Abstract
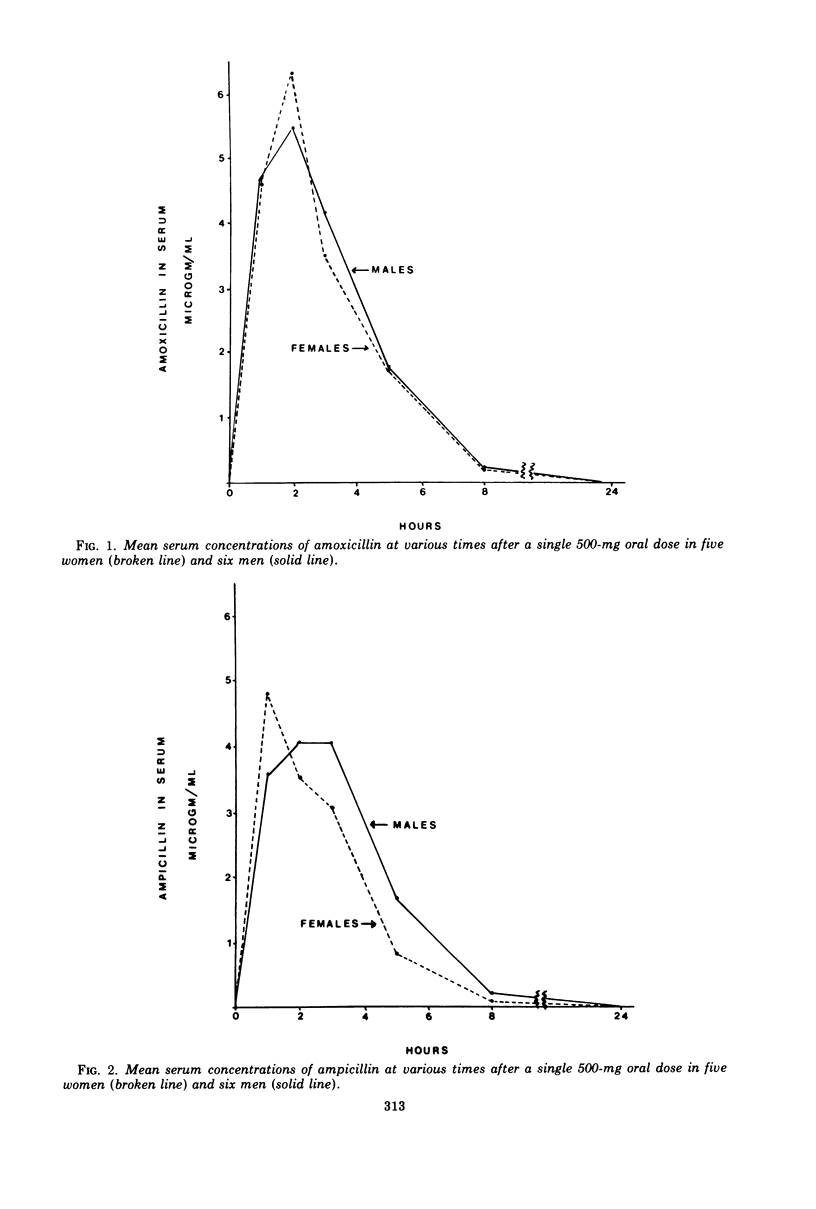
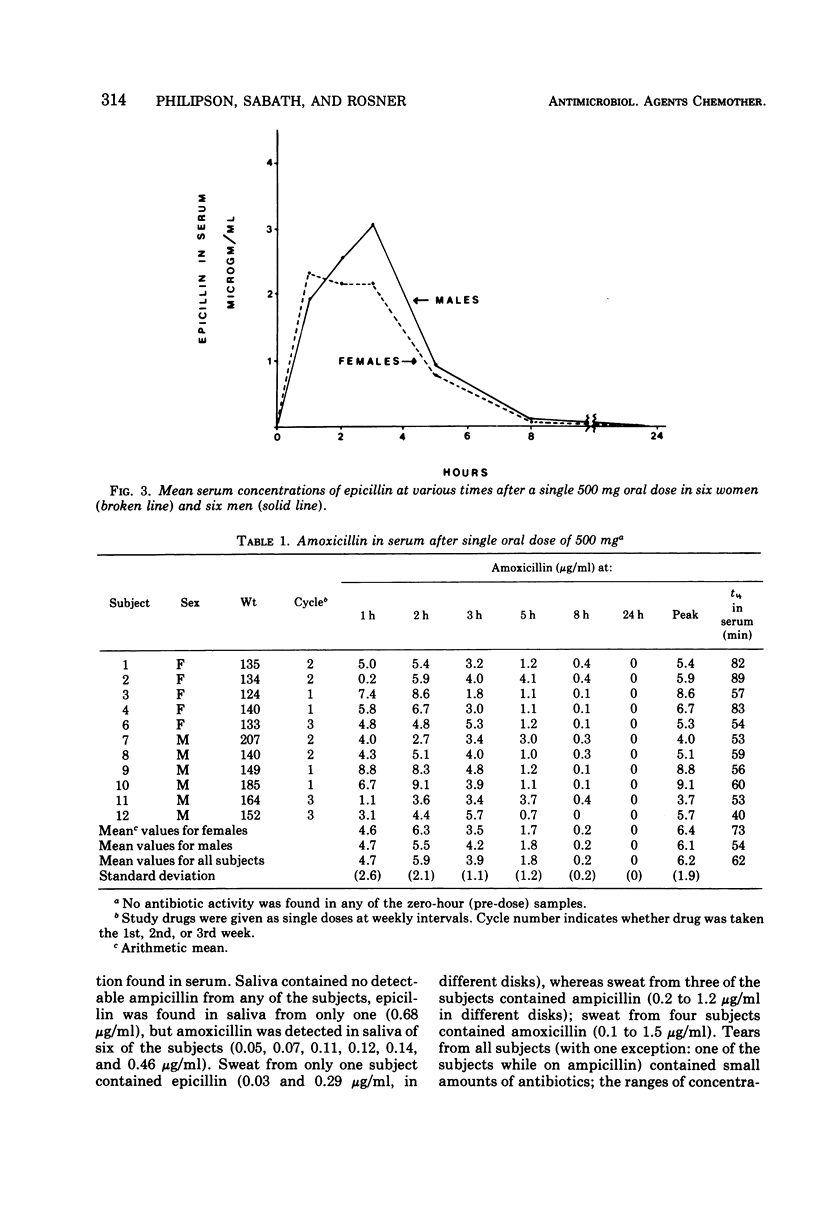
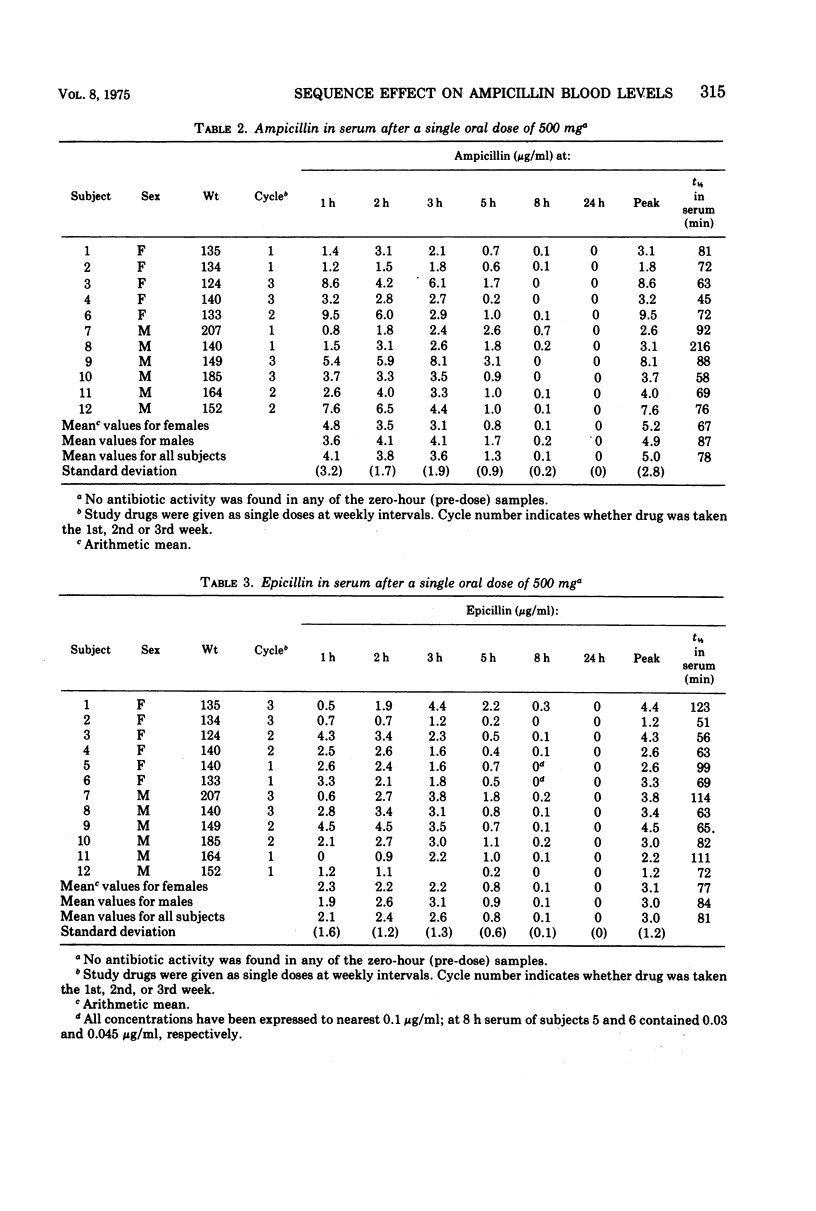
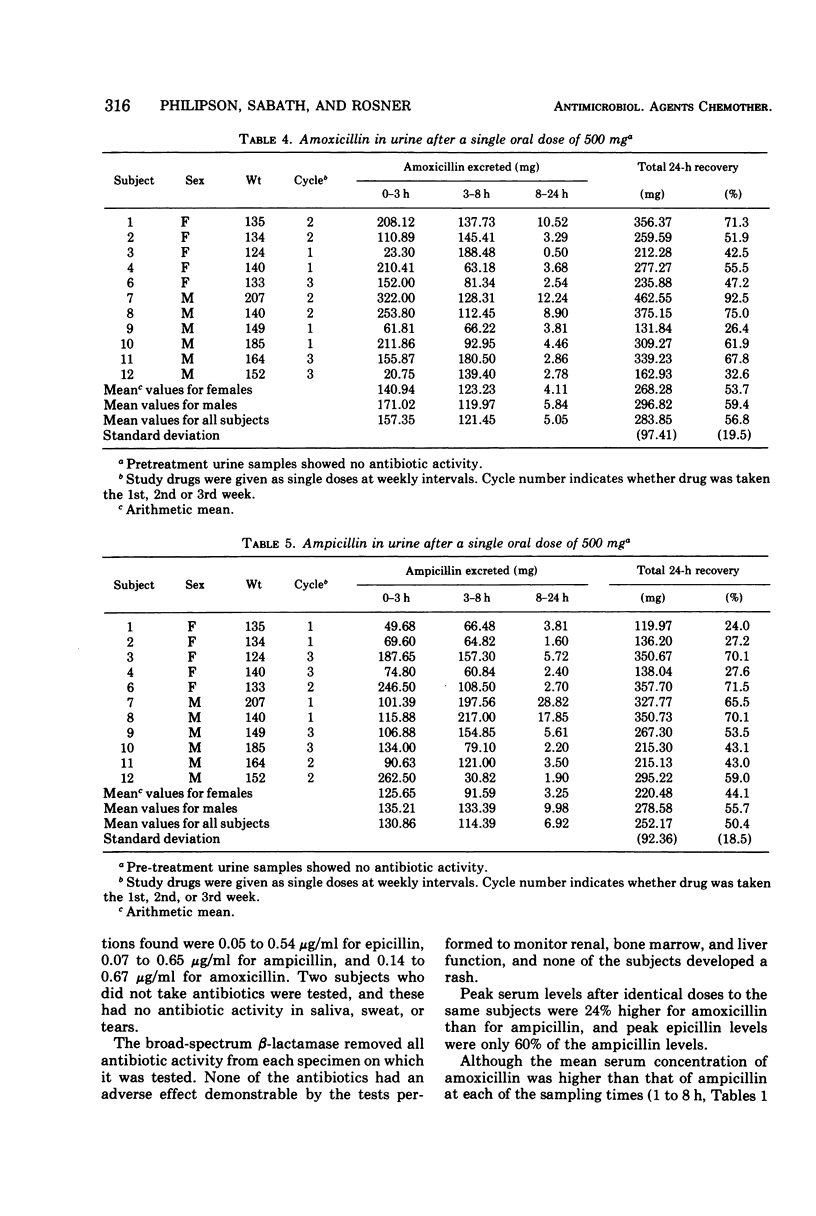
Amoxicillin, ampicillin, and epicillin (500 mg of each) were given orally to fasting men and women in a triple crossover study. Peak serum concentrations were significantly higher for amoxicillin than for ampicillin and significantly lowest for epicillin. The concentrations of antibiotics in serum were comparable in men and women. Total urine recovery was highest for amoxicillin (56.7%) and lowest for epicillin (27.5%), and higher in men than in women for each of the three antibiotics. Saliva, sweat, and tears contained only very small amounts of amoxicillin and, rarely, ampicillin or epicillin. A significant (P < 0.02) sequence effect was noted in that peak serum concentrations of ampicillin were higher (6.4 μg/ml) if epicillin had been taken the previous week than when ampicillin was taken first (2.7 μg/ml).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Nance J. Amoxicillin: in vitro and pharmacological studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):358–362. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H., Miraglia G., Pansy F., Renz K. Epicillin: experimental chemotherapy, pharmacodynamics, and susceptibility testing. Infect Immun. 1971 Jul;4(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.1.50-53.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Comparative clinical pharmacology of amoxicillin and ampicillin administered orally. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):504–507. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN J. O., FINLAND M. Ampicillin activity in vitro and absorption and excretion in normal young men. Am J Med Sci. 1963 May;245:544–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNUDSEN E. T., ROLINSON G. N., STEVENS S. Absorption and excretion of "Penbritin". Br Med J. 1961 Jul 22;2(5246):198–200. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5246.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M., Kind A. C. Clinical pharmacology of ampicillin and hetacillin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Finkelberg Z. Oral cephalexin and ampicillin: antimicrobial activity, recovery in urine, and persistence in blood of uremic patients. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):349–356. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara S., Adams E. P., Abraham E. P. The composition of beta-lactamase I and beta-lactamase II from Bacillus cereus 569-H. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(3):475–480. doi: 10.1042/bj1180475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Foltz E. L., Wallick H., Kwan K. C. Pharmacokinetics of pivampicillin and ampicillin in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Jul;16(1):35–43. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974161part135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Casey J. I., Ruch P. A., Stumpf L. L., Finland M. Rapid microassay of gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and vancomycin in serum or plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Finland M. Thiol-group binding of zinc to a beta-lactamase of Bacillus cereus: differential effects on enzyme activity with penicillin and cephalosporins as substrates. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1513–1519. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1513-1519.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. Triple crossover study on absorption and excretion of ampicillin, pivampicillin, and amoxycillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):588–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



