Abstract
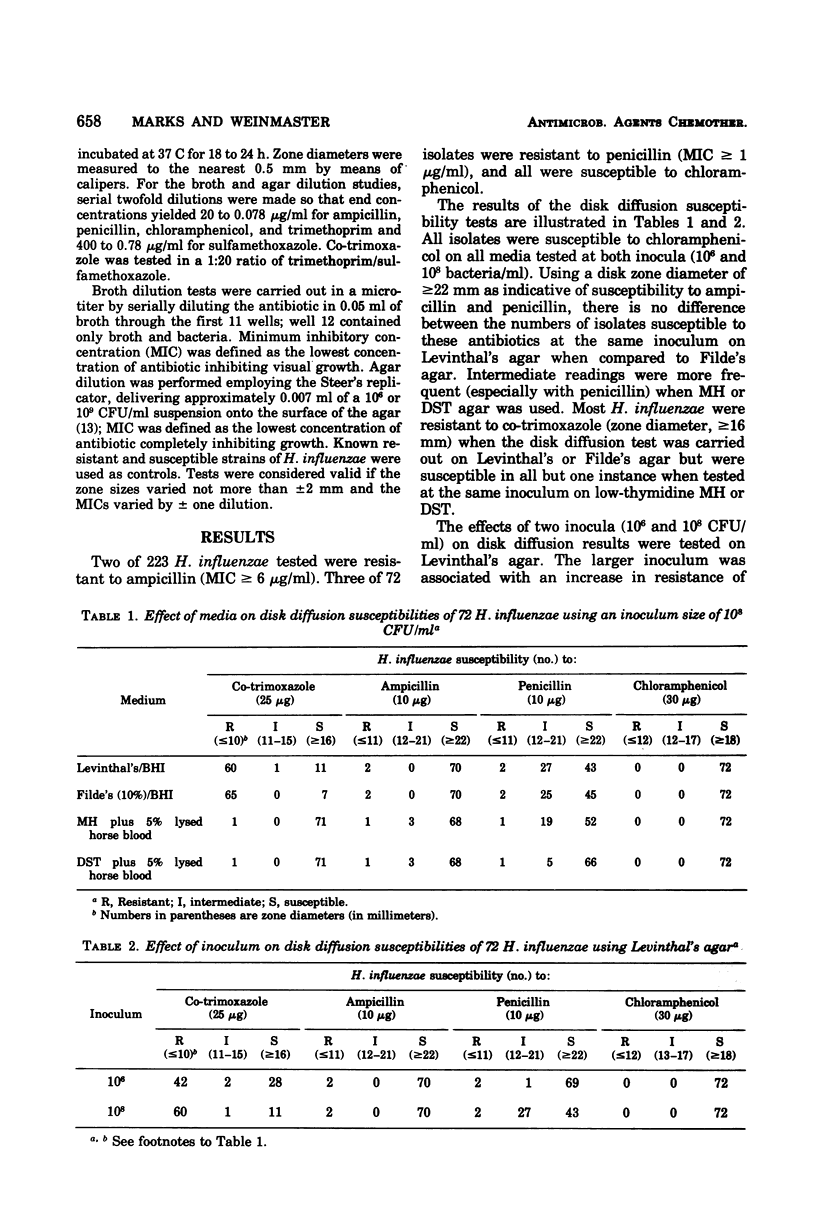
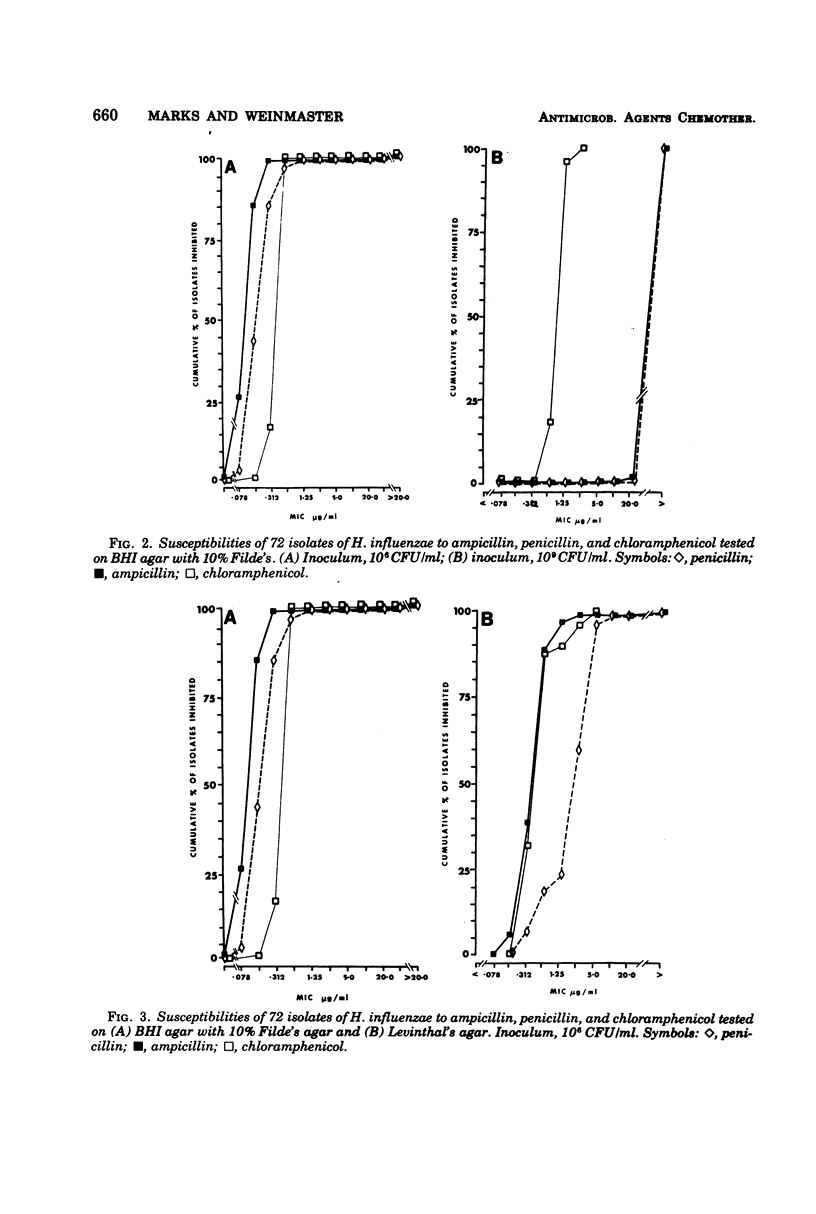
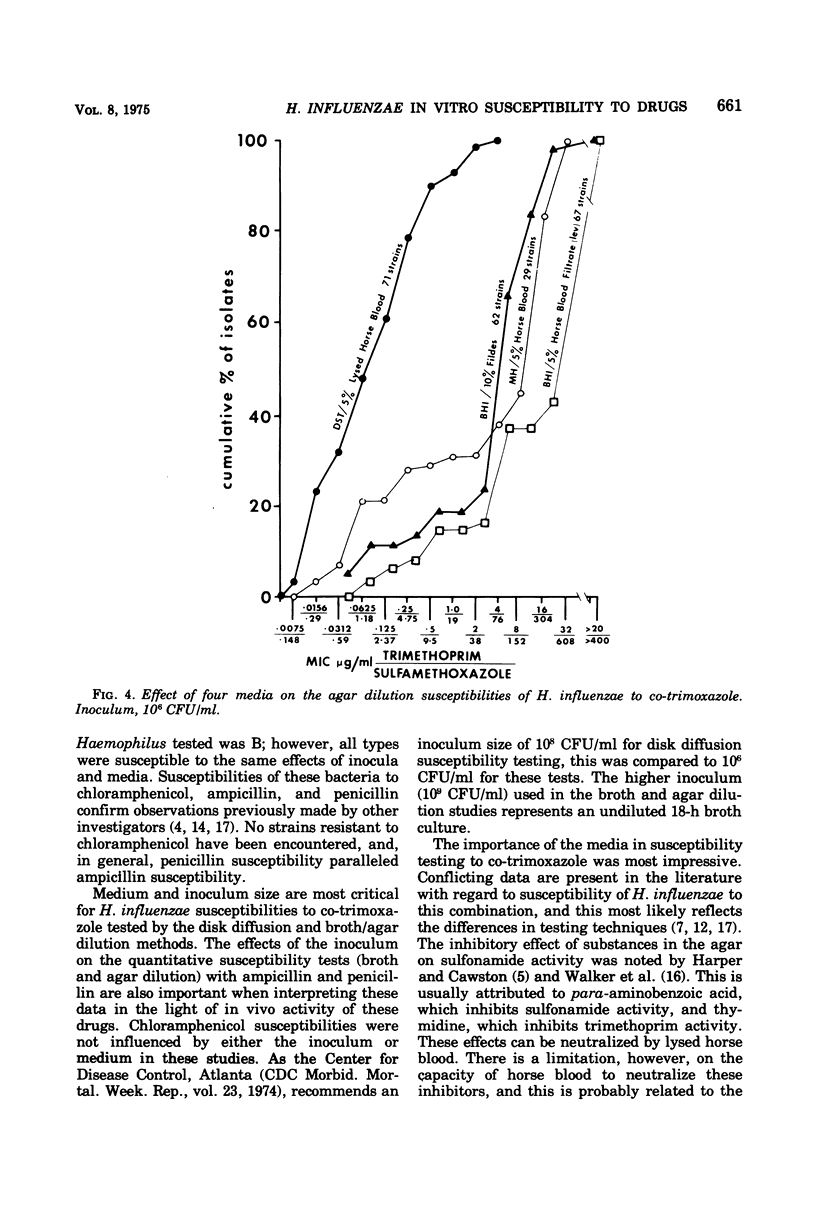
The effects of inocula and media on the activities of ampicillin, penicillin, chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole against Haemophilus influenzae were examined in vitro. Two inocula and four media were tested by the disk diffusion, broth dilution, and agar dilution methods. Chloramphenicol activity versus H. influenzae was least affected by changes in inocula and media, whereas co-trimoxazole was most susceptible to these effects. Filde's and Levinthal's agar dilution tests were most satisfactory for ampicillin. Penicillin was less active on Levinthal's than on Filde's agar. Both ampicillin and penicillin were less active when tested against the higher inoculum. Co-trimoxazole was most active (<1% H. influenzae was resistant) when tested at an inoculum of 106 colony-forming units/ml on diagnostic susceptibility test agar with 5% lysed horse blood added. The majority of H. influenzae appeared resistant to co-trimoxazole with increases in the test inocula and/or when tested on brain heart infusion with Filde's, Levinthal's or “low-thymidine” Mueller-Hinton medium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bushby S. R. Combined antibacterial action in vitro of trimethoprim and sulphonamides. The in vitro nature of synergy. Postgrad Med J. 1969 Nov;45(Suppl):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferone R., Bushby S. R., Burchall J. J., Moore W. D., Smith D. Identification of Harper-Cawston factor as thymidine phosphorylase and removal from media of substances interfering with susceptibility testing to sulfonamides and diaminopyrimidines. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jan;7(1):91–98. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. C., Thompson T. R., Stevens L. I., Carlson W. H. In vitro susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae to eight antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W., Ross S., Rodriguez W., Controni G., Saz A. K. Haemophilus influenzae type B resistant to ampicillin. A report of two cases. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirven L. A., Thornsberry C. In vitro susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):869–870. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut M. S., Attebery H. R., Finegold S. M., Sutter V. L. Detection of Haemophilus aphrophilus in the human oral flora with a selective medium. J Infect Dis. 1972 Aug;126(2):189–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLinn S. E., Nelson J. D., Haltalin K. C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Hemophilus influenzae. Pediatrics. 1970 May;45(5):827–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M. S., MacLowry J., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., McReynolds J. W., Thomas W. J., Bailey D. W., Clarke E. J., Jr, Mueller E. J., Escamilla J. Clinical, bacteriological, and immunological characterisation of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):257–259. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):620–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomeh M. O., Starr S. E., McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Nahmias A. J. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B infection. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):295–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Andrews J. Sensitivity of Haemophilus influenzae to antibiotics. Br Med J. 1974 Jan 26;1(5899):134–137. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5899.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. H. In vitro sensitivity studies of Hemophilus infuenzae--typable and non-typable strains. Pediatrics. 1967 Feb;39(2):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



