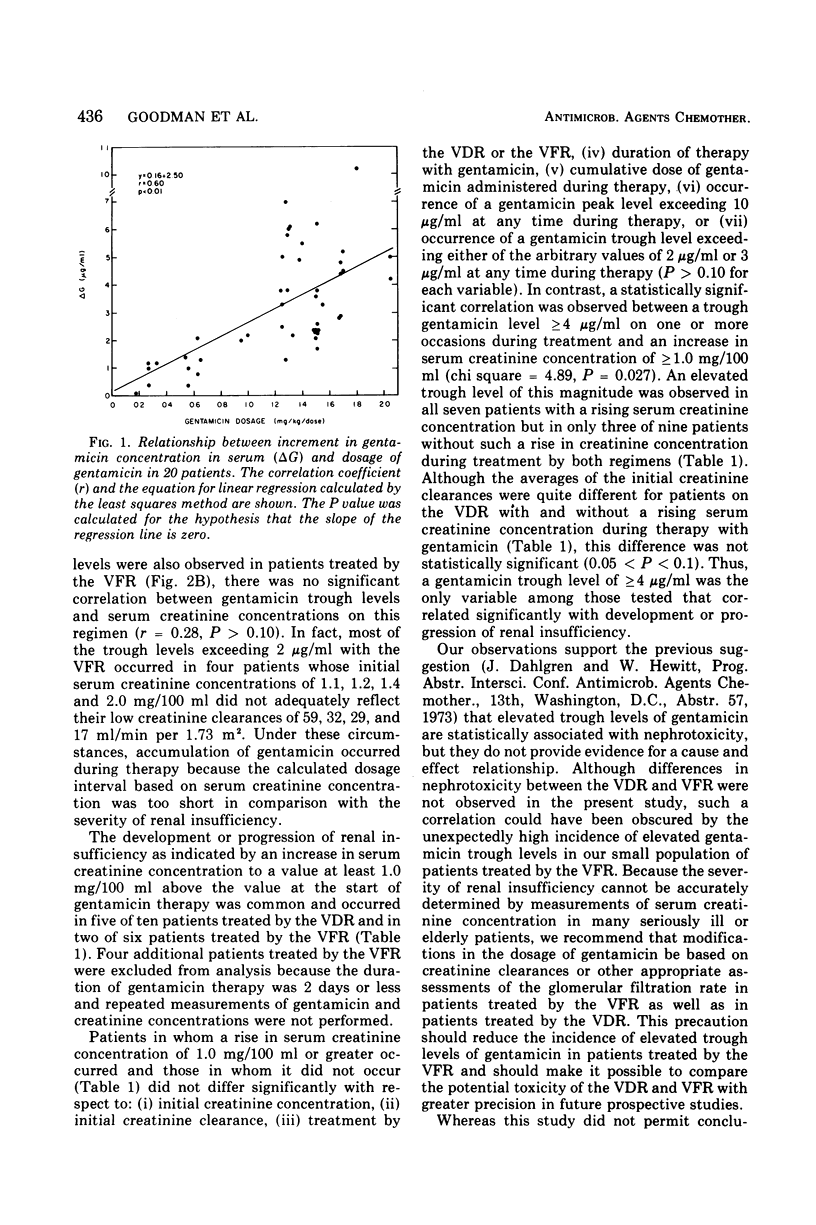
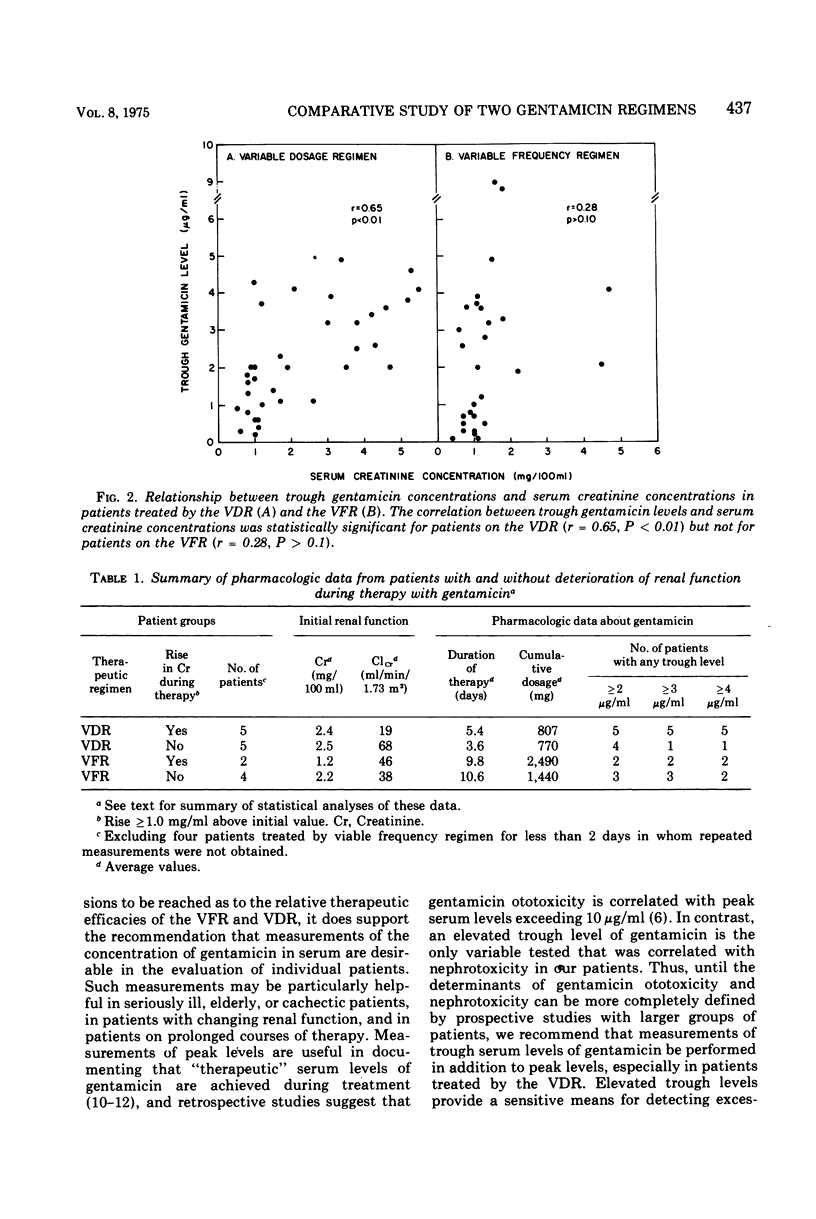
Abstract
In patients with impaired renal function, careful adjustment of gentamicin dosage is required to achieve therapeutic yet nontoxic concentrations. Two regimens that differ in pharmacodynamic characteristics have been recommended for this purpose: prolonging the intervals between administration of equal doses (variable frequency regimen [VFR]) or administering a loading dose followed at the usual intervals by reduced maintenance doses (variable dosage regimen [VDR]). These regimens were compared in a prospective, randomized study of 20 seriously ill hospitalized patients, 10 on VFR and 10 on VDR. Wide variability in peak serum levels of gentamicin was observed both between patients and in individual patients after separate injections of the same dosage. As predicted by the design of these regimens, the trough serum levels of gentamicin correlated significantly with the serum creatinine concentrations in patients on the VDR but not in patients on the VFR. A gentamicin trough level of ≥4 μg/ml was the only variable among those tested that correlated significantly with development or progression of renal insufficiency during treatment with gentamicin, but such trough levels were observed frequently on both regimens. Whereas this study does not permit a direct comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of VDR and VFR, no difference in the risk of nephrotoxicity with these regimens was observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcieri G. M., Falco F. G., Smith H. M., Hobson L. B. Clinical research experience with gentamicin. Incidence of adverse reactions. Med J Aust. 1970 Jun 13;1(Suppl):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. A., Benner E. J., Hoeprich P. D. Gentamicin therapy in renal failure: a nomogram for dosage. Ann Intern Med. 1972 May;76(5):773–778. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-5-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. E., Gyselynck A. M., Fleet W. P., Forrey A. W. Correlation of serum creatinine concentration and gentamicin half-life. JAMA. 1972 Feb 21;219(8):1037–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell J. C., Waterworth P. M. Dose of gentamicin in patients with normal renal function and renal impairment. Br Med J. 1968 Apr 6;2(5596):19–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5596.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Sanford J. P. Enzymatic assay for gentamicin and related aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):519–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G., Arcieri G. Ototoxicity of gentamicin in man: a survey and controlled analysis of clinical experience in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S130–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelliffe R. W. Letter: Creatinine clearance: bedside estimate. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Oct;79(4):604–605. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-4-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Levison M. E., Labovitz E. D. The unpredictability of serum concentrations of gentamicin: pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in patients with normal and abnormal renal function. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):150–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry M. C., Gavan T. L., Gifford R. W., Jr, Geurkink N. A., Van Ommen R. A., Town M. A., Wagner J. G. Gentamicin dosages for renal insufficiency. Adjustments based on endogenous creatinine clearance and serum creatinine concentration. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Feb;74(2):192–197. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-2-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone P., Parsons T. M., Pattison J. R., Slack R. C., Garfield-Davies D., Hughes K. Experience in monitoring gentamicin therapy during treatment of serious gram-negative sepsis. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 16;1(5906):477–481. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5906.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Jackson G. G. Pharmacology of gentamicin in man. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S98–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters R. E., Litwack K. D., Hewitt W. L. Relation between dose and levels of gentamicin in blood. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



