Abstract
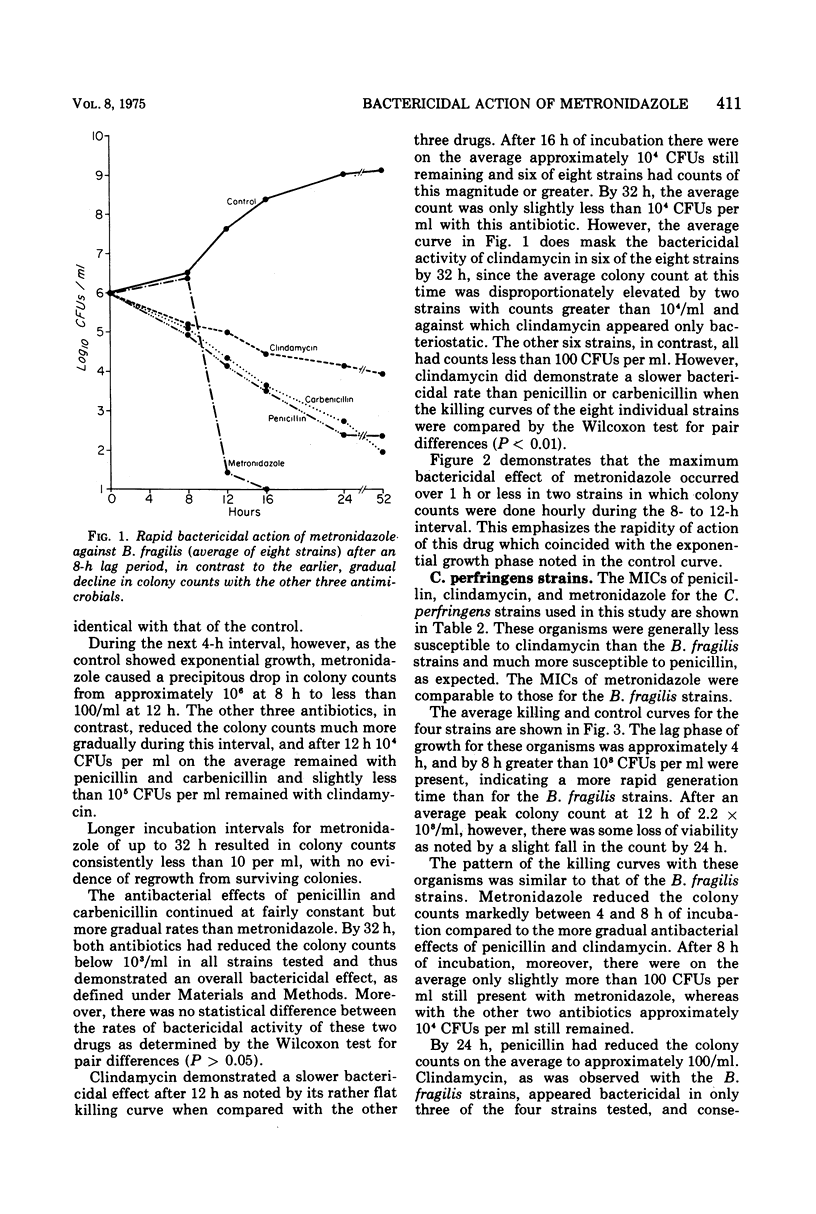
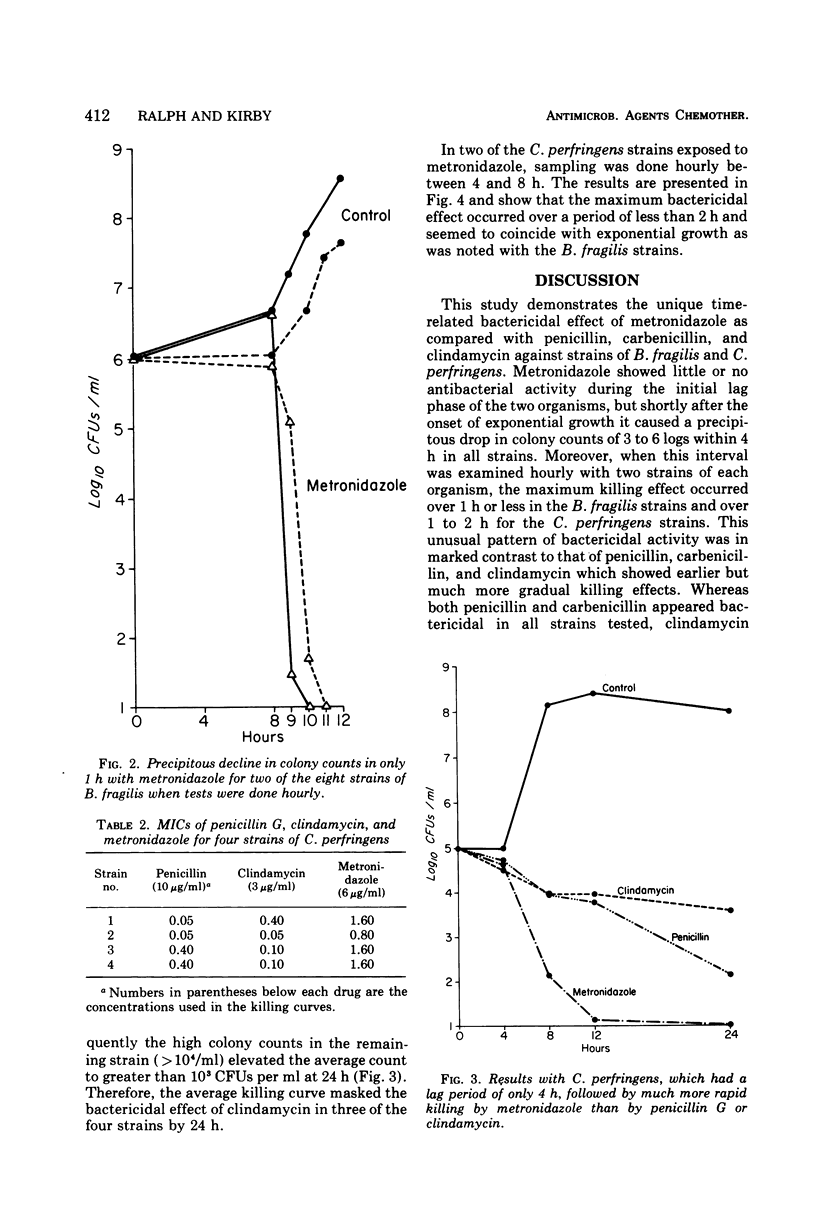
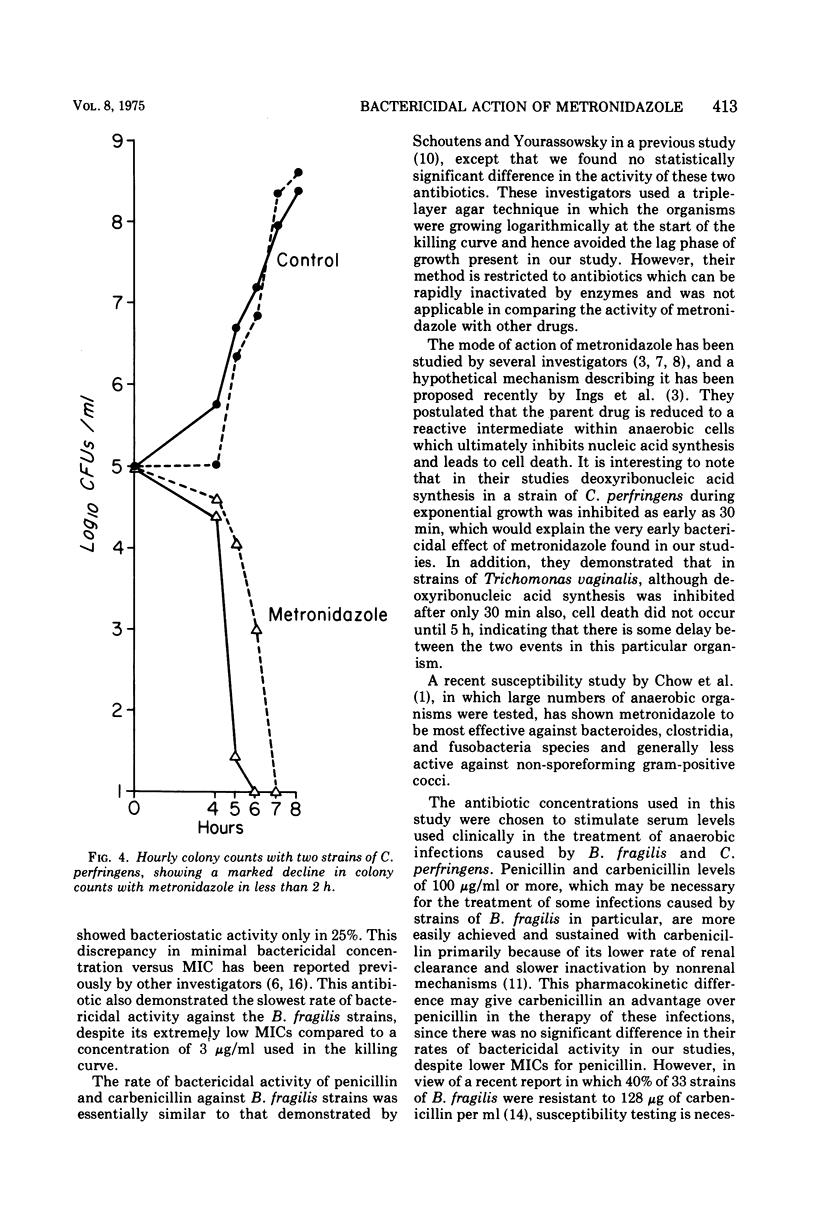
The comparative bactericidal activity of penicillin G, carbenicillin, clindamycin, and metronidazole against eight susceptible strains of Bacteroides fragilis and four strains of Clostridium perfringens was determined by performing colony counts anaerobically of cultures incubated in brucella broth. With the B. fragilis strains, there was a lag phase of growth of approximately 8 h, during which time metronidazole did not reduce the colony counts. However, within 4 h of the onset of exponential growth, metronidazole caused an abrupt decrease in counts to less than 100 colonies per ml in all strains tested. Moreover, in two strains in which the bactericidal rate was followed hourly, a 3- to 6-log decrease occurred over 1 h or less. In contrast, penicillin G and carbenicillin caused a gradual decline in colony counts from the start of approximately 1 log for each 8-h interval and were bactericidal for all strains tested. Clindamycin demonstrated the slowest bactericidal activity and for 25% of the strains was only bacteriostatic. With the C. perfringens strains, after a lag phase of 4 h, an abrupt decrease in colony counts also occurred with metronidazole, whereas penicillin and clindamycin again demonstrated more gradual killing effects. These studies showed a unique, time-related bactericidal action of metronidazole as compared with the other three antimicrobial agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow A. W., Patten V., Guze L. B. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to metronidazole: relative resistance of non-spore-forming gram-positive baccilli. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):182–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaan R. M., Metzler C. M., Schellenberg D., Vandenbosch W. D. Pharmacokinetic studies of clindamycin phosphate. J Clin Pharmacol. 1973 May-Jun;13(5):190–209. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The mode of action of metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis and other micro-organisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(9):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislak J. W. The susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to 24 antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):295–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastro L. J., Finegold S. M. Bactericidal activity of five antimicrobial agents against Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):104–107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. W., Morris J. G. Effect of metronidazole on hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):225–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00425200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. N., Grunberg E., Titsworth E., DeLorenzo W. F. Effects of l-(2-nitro-l-imidazolyl)-3-methoxy-2-propanol and 2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole-l-ethanol against anaerobic and aerobic bacteria and protozoa. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):728–730. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.728-730.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Clarke J. T., Libke R. D., Luthy R. P., Kirby W. M. Pharmacokinetics of metronidazole as determined by bioassay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):691–696. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoutens E., Yourassowsky E. Speed of bactericidal action of penicillin G, ampicillin, and carbenicillin on Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):227–231. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. C., Jordan M. C., Kirby W. M. Clinical pharmacology of carbenicillin compared with other penicillins. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(Suppl):S9–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.supplement_1.s9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Washington J. A., 2nd Antimicrobial susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria: recent clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Sep;6(3):311–315. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of penicillins against anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Apr;7(4):413–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J. P., Hale J. H. Bactericidal activity of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jun;26(6):393–395. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.6.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabransky R. J., Johnston J. A., Hauser K. J. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of various antibiotics against Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):152–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


