Abstract
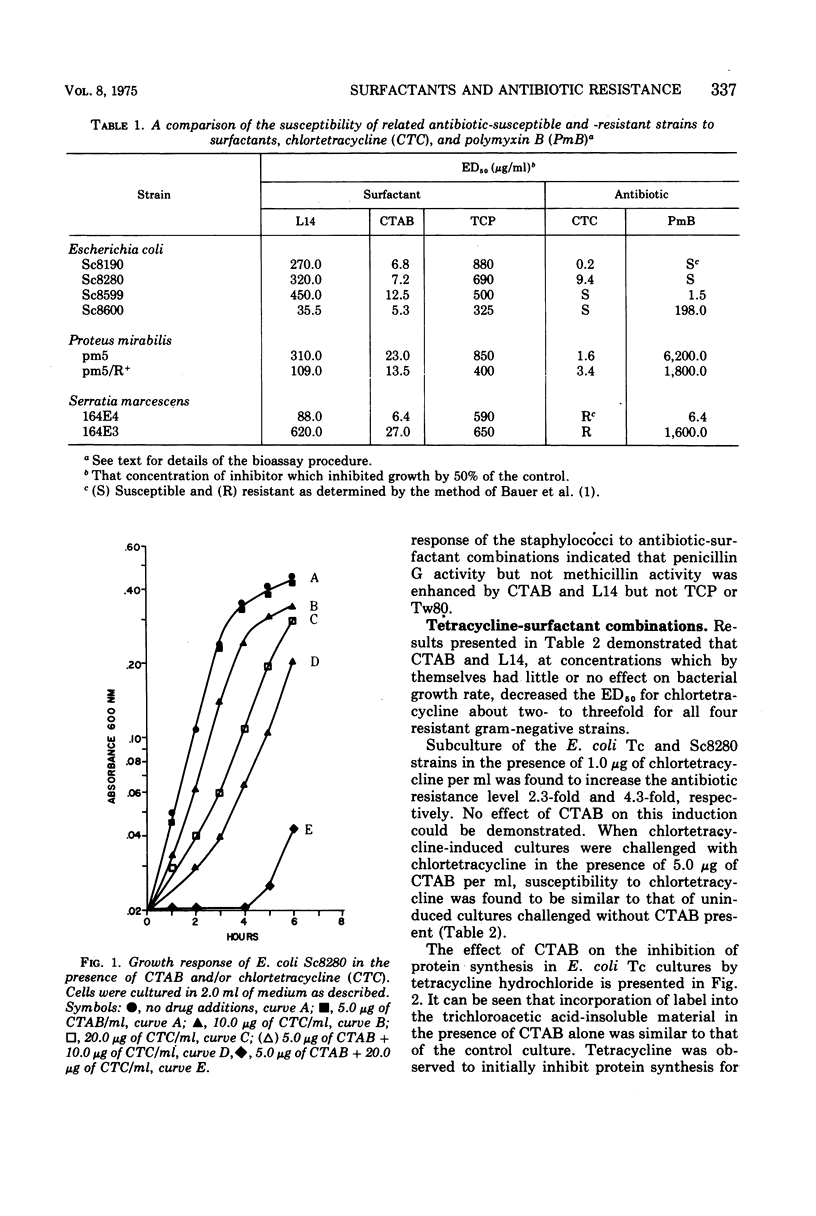
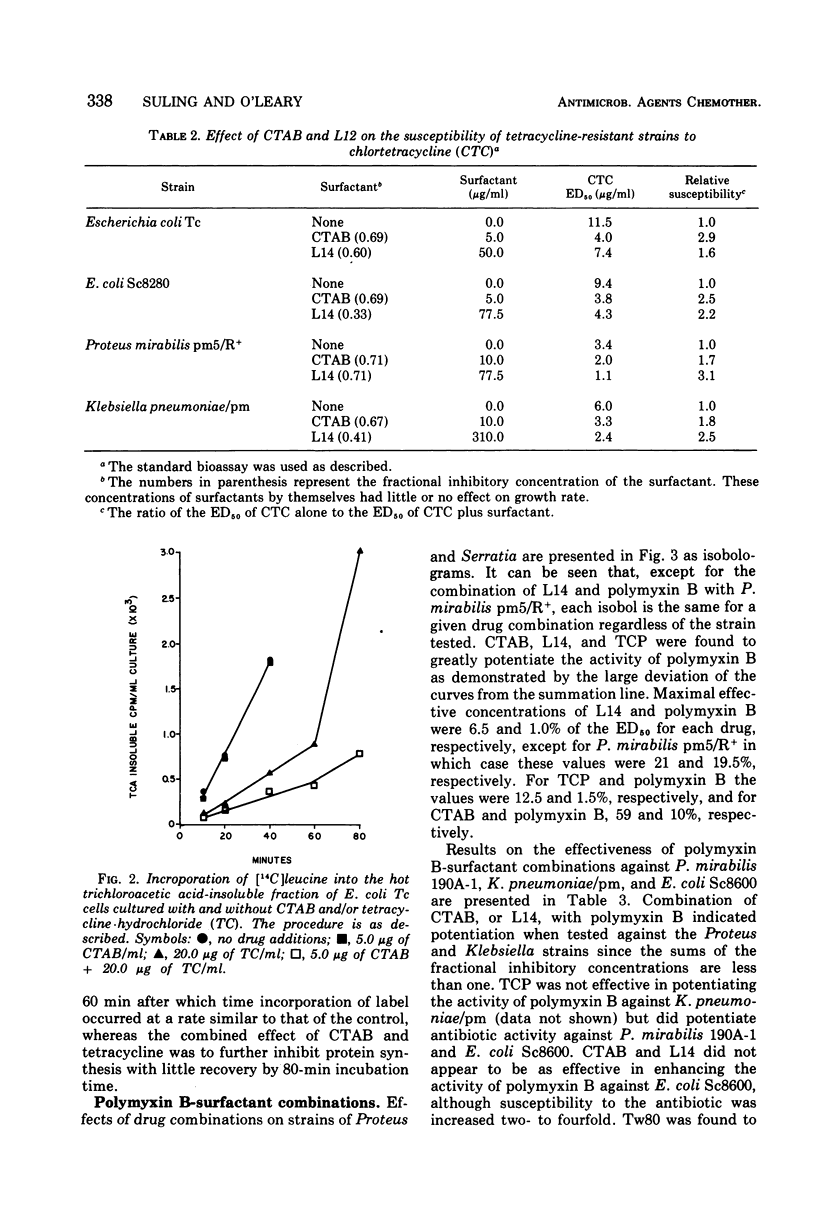
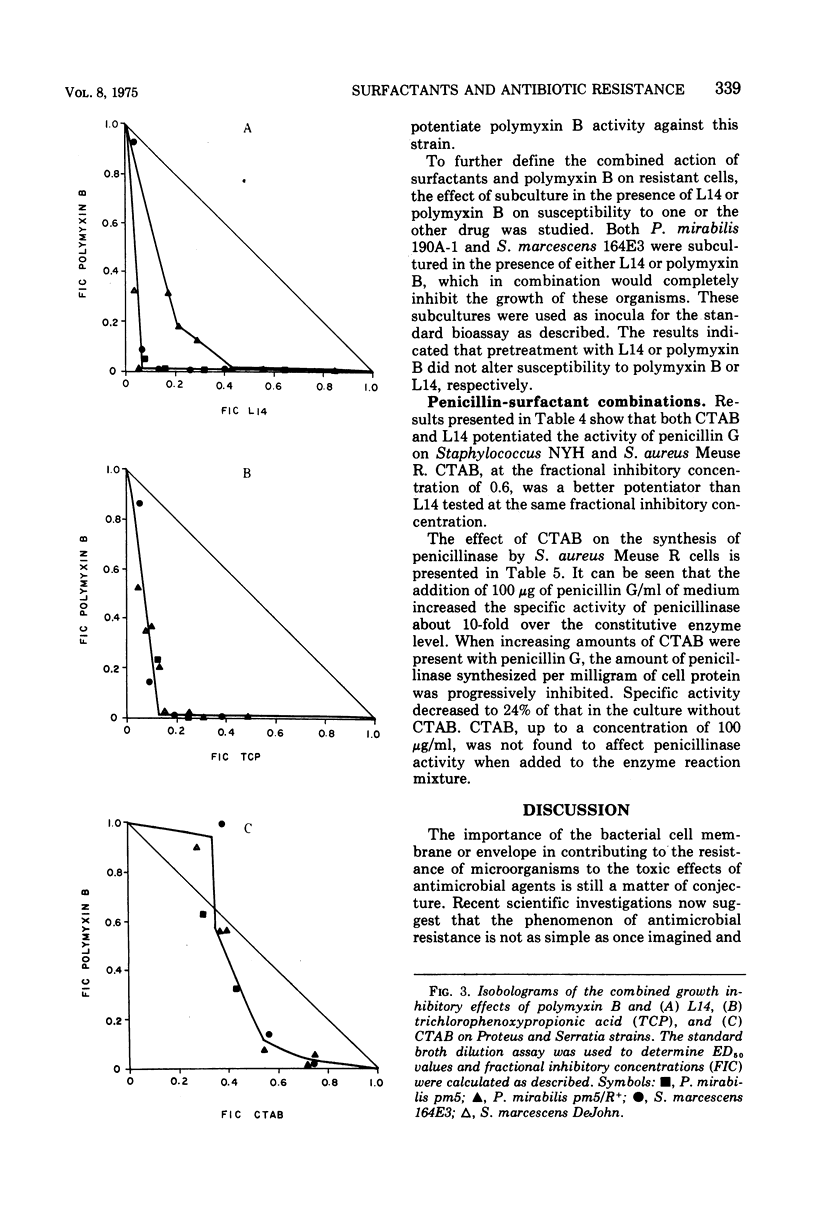
The effectiveness of surfactants as potentiators of antibiotic activity on several resistant strains of bacteria, selected from clinical sources and laboratory collections, was studied using a tube dilution assay. Bacterial strains included members of the Enterobacteriaceae and staphylococci. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), Tween 80 (Tw80), a mixture of n-alkyldimethyl betaines (L14), and alpha-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy) propionic acid (TCP) were tested in combination with pencillin G (PenG), methicillin (Met), streptomycin (Sm), polymyxin B (PmB), and chlortetracycline (CTC). Growth response to the drug combinations was compared with the response to each drug alone. CTAB and L14 but not Tw80 or TCP were found to potentiate the activity of CTC on strains of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Studies on the inhibition of protein synthesis by CTC in cells of a strain of E. coli suggested that the surfactants increased the uptake of antibiotic into the cells. CTAB and L14 almost completely sensitized strains of P. mirabilis, Serratia marcescens, K. pneumoniae, and E. coli to PmB. With the exception of K. pneumoniae, TCP was also effective in potentiating the activity of PmB on the above strains whereas Tw80 showed potentiation only with a strain of E. coli. CTAB and L14 but not TCP or Tw80 potentiated the activity of PenG but not Met on strains of staphylococci. Studies of penicillinase in the cells suggested that the surfactants inhibited the formation of this enzyme possibly at the level of induction. None of the surfactants were found to potentiate the activity of Sm.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLISS E. A., WARTH P. T. The effect of surface-active agents on antibiotics: an informal report. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Aug;53(1):38–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb31929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Winsley B. E. Synergism between polymyxin and polysorbate 80 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Nov;68(3):367–373. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick J. K., O'Leary W. M. Correlation of bacteria lipid composition with antibiotic resistance. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):892–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.892-900.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Foster S. J. Effect of osmotic shock on tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli bearing an R-factor. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):287–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1210287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Damaging effects of ethylenediaminetetra-acetate and penicillins on permeability barriers in Gram-negative bacteria. Biochem J. 1966 Sep;100(3):675–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1000675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsande J. Repressor and antirepressor in the regulation of staphylococcal penicillinase synthesis. Genetics. 1973 Sep;75(1):1–17. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMINSKI Z. C. EFFECT OF RELATED ANIONIC DETERGENTS ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL PENICILLINASE. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1182–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1182-1183.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski C., Shapiro B. M. Isolation and some properties of cell envelope altered mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):495–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.495-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragoudakis M. E. On the mode of action of lipid-lowering agents. VI. Inhibition of lipogenesis in rat mammary gland cell culture. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):4046–4052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monner D. A., Jonsson S., Boman H. G. Ampicillin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with lipopolysaccharide alterations affecting mating ability and susceptibility to sex-specific bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):420–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.420-432.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordarska H., Tkaczowa A., Matej M., Mordarski M. Cell lipids and sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(2):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Gustafson L. Antibiotic, detergent, and complement sensitivity of Salmonella typhi after ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid treatment. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2010–2013. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2010-2013.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin F. A., Smith D. H. Characterization of R factor beta-lactamases by the acidimetric method. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Effect of polymyxin B on antibiotic-resistant Proteus mirabilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 May;1(5):417–421. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.5.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Mechanism of polymyxin B resistance in Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):289–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.289-294.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. Increase in sensitivity to antibiotics and lysozyme on deletion of lipopolysaccharides in Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):453–454. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.453-454.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M. Susceptibility to polymyxin B in penicillin G-induced Proteus mirabilis L forms and spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):347–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.347-350.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng J. T., Bryan L. E. Mechanisms of R factor R931 and chromosomal tetracycline resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 May;3(5):638–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.5.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S. The transport of beta-galactosides across the membrane of permeaseless Escherichia coli ML35 cells after treatment with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):533–541. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Vagelos P. R. Saturated fatty acid biosynthesis and its regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:21–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss J. G. Effects of organic cations on the gram-negative cell wall and their bactericidal activity with ethylenediaminetetra-acetate and surface active agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Sep;48(3):391–400. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser R., Wimpenny J., Asscher A. W. Synergistic effect of edetic-acid/antibiotic combinations on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1969 Sep 20;2(7621):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90328-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousef R. T., Ghobashy A. A. Solubilization of chloramphenicol by benzalkonium chloride and study of their combined activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Pharm Suec. 1968 Sep;5(4):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



