Abstract
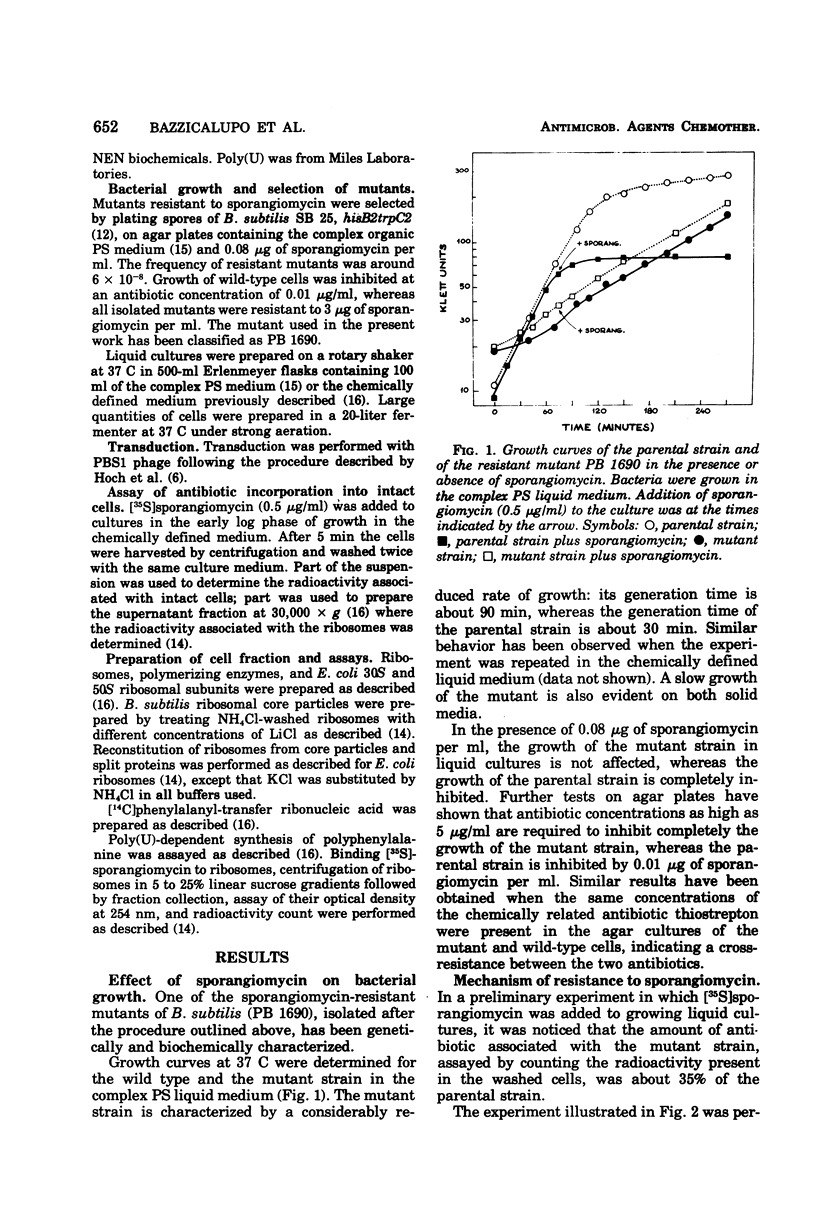
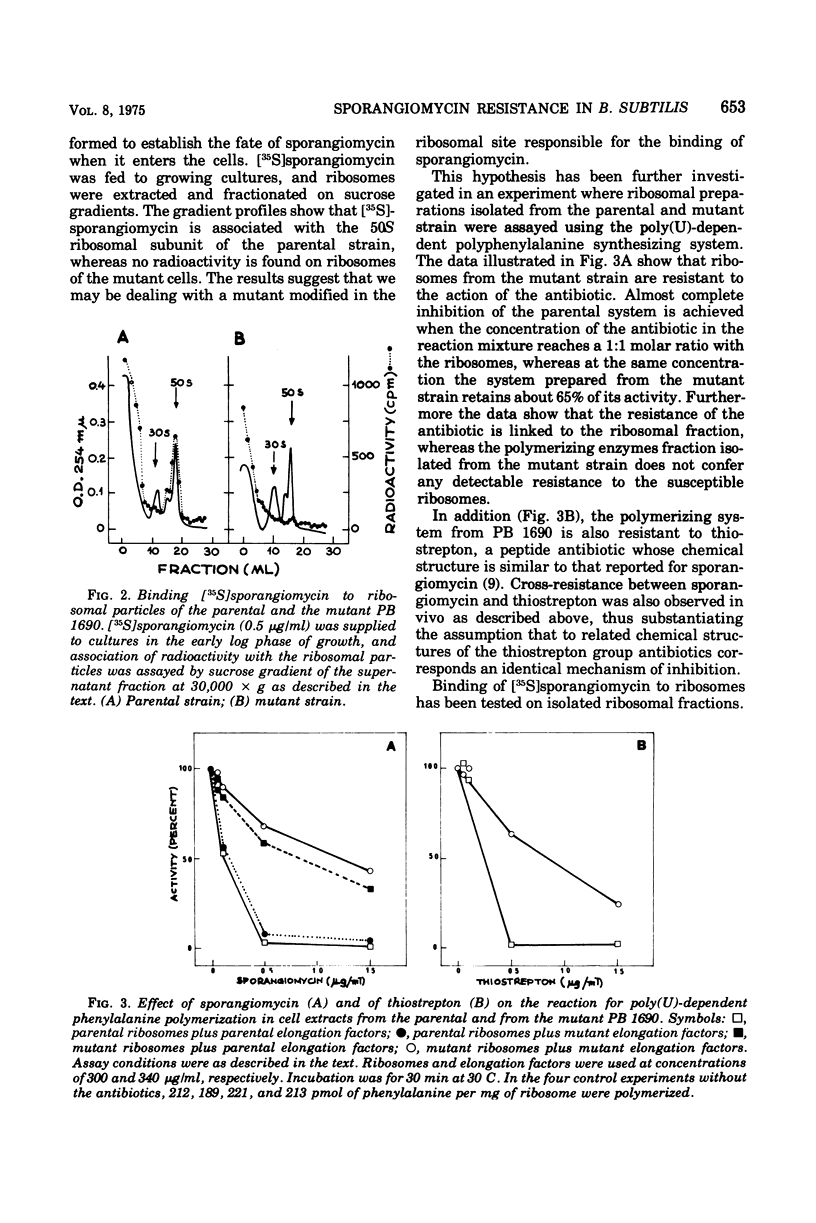
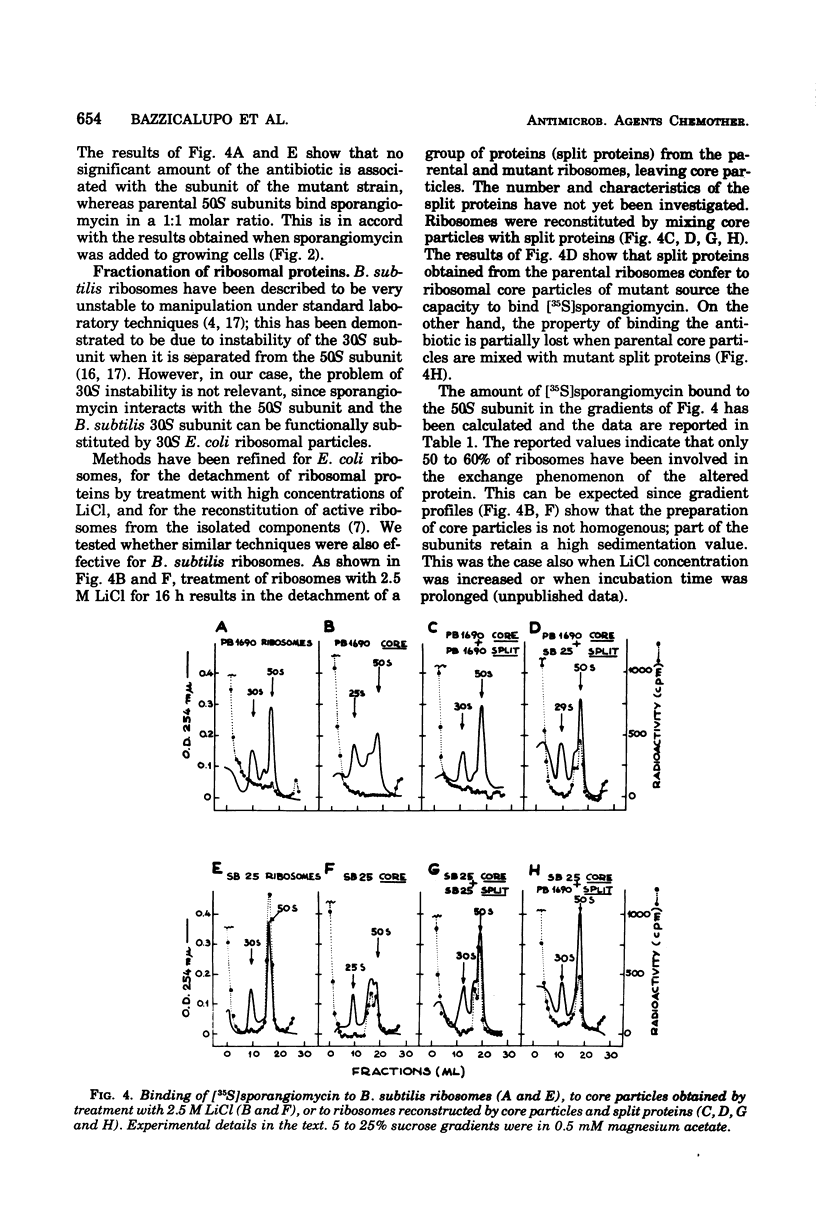
The antibiotic sporangiomycin affects the growth of Bacillus subtilis by inhibiting protein synthesis. Mutants of B. subtilis resistant to sporangiomycin have been isolated. One of these, PB 1690, has been further studied. The analysis of subcellular fractions from the mutant has shown that the biochemical effect of the mutation is an alteration of a site on the 50S ribosomal subunit responsible for the binding of the antibiotic: the mutant ribosomes do not bind sporangiomycin and are capable of carrying out phenylalanine polymerization in the presence of sporangiomycin. The resistance mutation maps on the chromosomal region where the ribosomal markers map. The mutant strain is also resistant to the action of the chemically related antibiotic thiostrepton. Treatment of B. subtilis ribosomes with LiCl results in the detachment of a group of proteins including the one responsible for sporangiomycin resistance. Active ribosomes can be reconstructed by mixing “split proteins” and “core particles” of either parental or mutant origin. The fate of the mutant protein can now be followed by assaying reconstructed ribosomes for capacity to bind sporangiomycin and for resistance to the action of the antibiotic in the reactions for phenylalanine polymerization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodley J. W., Lin L., Highland J. H. Studies on translocation. VI. Thiostrepton prevents the formation of a ribosome-G factor-guanine nucleotide complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1406–1411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90543-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Tate W. P., Caskey C. T., Weissbach H. The requirement for ribosomal proteins L7 and L12 in peptide-chain termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):89–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon Michael, Burns Kay. Modes of action of erythromycin and thiostrepton as inhibitors of protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite C., Dubnau D., Smith I. Genetic mapping of antibiotic resistance in markers Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):96–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Otaka E., Osawa S. Release of ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli ribosomes with high concentrations of lithium chloride. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Liou Y., Tanaka N. Inhibition by thiopeptin of ribosomal functions associated with T and G factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):859–863. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90790-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyairi N., Miyoshi T., Aoki H., Kosaka M., Ikushima H. Studies on thiopeptin antibiotics. I. Characteristics of thiopeptin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Mar;23(3):113–119. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Cabrer B., Parmeggiani A., Vazquez D. Inhibition by siomycin and thiostrepton of both aminoacyl-tRNA and factor G binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Vazquez D., Monro R. E. Ribosomes, G-factor and siomycin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 24;230(12):109–112. doi: 10.1038/newbio230109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTER E. W., LEDERBERG J. Linkage of genetic units of Bacillus subtilis in DNA transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jan 15;47:52–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Thiostrepton: a ribosomal inhibitor of translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 11;40(3):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90956-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirali G., Lancini G. C., Parisi B., Sala F. Interaction of sporangiomycin with the bacterial ribosome. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Oct;25(10):561–568. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala F., Bazzicalupo M., Parisi B. Protein synthesis in Bacillus subtilis: differential effect of potassium ions on in vitro peptide chain initiation and elongation. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.821-829.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Lipmann F. Comparison of amino Acid polymerization in B. Subtilis and e. Coli cell-free systems; hybridization of their ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1875–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann J. E., Coronelli C., Pagani H., Beretta G., Tamoni G. Antibiotic production by new form-genera of the Actinomycetales. I. Sporangiomycin, an antibacterial agent isolated from Planomonospora parontospora var. antibiotica var. nov. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Sep;21(9):525–531. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Tanaka K. Effect of siomycin on the acceptor site of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):728–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90477-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Demohn V. Inhibition by thiostrepton of the formation of a ribosome-bound guanine nucleotide complex. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


