Abstract
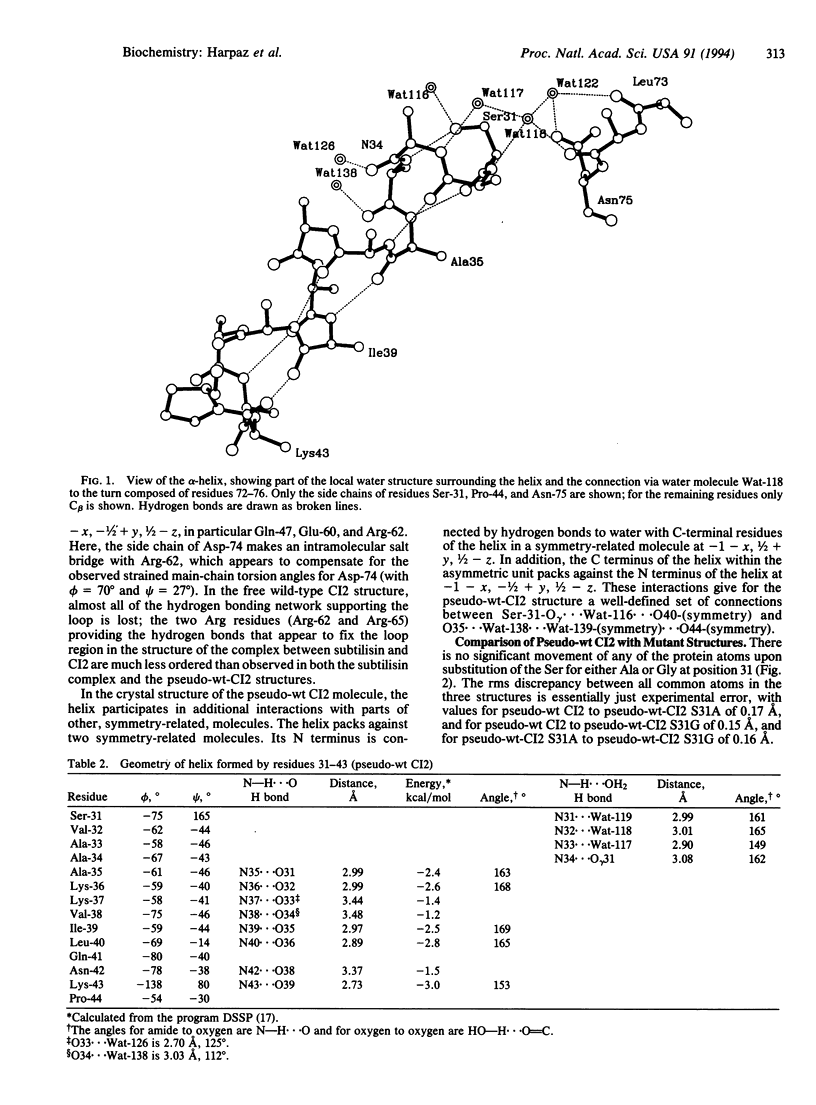
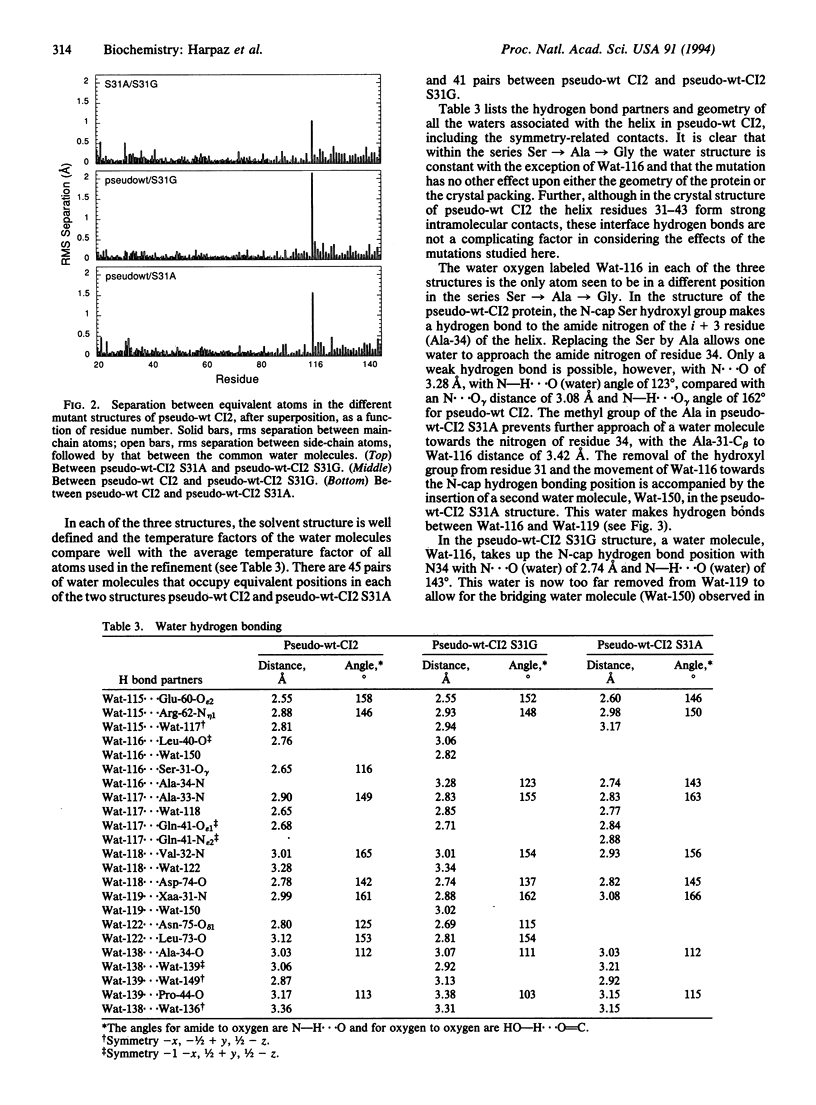
The structural basis for the stability of N termini of helices has been analyzed by thermodynamic and crystallographic studies of three suitably engineered mutants of the barley chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 with Ser, Gly, or Ala at the N-cap position (residue 31). Each mutant has a well-organized shell of hydration of the terminal NH groups of the helix. The three structures are virtually superimposable (rms separations for all atoms, including the common water molecules, are 0.15-0.17 A) and show neither changes in conformation at the site of substitution nor changes in the crystal packing. The only changes on going from Ser-31 to Ala-31 to Gly-31 are in the position of a water molecule (Wat-116). This is bound to the Ser-O gamma atom in the Ser-31 structure but is in a weak hydrogen bonding position with the NH of residue 34 (O ... N = 3.28 A) in the Ala-31 mutant, partly replacing the strong Ser-31-O gamma ... N34 hydrogen bond (O ... N = 2.65 A). The corresponding water molecule completely replaces the Ser hydroxyl hydrogen bond to N34 on mutation to Gly (2.74 A). The only other change between the three structures is an additional water molecule in the Ala-31 structure (Wat-150) that partly compensates for the weak Wat-116 ... N34 hydrogen bond. Perturbation of solvation by the side chain of Ala is consistent with earlier hypotheses on the importance of exposure of the termini of helices to the aqueous solvent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. A., Becktel W. J., Sauer U., Baase W. A., Matthews B. W. Dissection of helix capping in T4 lysozyme by structural and thermodynamic analysis of six amino acid substitutions at Thr 59. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 14;31(14):3590–3596. doi: 10.1021/bi00129a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta S., Bell J. A. Design of helix ends. Amino acid preferences, hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1993 May;41(5):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. E., Fersht A. R. Folding of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2. 1. Evidence for a two-state transition. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10428–10435. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. E., Moracci M., elMasry N., Johnson C. M., Fersht A. R. Effect of cavity-creating mutations in the hydrophobic core of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11259–11269. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsen S., Shen H. Y., Kjaer M., Madsen J. C., Poulsen F. M. Refinement of the three-dimensional solution structure of barley serine proteinase inhibitor 2 and comparison with the structures in crystals. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):621–635. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Nicholson H., Becktel W. J. Enhanced protein thermostability from site-directed mutations that decrease the entropy of unfolding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6663–6667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhalen C. A., James M. N. Crystal and molecular structure of the serine proteinase inhibitor CI-2 from barley seeds. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):261–269. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhalen C. A., Svendsen I., Jonassen I., James M. N. Crystal and molecular structure of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 from barley seeds in complex with subtilisin Novo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7242–7246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta L. G., Rose G. D. Helix signals in proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1632–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.2837824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano L., Fersht A. R. Capping and alpha-helix stability. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):296–299. doi: 10.1038/342296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano L., Neira J. L., Sancho J., Fersht A. R. Effect of alanine versus glycine in alpha-helices on protein stability. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):453–455. doi: 10.1038/356453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano L., Sancho J., Hirshberg M., Fersht A. R. Alpha-helix stability in proteins. I. Empirical correlations concerning substitution of side-chains at the N and C-caps and the replacement of alanine by glycine or serine at solvent-exposed surfaces. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):544–559. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90906-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



