VOLUME 286 (2011) PAGES 38159–38167
PAGE 38161:
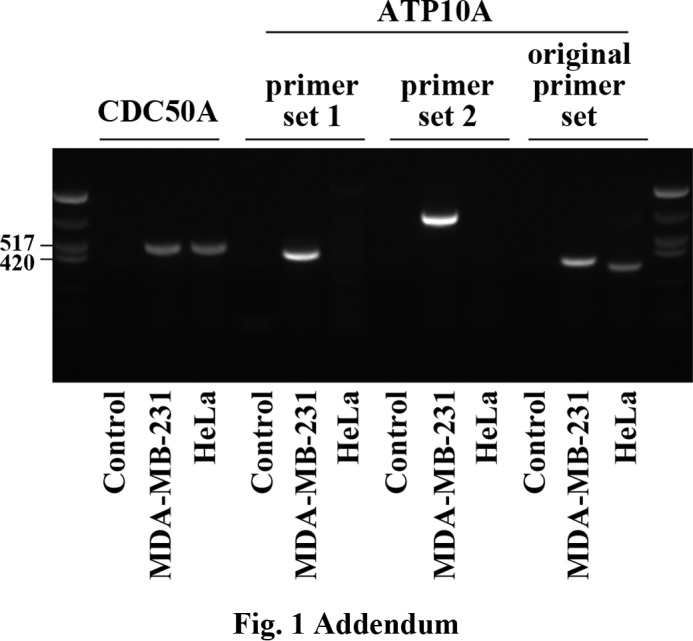
The evidence shown in Fig. 1 that ATP10A is expressed in HeLa cells is not correct. ATP10A expression was measured using RT-PCR with the sense (ccttatccccagtcacagctg) and anti-sense (ccgagtctgcctcttggtacc) primer pair. However, subsequent cloning and sequencing of the RT-PCR product showed that the original primer pair amplified glucosidase, beta, acid (GBA, XM006726211.1) by annealing to the mRNA of GBA (XM006726211.1) at positions 541 and 823 (marked with an asterisk in the revised Fig. 1) rather than ATP10A mRNA. When we examined ATP10A expression using two other primer pairs (pair 1, cacaatgttcgtgggcctcc (sense) and aaggacactgaagccacacg (anti-sense); pair 2, gtctccgaattcaatcctttgac (sense) and ccgagtctgcctcttggtacc (anti-sense)), we detected ATP10A expression in MDA-MB-231 cells but not in HeLa cells (Fig. 1 Addendum). Therefore, we conclude that the band identified as ATP10A in the original Fig. 1 was a product of GBA mRNA amplification, and ATP10A expression was not detected in HeLa cells. This correction does not affect the results or conclusions of this work.