Abstract
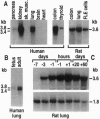
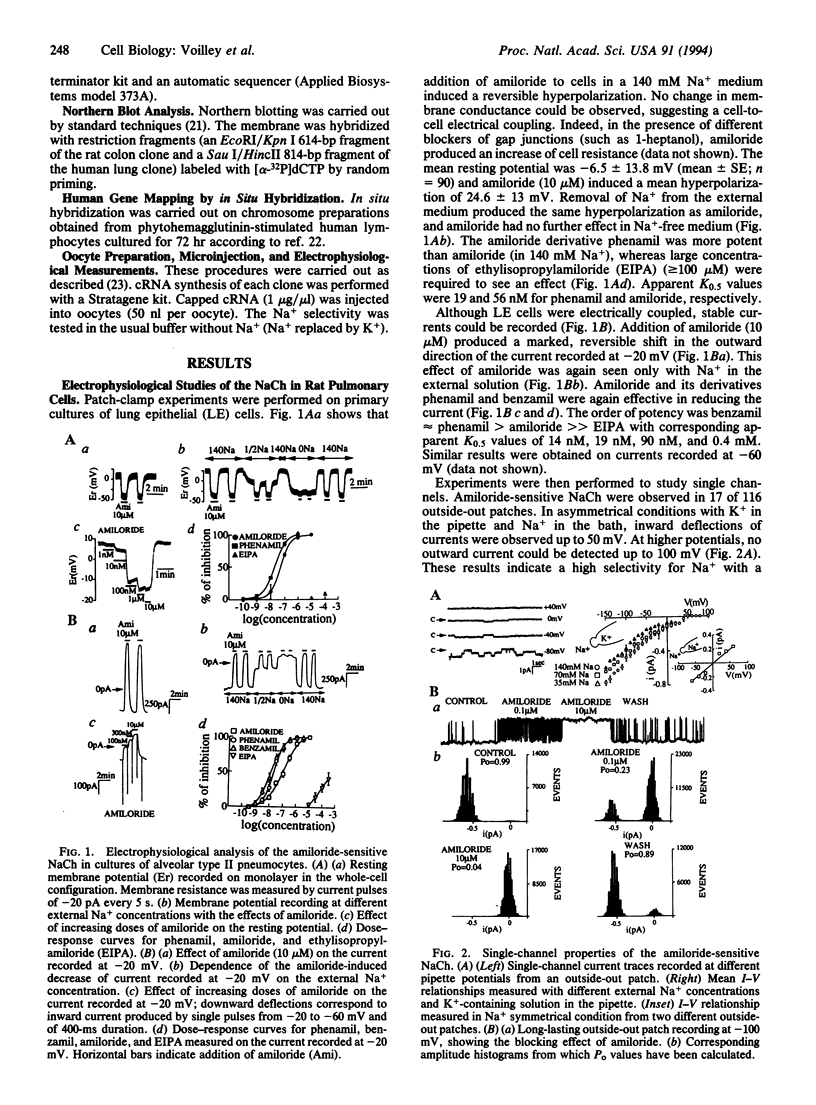
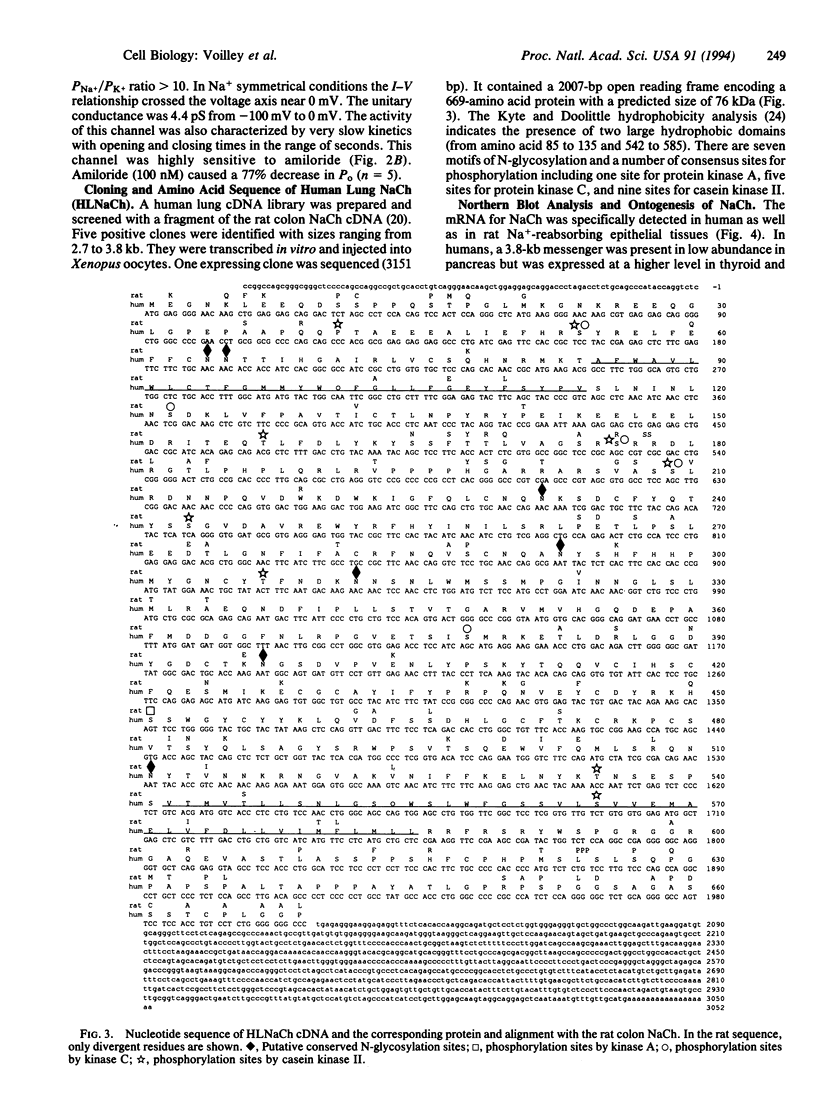
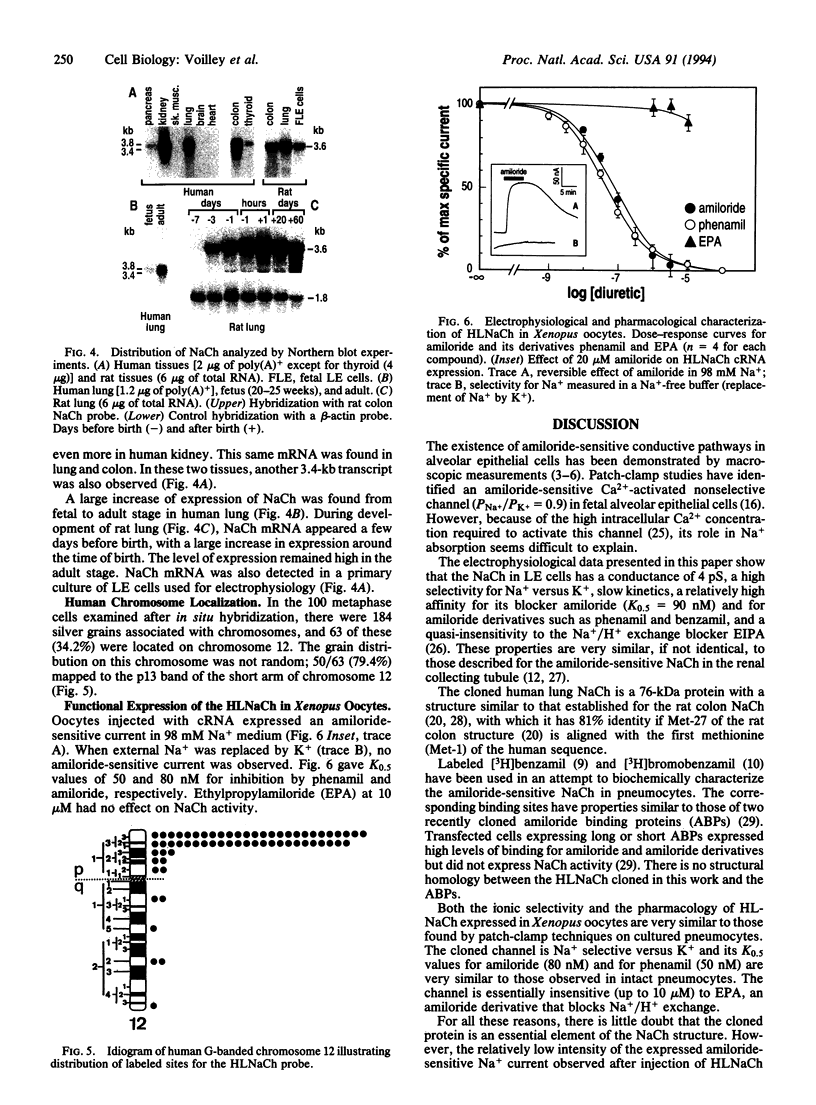
Water balance in the lung is controlled via active Na+ and Cl- transport. Electrophysiological measurements on lung epithelial cells demonstrated the presence of a Na+ channel that is inhibited by amiloride (K0.5 = 90 nM) and some of its derivatives such as phenamil (K0.5 = 19 nM) and benzamil (K0.5 = 14 nM) but not by ethylisopropylamiloride. An amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel of 4 pS was recorded from outside-out patches excised from the apical membrane. This channel is highly selective for Na+ (PNa+/PK+ > or = to 10). Isolation of a human lung cDNA led to the primary structure of the lung Na+ channel. The corresponding protein is 669 residues long and has two large hydrophobic domains. An amiloride-sensitive Na(+)-selective current apparently identical to the one observed in lung epithelial cells was recorded after expression of the cloned channel in oocytes. The level of the mRNA for the Na+ channel was highly increased from fetal to newborn and adult stages. This observation indicates that the increased Na+ reabsorption that occurs at birth as a necessary event to pass to an air-breathing environment is probably associated with control of transcription of this Na+ channel. The human gene for the lung Na+ channel was mapped on chromosome 12p13.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Röper J. Transporters, channels and human disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90139-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset G., Crone C., Saumon G. Significance of active ion transport in transalveolar water absorption: a study on isolated rat lung. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:311–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland R. D. Lung epithelial ion transport and fluid movement during the perinatal period. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):L30–L37. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.2.L30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cotton C. U., Gatzy J. T., Knowles M. R., Yankaskas J. R. Evidence for reduced Cl- and increased Na+ permeability in cystic fibrosis human primary cell cultures. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:77–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek J. M., Kim K. J., Crandall E. D. Tight monolayers of rat alveolar epithelial cells: bioelectric properties and active sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C688–C693. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalemans W., Barbry P., Champigny G., Jallat S., Dott K., Dreyer D., Crystal R. G., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Lazdunski M. Altered chloride ion channel kinetics associated with the delta F508 cystic fibrosis mutation. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):526–528. doi: 10.1038/354526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H., Benos D. J. Characteristics and regulatory mechanisms of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel. Physiol Rev. 1988 Apr;68(2):309–373. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Kim K. J., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active sodium transport across alveolar epithelium of isolated rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jun;62(6):2460–2466. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.6.2460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemare E., Honoré E., Pradier L., Lesage F., Schweitz H., Attali B., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Effects of the level of mRNA expression on biophysical properties, sensitivity to neurotoxins, and regulation of the brain delayed-rectifier K+ channels Kv1.2. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12463–12468. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gögelein H., Greger R. Na+ selective channels in the apical membrane of rabbit late proximal tubules (pars recta). Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):198–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00586683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. L., Eaton D. C. Single-channel recordings from two types of amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels. Membr Biochem. 1986;6(2):149–171. doi: 10.3109/09687688609065447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Lazdunski M. Calcium channels: molecular pharmacology, structure and regulation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):81–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01870922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Church N. L., Waltner W. E., Yankaskas J. R., Gilligan P., King M., Edwards L. J., Helms R. W., Boucher R. C. A pilot study of aerosolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1189–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Renard S., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Chassande O., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Molecular cloning and functional expression of different molecular forms of rat amiloride-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 1;216(2):679–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Waldmann R., Lazdunski M., Barbry P. Expression cloning of an epithelial amiloride-sensitive Na+ channel. A new channel type with homologies to Caenorhabditis elegans degenerins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Tohda H., Hagiwara N., O'Brodovich H. Cytosolic Ca(2+)-induced modulation of ion selectivity and amiloride sensitivity of a cation channel and beta agonist action in fetal lung epithelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91244-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon S., Bauer M. L., Benos D. J., Kleyman T. R., Lin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, O'Brodovich H. Fetal lung epithelial cells contain two populations of amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):L357–L364. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.264.4.L357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon S., Kirk K. L., Bubien J. K., Oh Y., Hu P., Yue G., Shoemaker R., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Benos D. J. Immunocytochemical and functional characterization of Na+ conductance in adult alveolar pneumocytes. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1228–C1238. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Philip N., Passage E., Moisan J. P., Mandel J. L., Mattei J. F. DNA probe localization at 18p113 band by in situ hybridization and identification of a small supernumerary chromosome. Hum Genet. 1985;69(3):268–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00293038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Doucet A. Hormonal control of kidney functions at the cell level. Physiol Rev. 1986 Apr;66(2):377–468. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H. Epithelial ion transport in the fetal and perinatal lung. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):C555–C564. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.4.C555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Matalon S., Kleyman T. R., Benos D. J. Biochemical evidence for the presence of an amiloride binding protein in adult alveolar type II pneumocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18498–18504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orser B. A., Bertlik M., Fedorko L., O'Brodovich H. Cation selective channel in fetal alveolar type II epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 13;1094(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90021-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrier B., Champigny G., Barbry P., Gerard C., Mauchamp J., Lazdunski M. Identification and properties of a novel type of Na+-permeable amiloride-sensitive channel in thyroid cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):499–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne P., Frelin C., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. Structure-activity relationships of amiloride and certain of its analogues in relation to the blockade of the Na+/H+ exchange system. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;25(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Molecular mechanisms of CFTR chloride channel dysfunction in cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1251–1254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90353-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]