Abstract
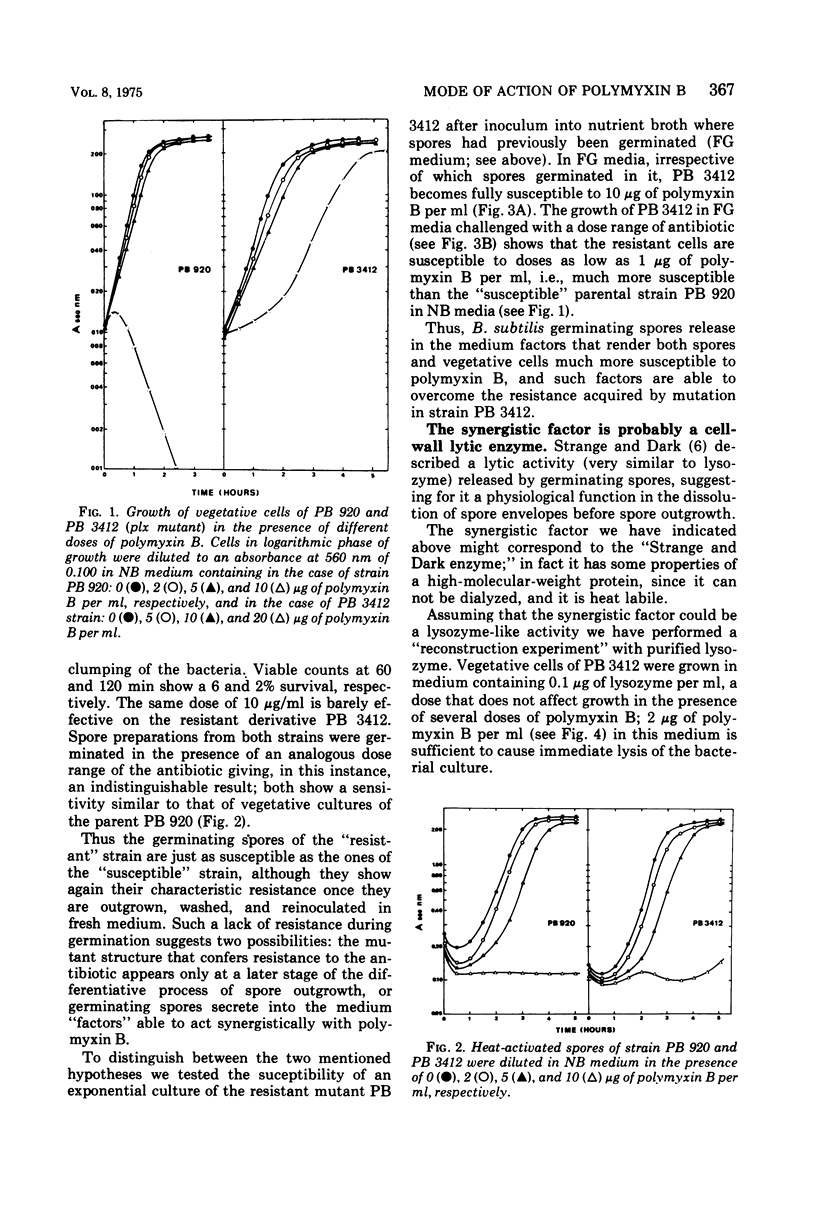
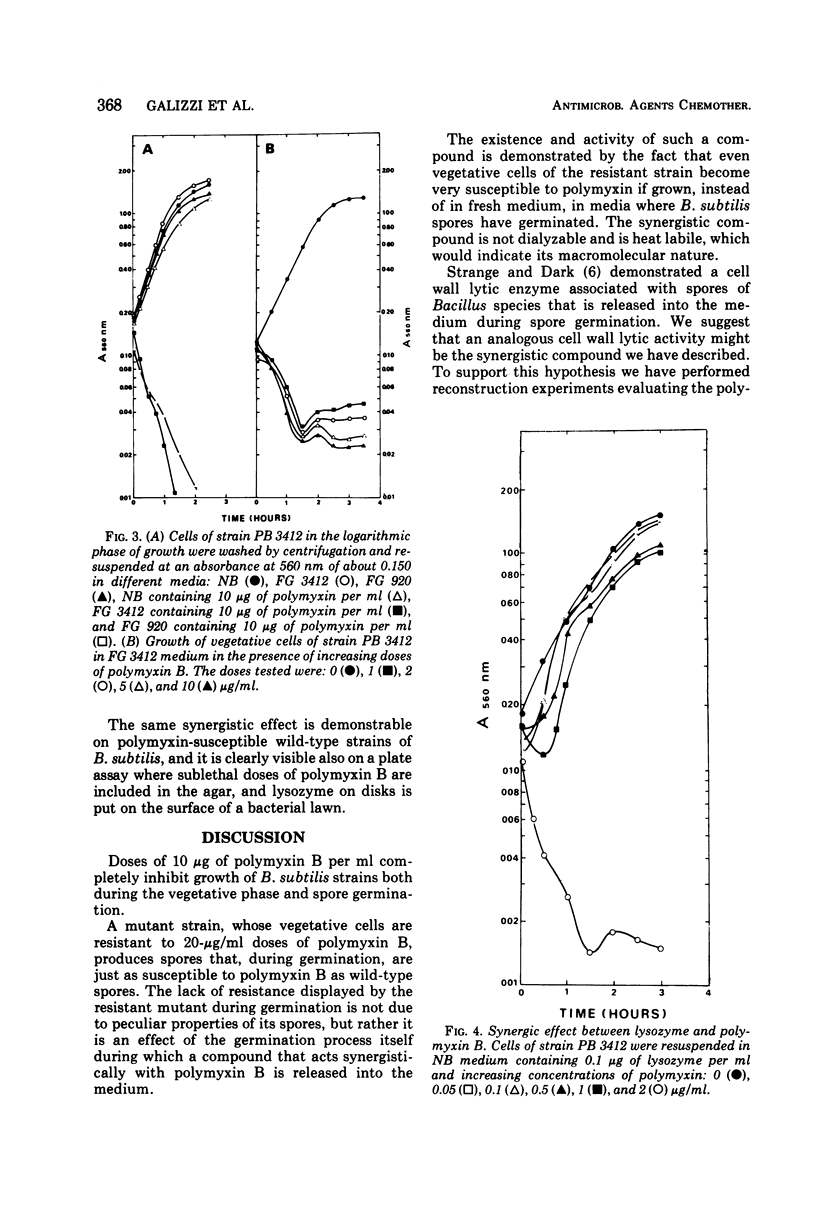
Polymyxin B resistance in Bacillus subtilis can be suppressed by the synergistic action of lysozyme or of an analogous cell wall lytic activity released by B. subtilis spores during germination.
Such a synergistic effect is probably due to partial cell-wall digestion by lysozyme that allows polymyxin to reach its site of action and is therefore distinct from the analogous synergistic effect described by other authors in Escherichia coli. In the latter case polymyxin B probably damaged the outer membrane, allowing lysozyme to reach and digest the cell wall.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FEW A. V., SCHULMAN J. H. Absorption of polymyxin by bacteria. Nature. 1953 Apr 11;171(4354):644–645. doi: 10.1038/171644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEW A. V., SCHULMAN J. H. The absorption of polymyxin E by bacteria and bacterial cell walls and its bactericidal action. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Dec;9(3):454–466. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-3-454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopy of effect of polymyxin on Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1128–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1128-1130.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. A fluorescent derivative of polymyxin: its preparation and use in studying the site of action of the antibiotic. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):226–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pache W., Chapman D., Hillaby R. Interaction of antibiotics with membranes: polymyxin B and gramicidin S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., DARK F. A. A cell-wall lytic enzyme associated with spores of Bacillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):236–249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M. Susceptibility to polymyxin B in penicillin G-induced Proteus mirabilis L forms and spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):347–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.347-350.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN G. H., GRAY J., YURCHENCO J. A. Effect of polymyxin on the lysis of Neisseria catarrhalis by lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):788–793. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.788-793.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


