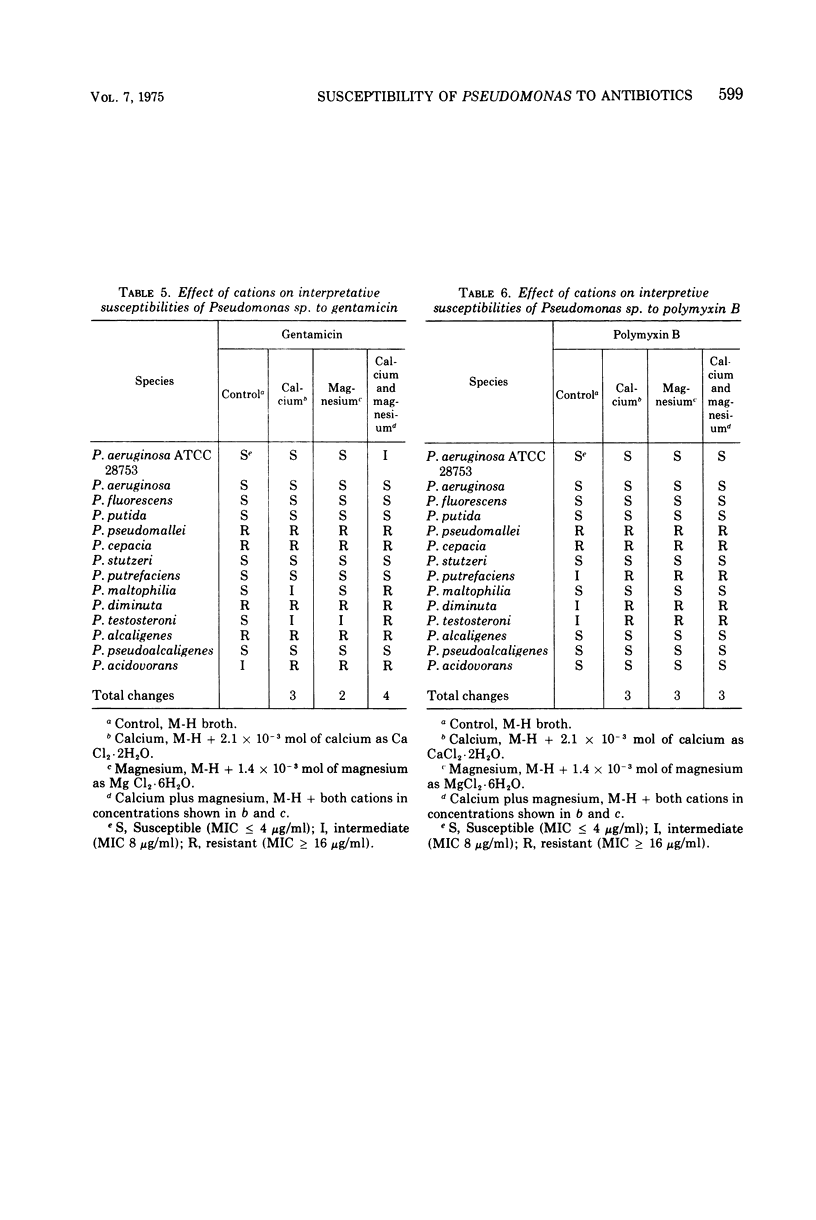
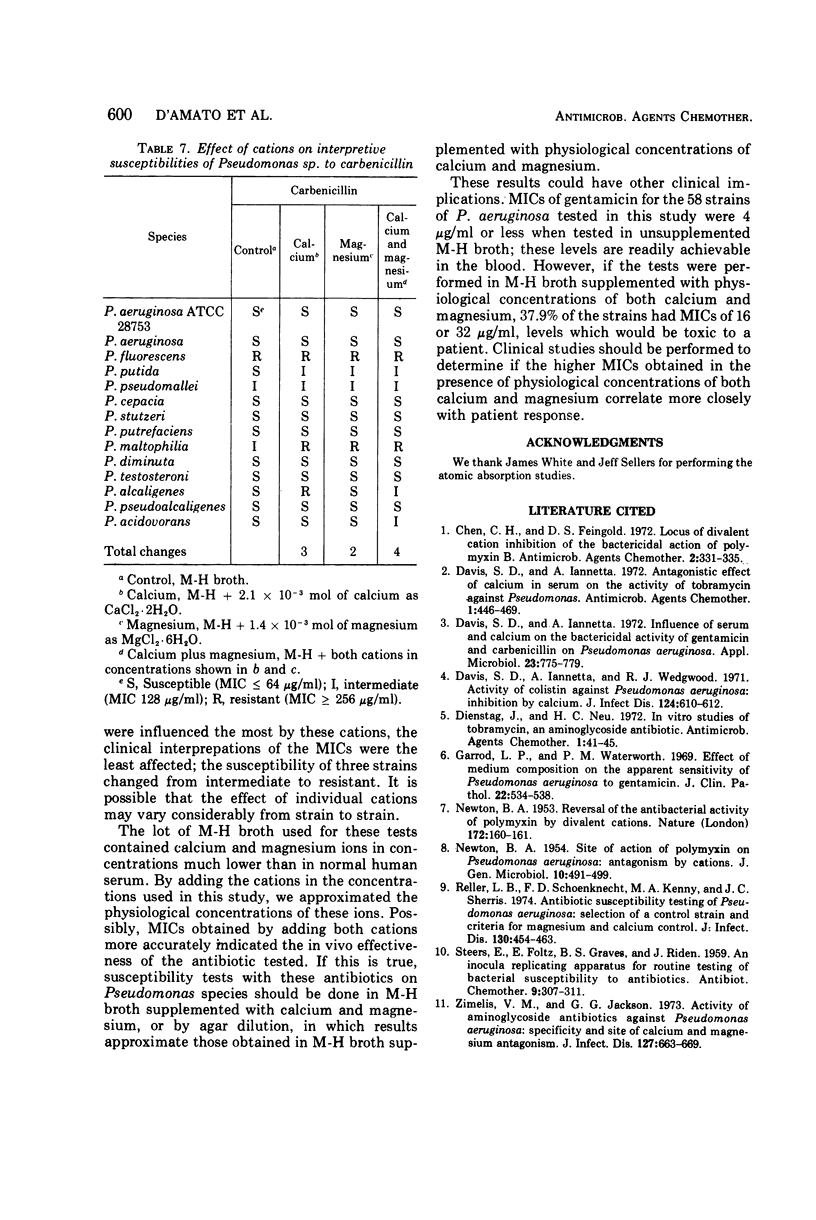
The effect of calcium and magnesium on the susceptibility of 13 species of Pseudomonas to tetracycline, gentamicin, polymyxin B, and carbenicillin was measured. The majority of the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of these antibiotics was increased if these cations were added to the test media. The increases in MICs caused by calcium or magnesium were similar, but the combination of both ions generally caused a greater change than either alone. Although the MIC of polymyxin B was most affected by calcium and magnesium, its interpretive susceptibilities (i.e., whether susceptible or resistant) were least changed. Susceptibility tests on Pseudomonas species probably should be done with Muller-Hinton broth supplemented with physiological concentrations of calcium and magnesium to better approximate the in vivo activity of these antibiotics. When the susceptibility tests were performed with Mueller-Hinton agar, the MICs were slightly less than those obtained with Mueller-Hinton broth supplemented with both cations but greater than those obtained with Mueller-Hinton broth supplemented with individual cations.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen C. C., Feingold D. S. Locus of divalent cation inhibition of the bactericidal action of polymyxin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Iannetta A. Antagonistic effect of calcium in serum on the activity of tobramycin against Pseudomonas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):466–469. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Iannetta A. Influence of serum and calcium on the bactericidal activity of gentamicin and carbenicillin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):775–779. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.775-779.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Iannetta A., Wedgwood R. J. Activity of colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inhibition by calcium. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):610–612. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J., Neu H. C. In vitro studies of tobramycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Effect of medium composition on the apparent sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to gentamicin. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):534–538. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Reversal of the antibacterial activity of polymyxin by divalent cations. Nature. 1953 Jul 25;172(4369):160–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Site of action of polymyxin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: antagonism by cations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):491–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B., Schoenknecht F. D., Kenny M. A., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: selection of a control strain and criteria for magnesium and calcium content in media. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):454–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimelis V. M., Jackson G. G. Activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics aganst Pseudomonas aeruginosa: specificity and site of calcium and magnesium antagonism. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):663–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



