Abstract
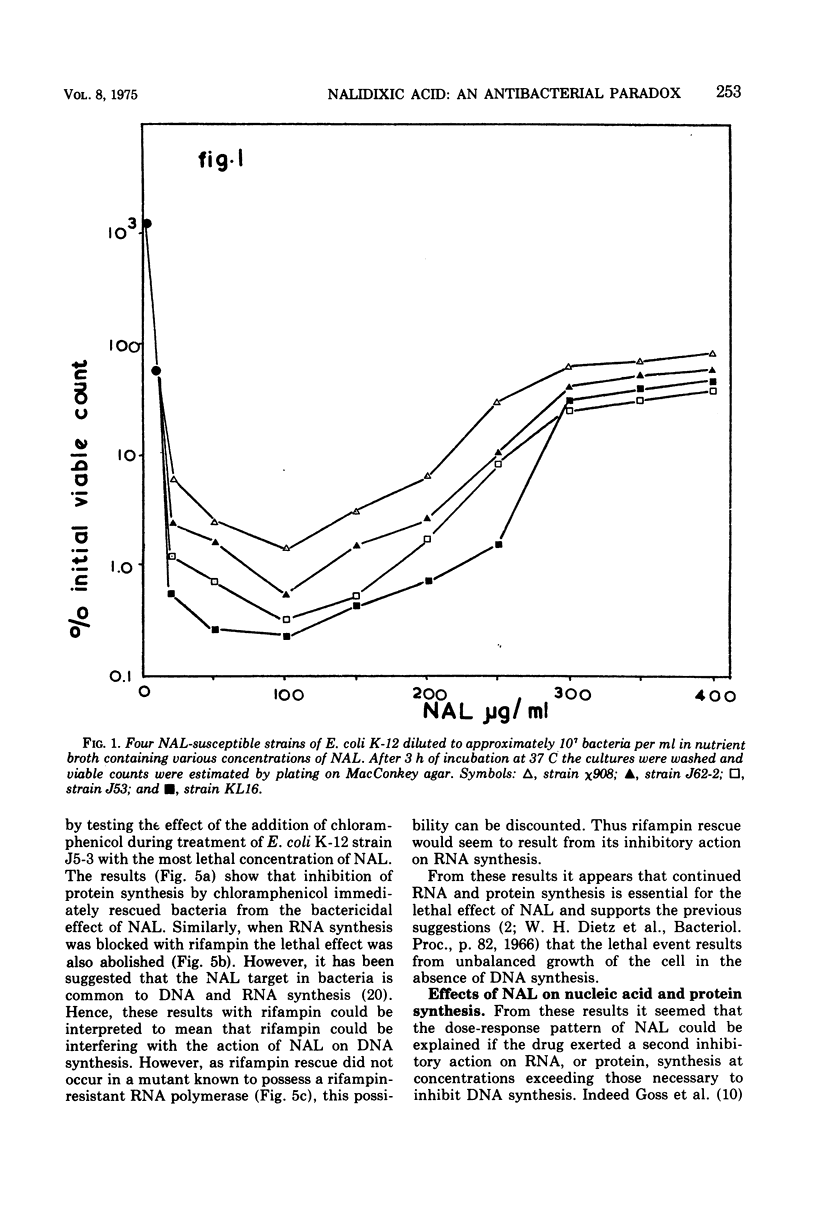
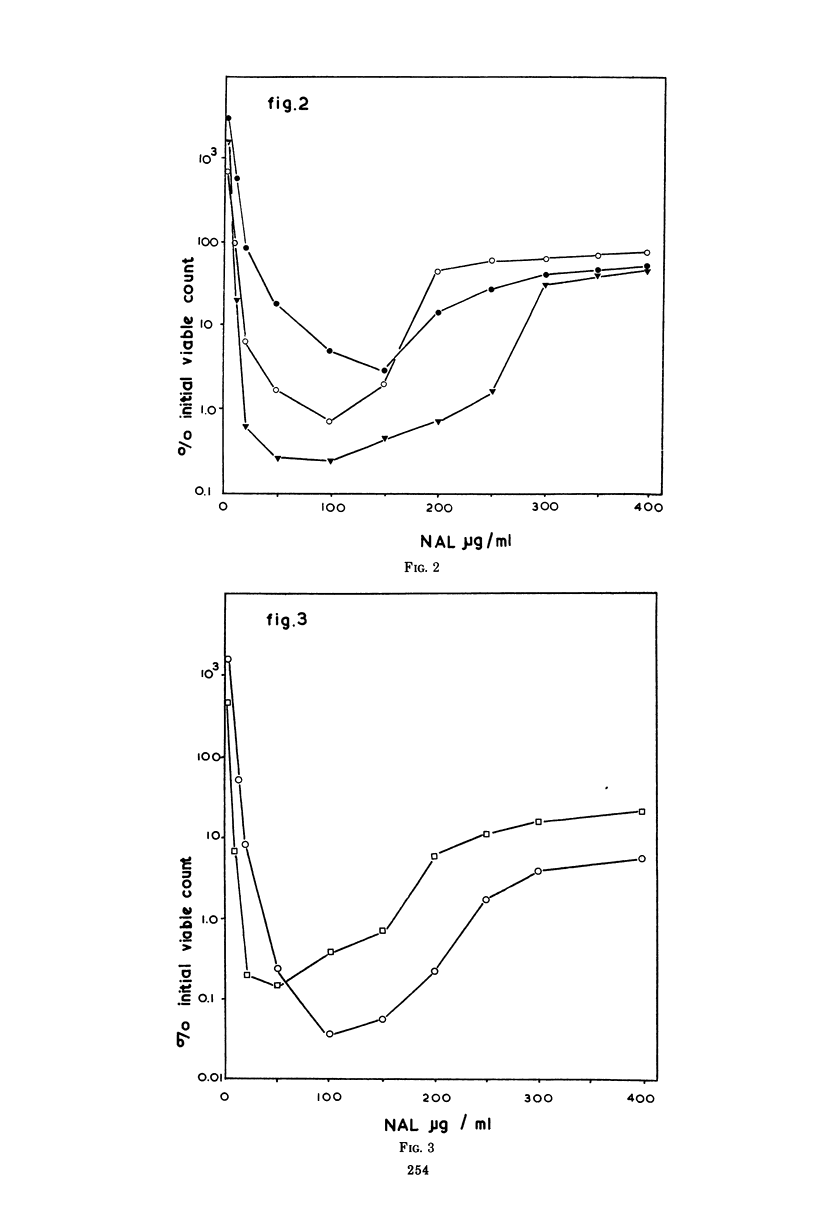
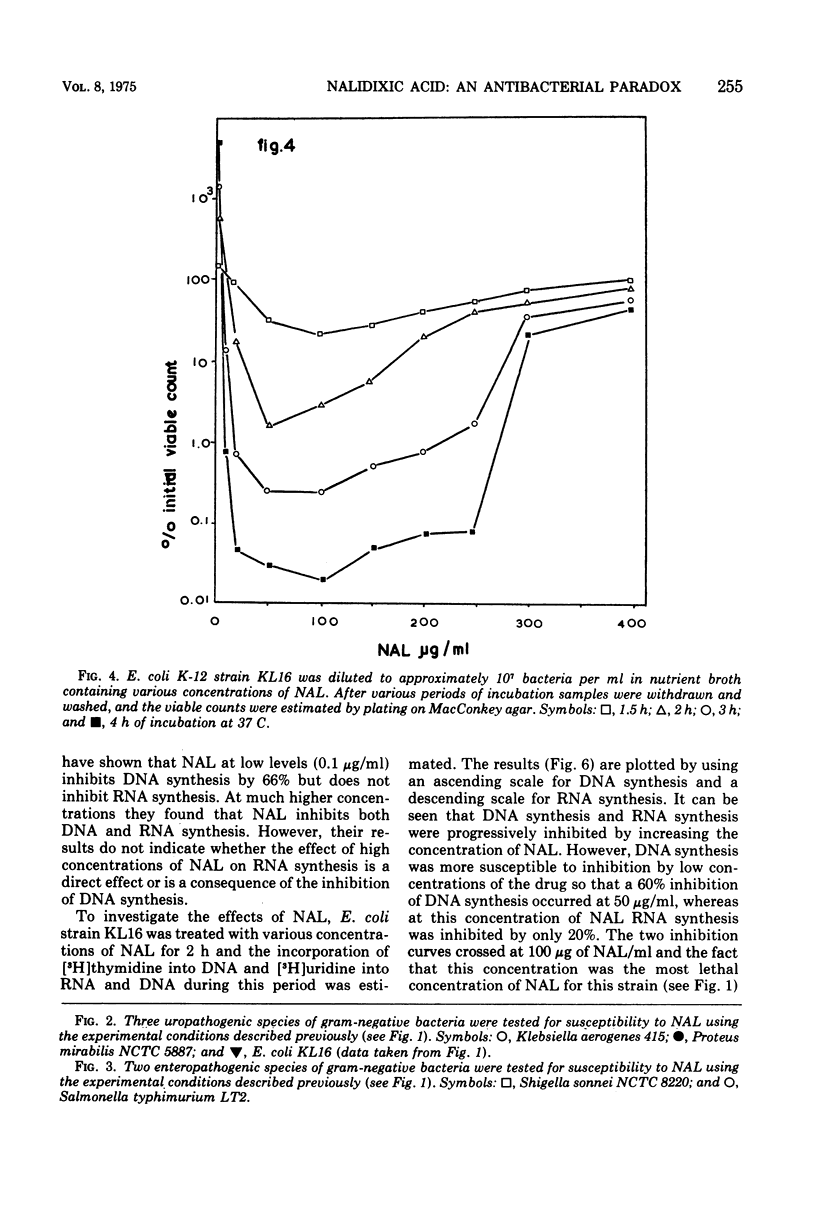
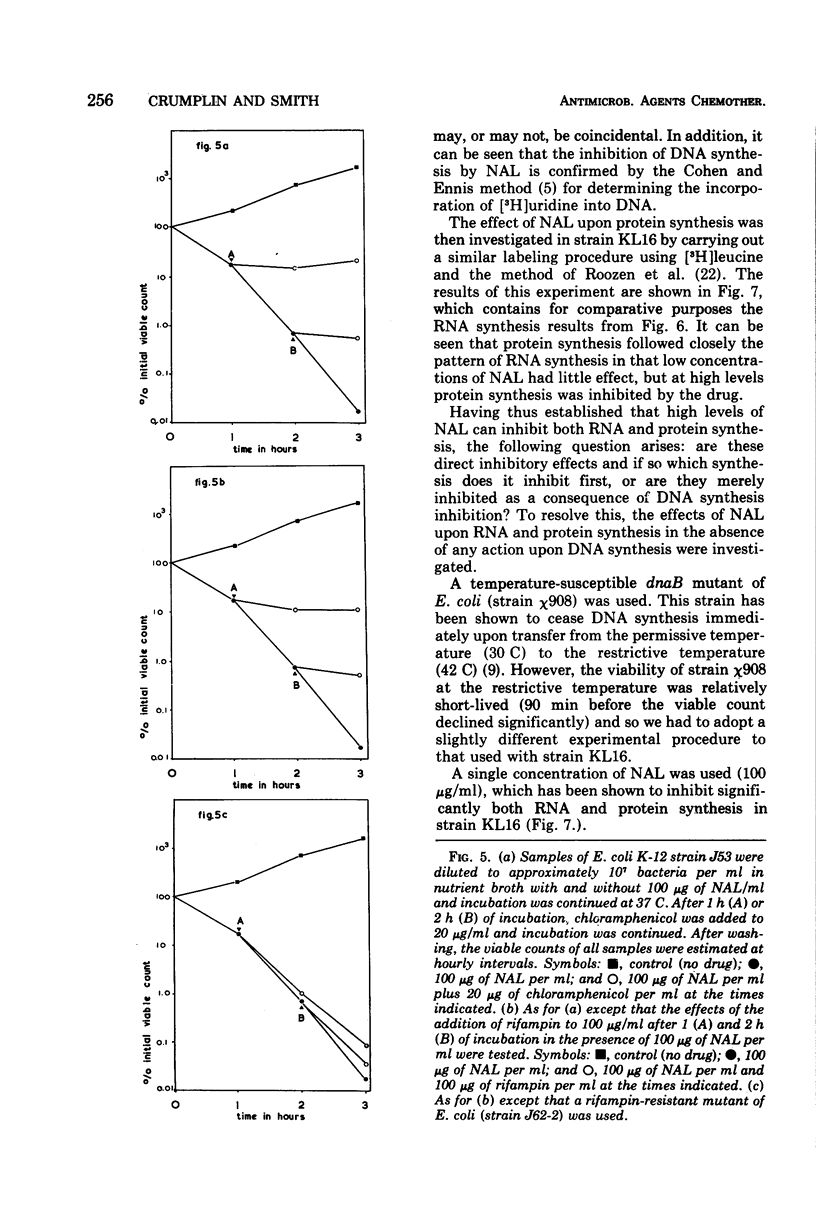
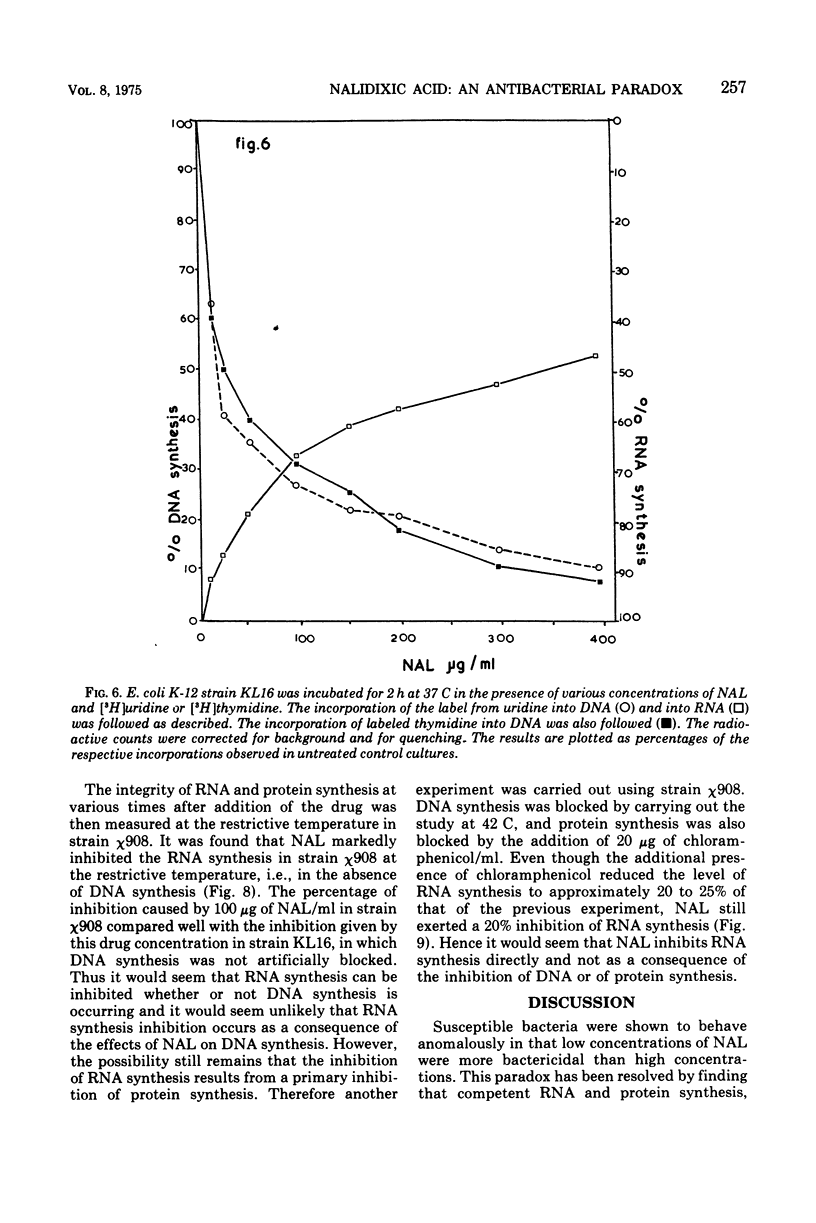
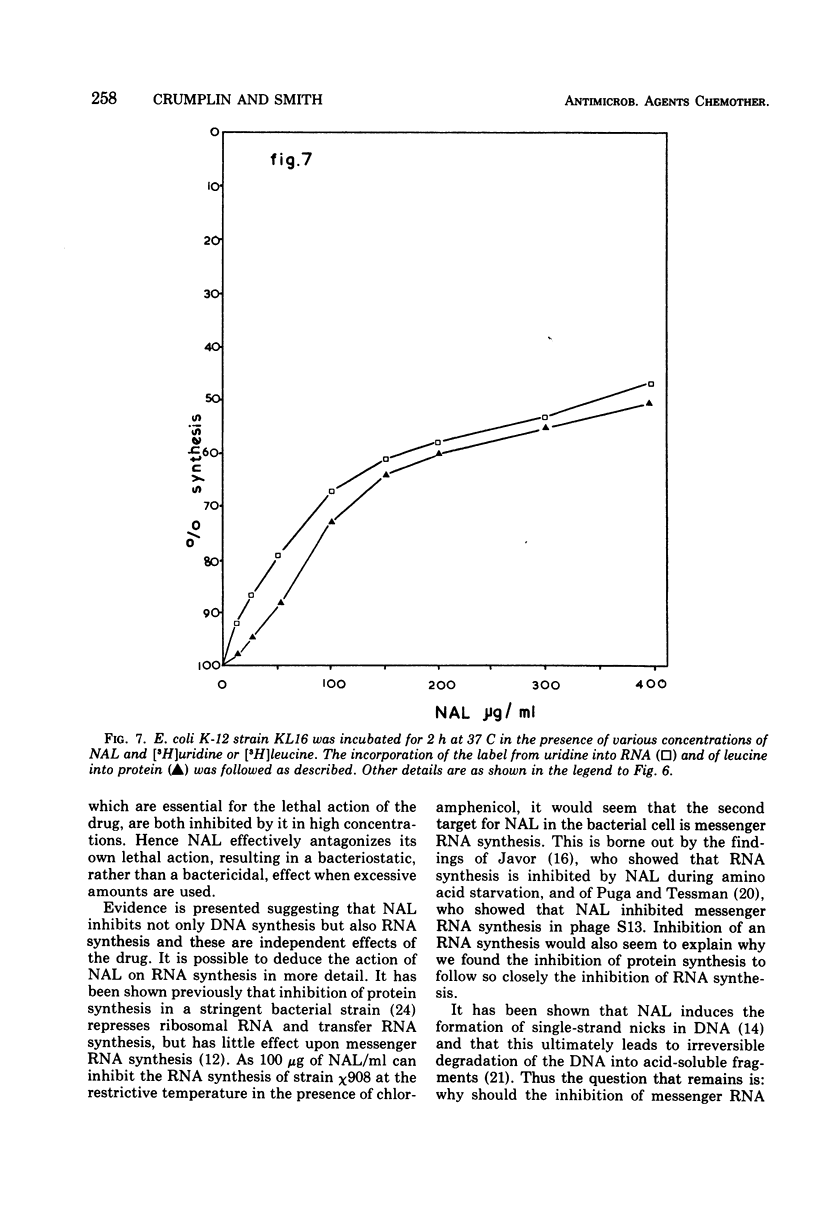
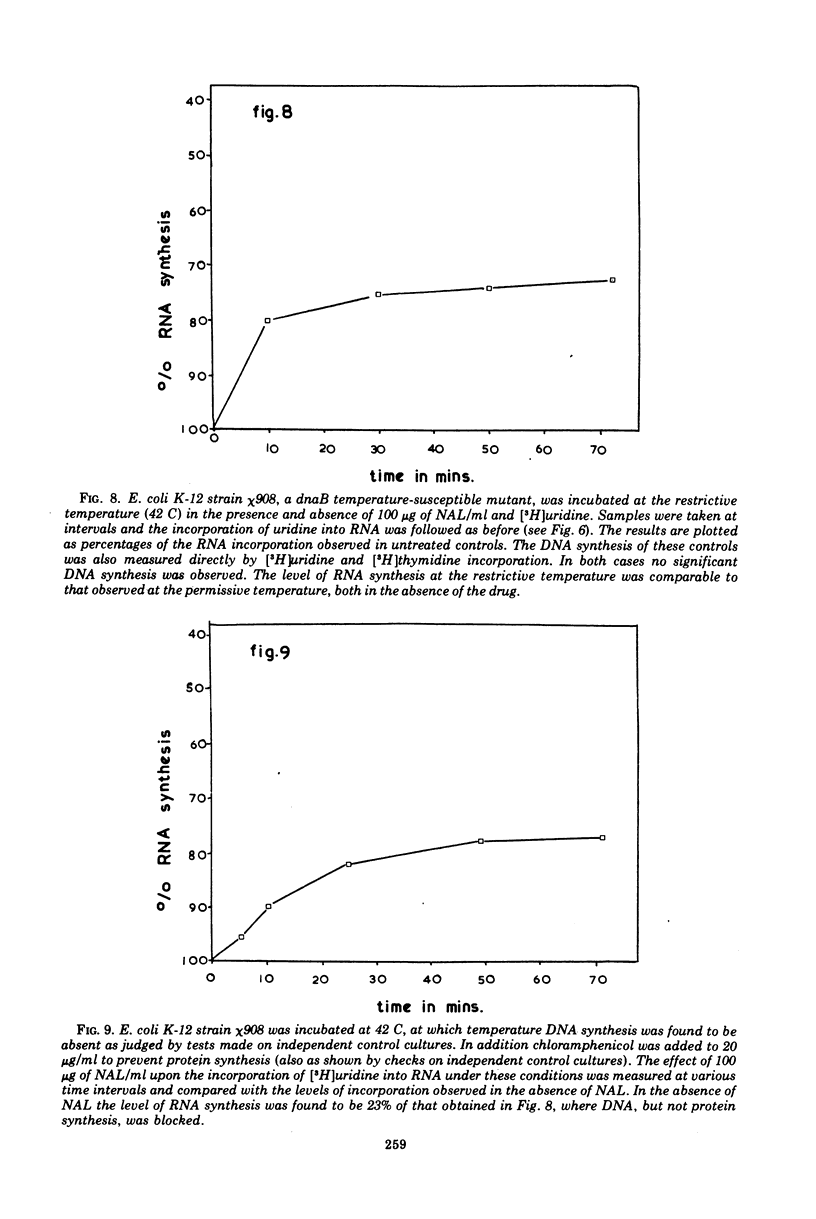
Nalidixic acid was found to be most bactericidal against various species of gram-negative bacteria at 50 to 200 μg/ml. With all species tested, increases in the concentration of nalidixic acid above this range reduced, rather than increased, its bactericidal effect so that, at levels in the region of 400 μg/ml, the drug was relatively bacteriostatic. Therefore, the mode of action of nalidixic acid at various concentrations was investigated. It was found that at the most bactericidal concentration deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, but no ribonucleic acid (RNA) or protein synthesis, was inhibited. However at higher concentrations, where the drug is least bactericidal, both RNA and protein synthesis were found to be inhibited. Results are presented which suggest that the protein synthesis inhibition is a secondary manifestation of the ability of the drug to inhibit RNA synthesis, and that of RNA synthesis is most likely the second target site for the action of the drug when bacteria are exposed to it in high concentrations. The clinical implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Grümmer G. Biochemical effects of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. Chemotherapy. 1965;10(2):95–102. doi: 10.1159/000220398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazill G. W. Lethal unbalanced growth in bacteria. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):346–349. doi: 10.1038/216346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Levitt M., Sternglanz R. Studies on the mechanism of action of nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):479–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. The requirement for potassium for bacteriophage T4 protein and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Trimethoprim resistance conferred by W plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitz W. H., Cook T. M., Goss W. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on Escherichia coli. 3. Conditions required for lethality. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):768–773. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.768-773.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick R. G., Jr, Curtiss R., 3rd Conjugal deoxyribonucleic acid replication by Escherichia coli K-12: stimulation in dnaB(ts) donors by minicells. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1212–1223. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1212-1223.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI.II. INHIBITION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1068-1074.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAWALT P. C. Involvement of synthesis of RNA in thymineless death. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:286–286. doi: 10.1038/198286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Modes of resistance to benzylpenicillin and ampicillin in twelve Klebsiella strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Fangman W. L. Single-strand breaks in deoxyribonucleic acid and viability loss during deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis inhibition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1329-1335.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javor G. T. Inhibition of ribonucleic acid synthesis by nalidixic acid in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):282–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.282-286.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCHESNEY E. W., FROELICH E. J., LESHER G. Y., CRAIN A. V., ROSI D. ABSORPTION, EXCRETION, AND METABOLISM OF A NEW ANTIBACTERIAL AGENT, NALIDIXIC ACID. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1964 May;6:292–309. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(64)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini A. M., Geroldi D., Siccardi A., Falaschi A. Studies on the mode of action of nalidixic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Tessman I. Mechanism of transcription of bacteriophage S13. II. Inhibition of phage-specific transcription by nalidixic acid. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 25;75(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramareddy G., Reiter H. Specific loss of newly replicated deoxyribonucleic acid in nalidixic acid-treated Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):724–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.724-729.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roozen K. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Curtiss R., 3rd Synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in plasmid-containing minicells of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):21–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.21-33.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., IYER V. N. CROSSLINKING OF DNA BY ENZYMATICALLY OR CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCINS, BIFUNCTIONALLY "ALKYLATING" ANTIBIOTICS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:946–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Whitmer J. D., Davern C. I. Genetic control of DNA initiation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. L., White J. R. Interaction of streptonigrin with DNA in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):648–651. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winshell E. B., Rosenkranz H. S. Nalidixic Acid and the Metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1168–1175. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1168-1175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


