Abstract
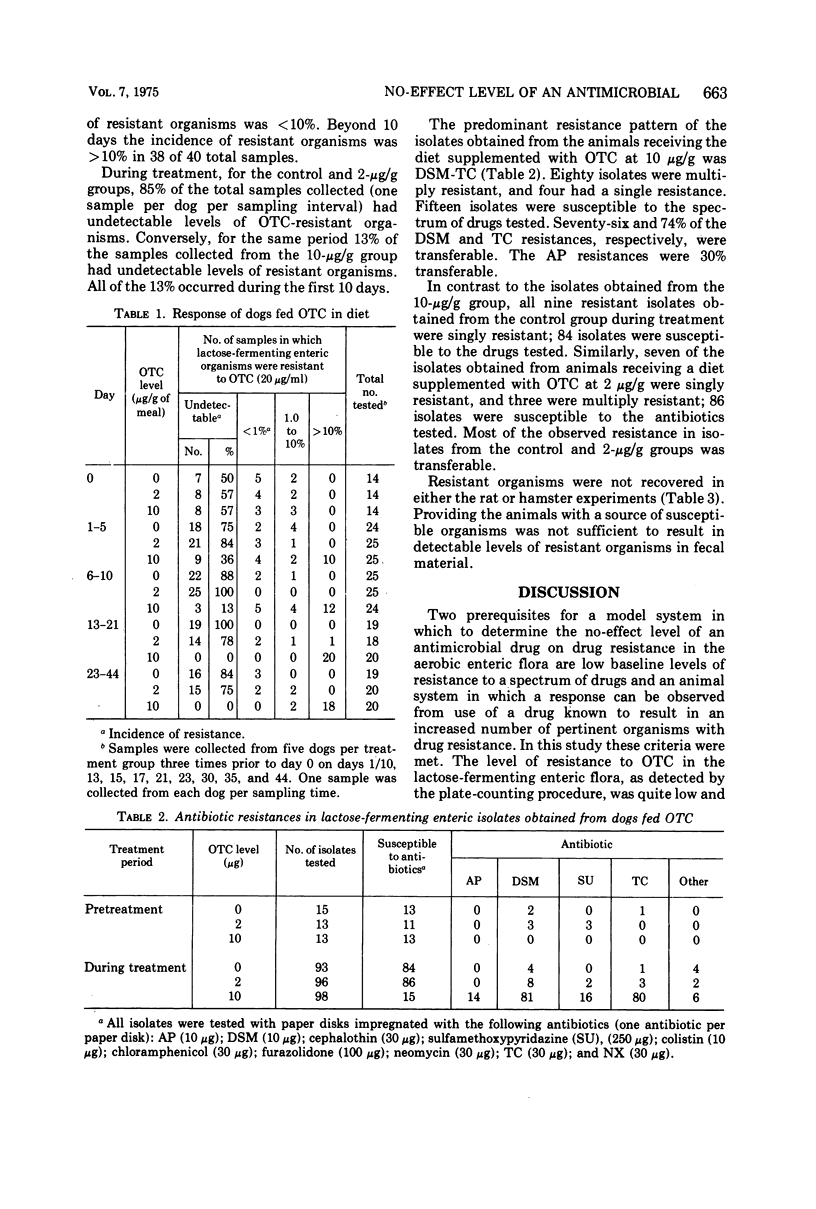
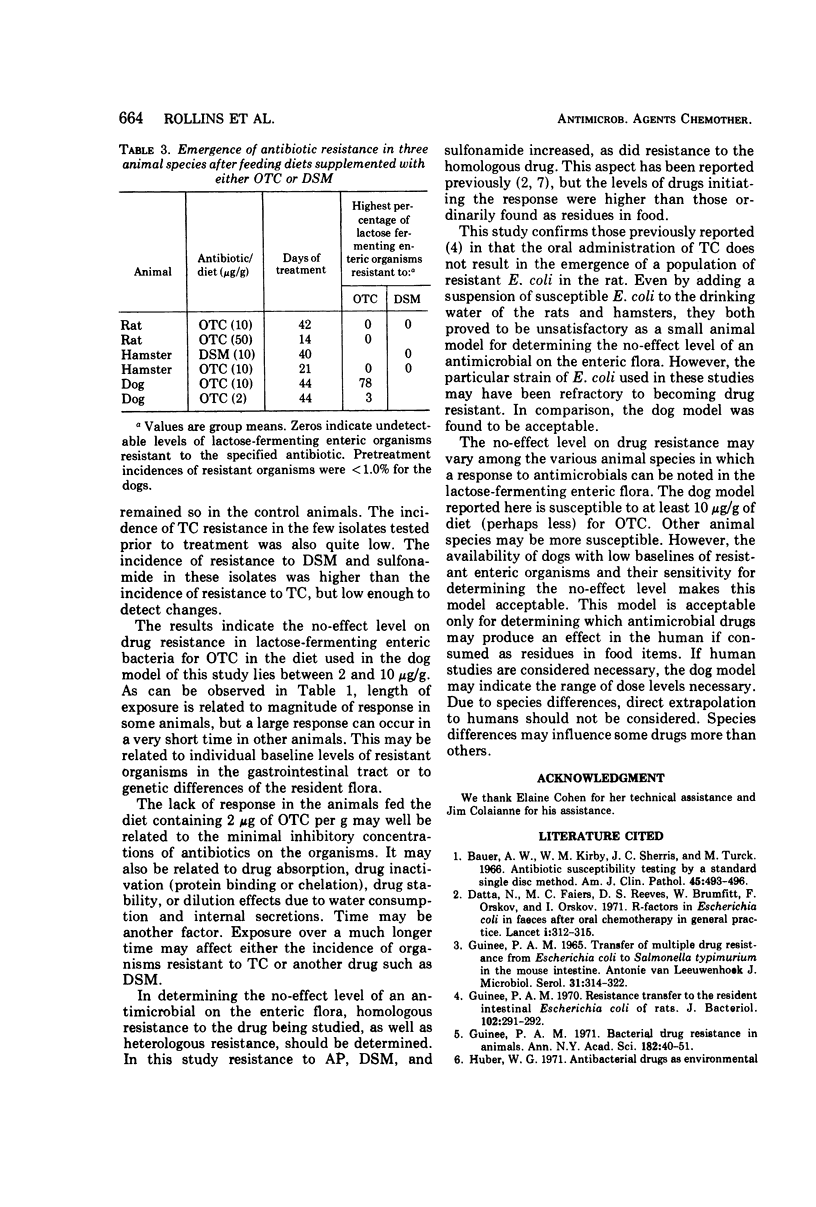
Mature beagles were fed a ground-meal diet containing 0, 2, or 10 μg of oxytetracycline per g for 44 days. The 10-μg/g diet resulted in a shift from a predominantly drug-susceptible population of enteric lactose-fermenting organisms to a multiply antibiotic-resistant population which peaked at 78% resistant organisms. Since a shift to drug-resistant organisms did not occur in the group fed 2 μg/g, the level of oxytetracycline that results in increased incidence of antibiotic resistance lies between 2 and 10 μg/g in this dog model. Rats and hamsters fed diets containing oxytetracycline (10 μg/g or greater) or dihydrostreptomycin (10 μg/g), and provided suspensions of drug-susceptible Escherichia coli, did not develop a population of antibiotic-resistant organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Faiers M. C., Reeves D. S., Brumfitt W., Orskov F., Orskov I. R Factors in Escherichia coli in faeces after oral chemotherapy in general practice. Lancet. 1971 Feb 13;1(7694):312–315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A. Prevalence of extrachromosomal drug resistance. Bacterial drug resistance in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:40–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A. Resistance transfer to the resident intestinal Escherichia coli of rats. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):291–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.291-292.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A. Transfer of multiple drug resistance from Escherichia coli to Salmonella typhi murium in the mouse intestine. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1965;31(3):314–322. doi: 10.1007/BF02045911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins L. D., Pocurull D. W., Reynolds S. Effect of racephenicol on antibiotic resistance of lactose-fermenting enteric bacteria in chickens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):277–280. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. A., Terry P. M., Bennett J. V. Antibiotic resistance and transfer factor in Salmonella, United States 1967. JAMA. 1968 Sep 23;205(13):903–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Effect of antibiotics on bacterial ecology in animals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1472–1479. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



