Abstract
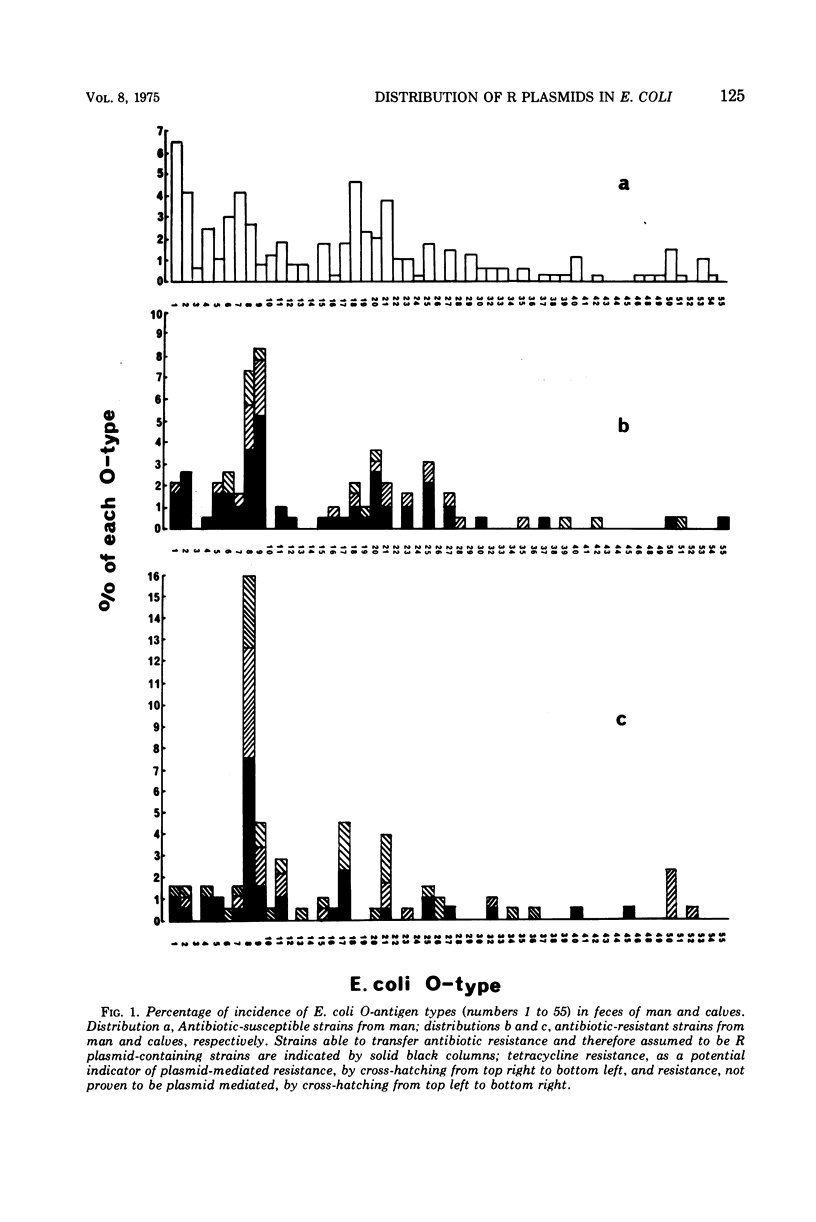
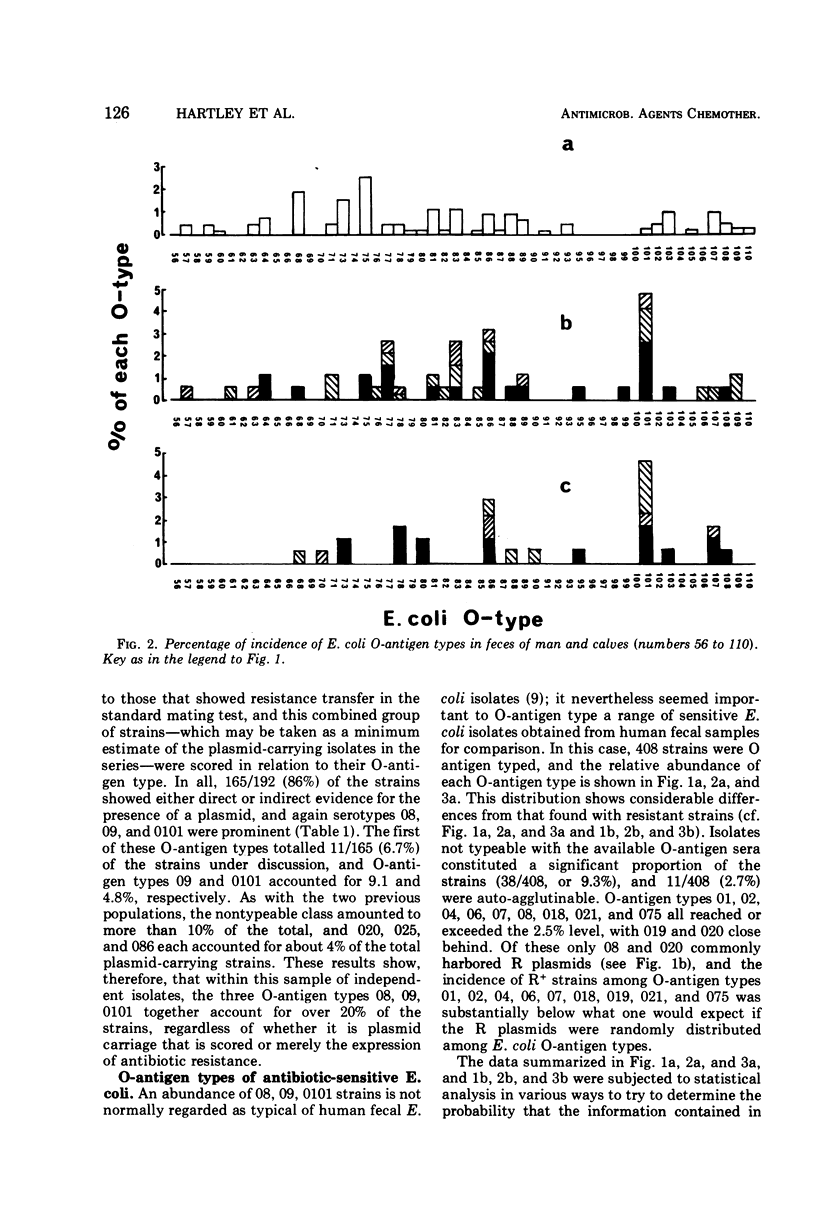
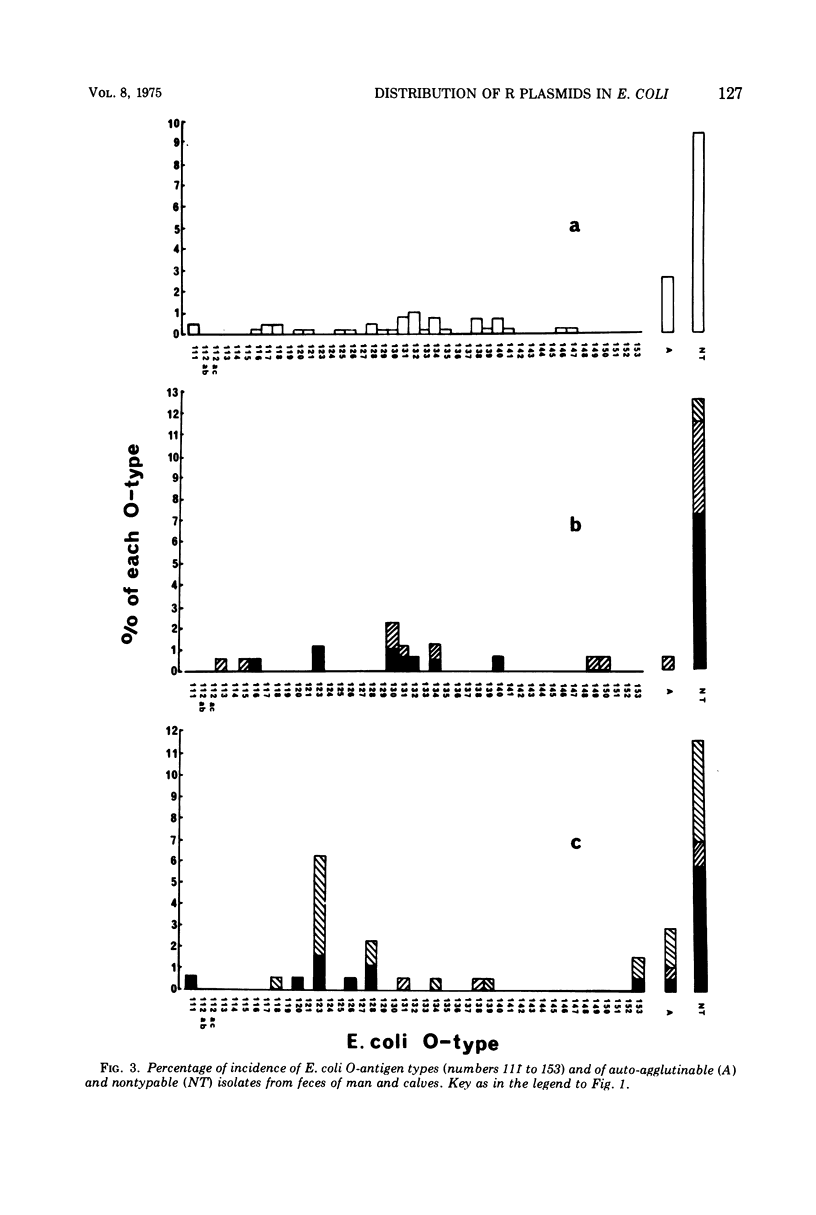
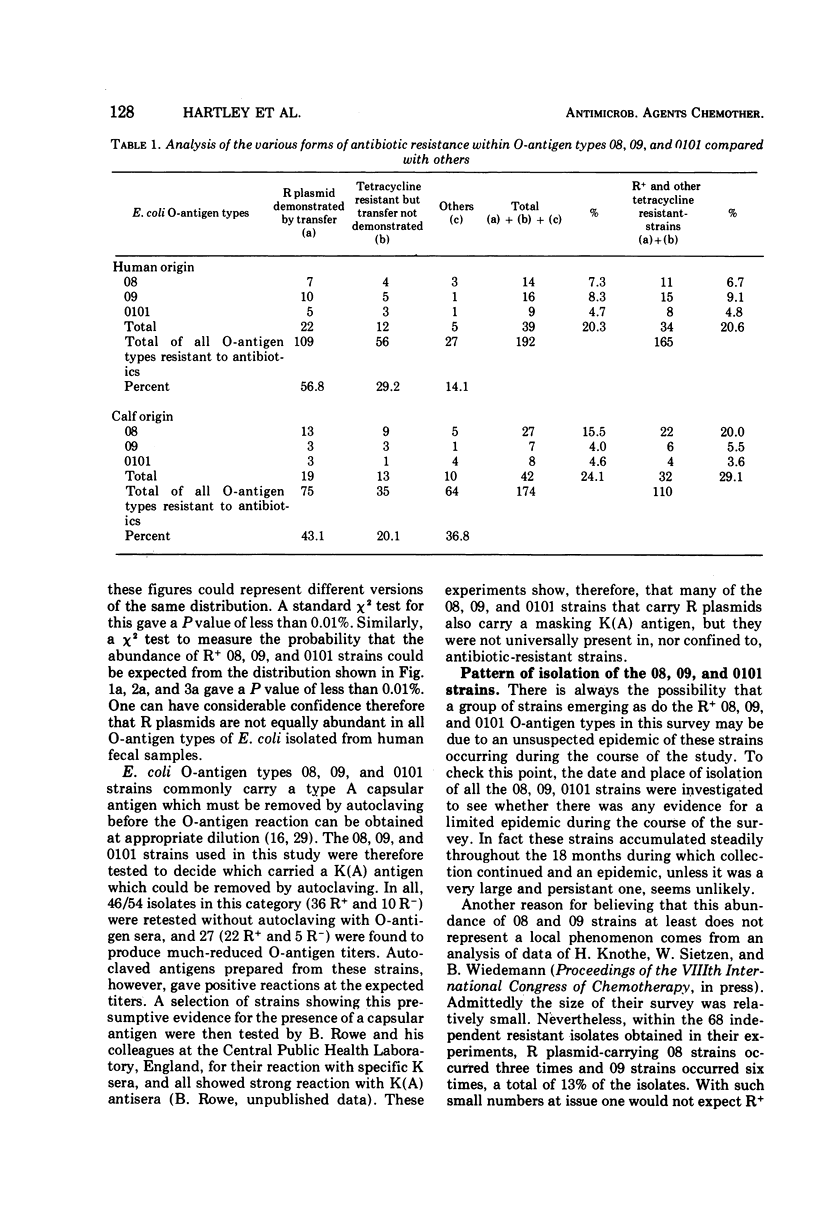
The O-antigen types of 600 independently isolated Escherichia coli strains from human feces have been determined, and the types have been related to the antibiotic resistance patterns of the strains. The relative abundance of each O-antigen type differed in the susceptible and resistant series of strains. The majority (86%) of the resistant strains carried R plasmids. Resistant E. coli (20.3%) were found associated with O-antigen types 8, 9 and 101, whereas the susceptible strains covered a wide range of O-antigen types. Examination of 174 resistant strains isolated from calf feces also showed a prevalence of O-antigen types 8, 9, 101 (24.1%), and it seems probable that strains expressing these three O-antigen types commonly carry R plasmids in the alimentary tracts of man and calves. The number of strains not typeable with the O sera available were similar in the human (12.5%) and the calf (11.5%) series. There are no grounds for distinguishing “human” from “calf” E. coli on the basis of their O-antigen reactions.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Lewis M. J. Characterization of a transfer factor associated with drug resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):843–849. doi: 10.1038/208843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S. The ecology of transferable drug resistance in the enterobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:131–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim K. A., Bushrod F. M., Chandler M. E., Cooke E. M., O'Farrell S., Shooter R. A. Escherichia coli serotype distribution in man and animals. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Dec;73(3):467–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N. Drug resistance and R factors in the bowel bacteria of London patients before and after admission to hospital. Br Med J. 1969 May 17;2(5654):407–411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5654.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Lilly H. A., Lowbury E. J. Gram-negative bacilli in burns. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Nov;22(6):634–641. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.6.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J. Resistance of Escherichia coli to tetracyclines. Changes in permeability to tetracyclines in Escherichia coli bearing transferable resistance factors. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):371–378. doi: 10.1042/bj1050371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A. Prevalence of extrachromosomal drug resistance. Bacterial drug resistance in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:40–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Meynell G. G. High frequency of antibiotic-resistant enterobacteria in the River Stour, Kent. Lancet. 1974 Aug 24;2(7878):451–453. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91829-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton K. B., Lee P. A., Richmond M. H., Gillespie W. A., Rowland A. J., Baker V. N. Antibiotic resistance and transmissible R-factors in the intestinal coliform flora of healthy adults and children in an urban and a rural community. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Mar;70(1):99–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton K. B., Richmond M. H., Bevan R., Gillespie W. A. Antibiotic resistance and R factors in coliform bacilli isolated from hospital and domestic sewage. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Feb;7(1):91–103. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhouse E. C., O'Grady M. F., O'Connor H. Isolation from sausages of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli with R factors. Lancet. 1969 Jul 5;2(7610):50–52. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92614-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Some environmental consequences of the use of antibiotics: or 'what goes up must come down'. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;35(2):155–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. R. Infectious drug resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from healthy farm animals. Lancet. 1966 Dec 10;2(7476):1300–1302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91705-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. R., Lewis L. E. Contamination of fresh and cooked meats by antibiotic-resistant coliform bacteria. Lancet. 1971 Jul 31;2(7718):255–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92586-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. R. The public health implications of drug-resistant bacteria in farm animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:358–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann B., Knothe H. Untersuchungen über die Stabilität der Koliflora des gesunden Menschen. 1. Uber das Vorkommen permanenter und passanter Typen. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1969 Aug;153(4):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



