Abstract
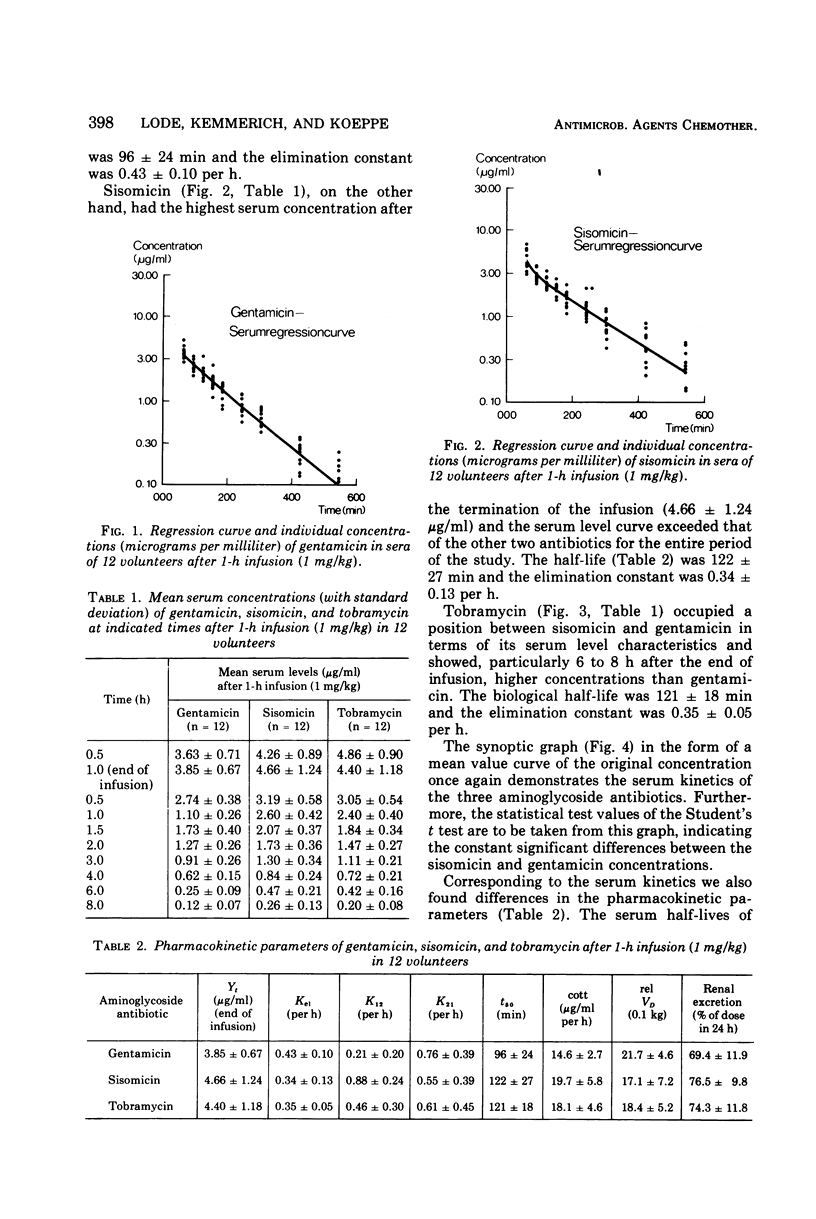
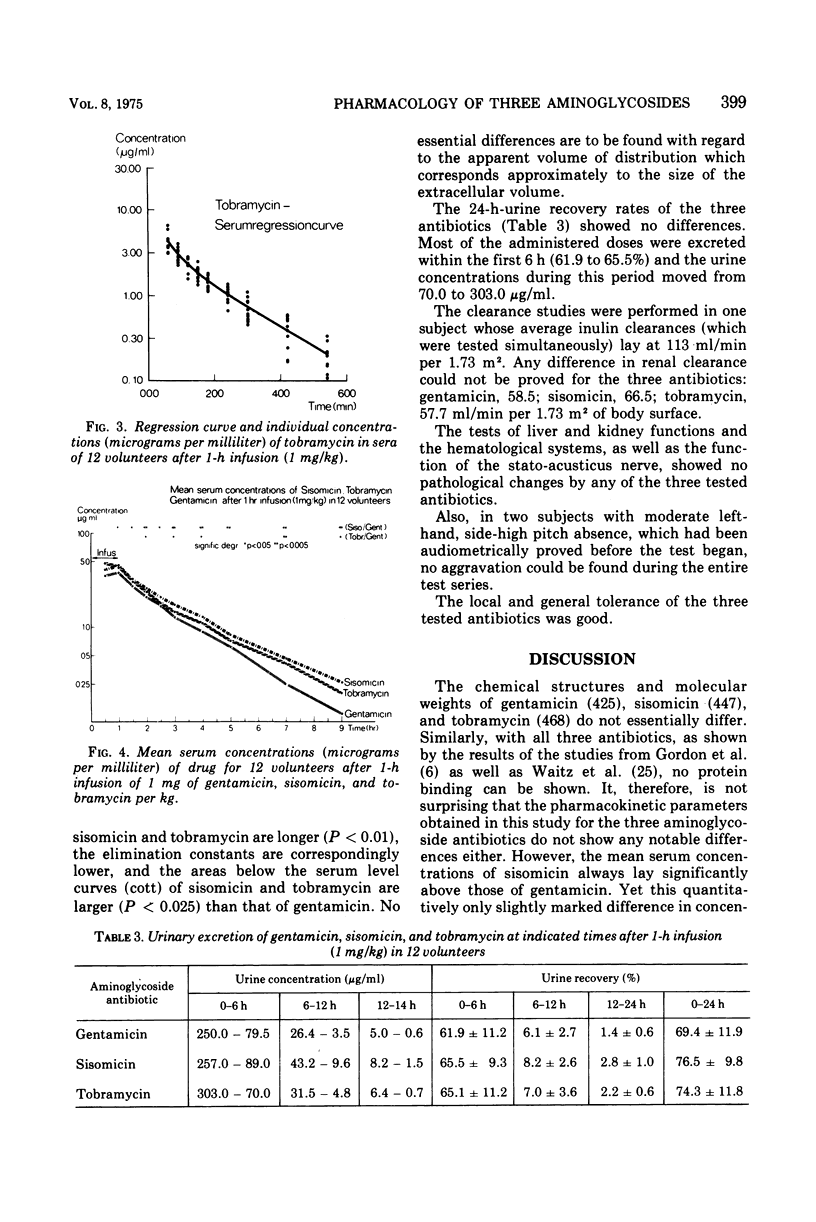
Using a randomized crossover design involving 12 normal subjects, we studied comparatively the pharmacokinetics and tolerance of three aminoglycoside antibiotics, gentamicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Serum concentrations were determined during 8 h and the urine recovery rate was determined within 24 h after a 1-h intravenous infusion of the respective antibiotic in a dose of 1 mg/kg of body weight. Microbiological assay was performed with the agar diffusion test (Bacillus subtilis); pharmacokinetic calculations were performed by means of a digital computer on the basis of a mathematical model of an open, two-compartment system. Of the three antibiotics studied, gentamicin showed the lowest concentration in serum after termination of the 1-h infusion (3.85 ± 0.67 μg/ml), and the serum-regression curve steadily lay below those of the two other antibiotics. Sisomicin had the highest serum concentrations (4,66 ± 1.24 μg/ml) and the serum-level curve exceeded that of the two other antibiotics. Tobramycin occupied a position between sisomicin and gentamicin in form of its serum level characteristics. Corresponding to the serum kinetics we also found slight differences in the pharmacokinetic parameters, especially in serum half-lives, elimination constants, and areas under the serum level curves. The test of liver and kidney functions and the hematological systems, as well as the function of the stato-acusticus nerve, showed no pathological changes by any of the three antibiotics tested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):109–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe C. C., Sanders E. Sisomicin: evaluation in vitro and comparison with gentamicin and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J., Neu H. C. In vitro studies of tobramycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jan;1(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. C., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Serum protein binding of the aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):214–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams P. J., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr In vitro bactericidal effectiveness of four aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):87–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAO R. L., JACKSON G. G. GENTAMICIN SULFATE, NEW ANTIBIOTIC AGAINST GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. LABORATORY, PHARMACOLOGICAL, AND CLINICAL EVALUATION. JAMA. 1964 Sep 14;189:817–822. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070110019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Levison M. E., Labovitz E. D. The unpredictability of serum concentrations of gentamicin: pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in patients with normal and abnormal renal function. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):150–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe P., Höffler D. Die Verwendung eines Digitalrechners zur Entwicklung von Dosierungsempfehlungen für eine Therapie mit Antibiotika. Arzneimittelforschung. 1972 Feb;22(2):311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood W. R., Bower J. D. Tobramycin and gentamicin concentrations in the serum of normal and anephric patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jan;3(1):125–129. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber K. G., Westenfelder S. R., Madsen P. O. Pharmacokinetics of the aminoglycoside antibiotic tobramycin in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):469–473. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann P., Auwärter W. Pharmakologische und therapeutische Eigenschaften von Gentamycin. Experimentelle Studien über Wirkstoffspiegel, Ausscheidung, Stabilität und therapeutische Indikationen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1968 Sep;18(9):1119–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Gordon R. C., Kirby W. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of tobramycin and gentamicin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 May-Jun;14(3):396–403. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973143396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Pharmacology of gentamicin in man. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S98–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon V. K., Mösinger E. U., Malerczy V. Pharmacokinetic studies of tobramycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):445–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford B. C., Dixson S., Cobcroft A. J. Serum levels of gentamicin and tobramycin after slow intravenous bolus injection. Lancet. 1974 Mar 9;1(7854):378–379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)93148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagman G. H., Testa R. T., Marquez J. A. Antibiotic 6640. II. Fermentation, isolation, and properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):555–558. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Drube C. G., Weinstein M. J. Comparative activity of sisomicin, gentamicin, kanamycin, and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):431–437. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Oden E. M., Weinstein M. J. Antibiotic 6640. 3. Biological studies with antibiotic 6640, a new broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Marquez J. A., Testa R. T., Wagman G. H., Oden E. M., Waitz J. A. Antibiotic 6640, a new Micromonospora-produced aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):551–554. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Activity of five aminoglycoside antibiotics in vitro against gram-negative bacilli and Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Dec;4(6):617–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



