Abstract
A sterile-filtered, liquid medium composed of one-half-strength APT broth and 4% (wt/vol) yeast extract was found to support the production of bacteriocins by Streptococcus mutans strains BHT and GS-5. Culture supernatants, adjusted to pH 7.0 and sterilized by filtration, contained bacteriocin-like activity, which could be demonstrated by spotting dilutions onto top agar lawns seeded with Streptococcus pyogenes as the sensitive indicator and by adding dilutions to log-phase indicator broth cultures. A quantitative assay was developed for BHT bacteriocin, based on its lethal effects. Bacteriocin production did not occur until after the log phase of growth had ceased and was not inducible by ultraviolet irradiation or treatment with mitomycin C. Non-bacteriocinogenic clones of strain BHT occurred spontaneously at high frequency, suggesting control by a plasmid, but this frequency was not increased by treatment with the plasmid-curing agents acridine orange and ethidium bromide.
Full text
PDF


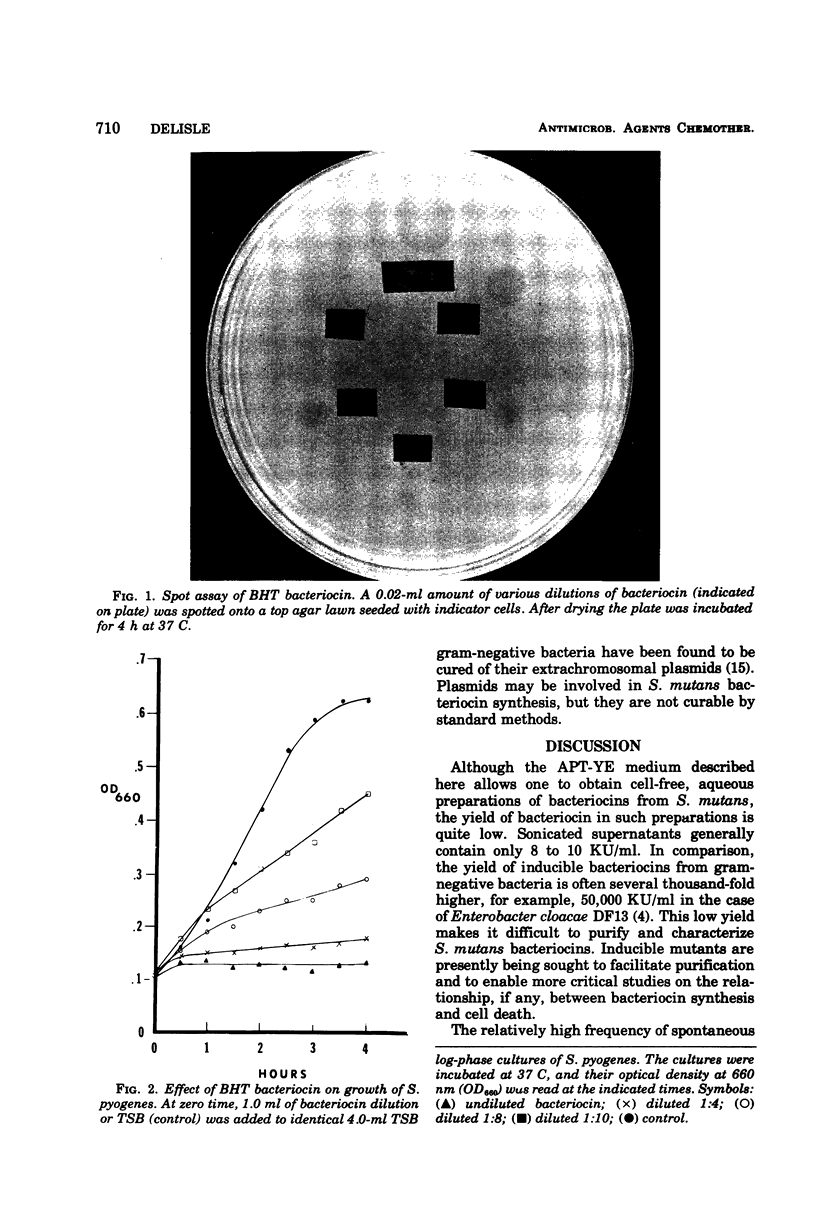


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D. Demonstration of five serological groups of streptococcal strains resembling Streptococcus mutans. Odontol Revy. 1970;21(2):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Nutritional requirements of Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1970;4(4):305–320. doi: 10.1159/000259653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman R. A., Perrella M. M., Fitzgerald R. J. Influence of incubation atmosphere on growth and amino acid requirements of Streptococcus mutans. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):86–92. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.86-92.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stoppelaar J. D., Van Houte J., Backer Dirks O. The relationship between extracellular polysaccharide-producing streptococci and smooth surface caries in 13-year-old children. Caries Res. 1969;3(2):190–199. doi: 10.1159/000259582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duany L. F., Zinner D. D., Jablon J. M. Identification of types of potentially cariogenic streptococci on human tooth surfaces by the fluorescent antibody technique. J Dent Res. 1970 Nov-Dec;49(6 Suppl):1527–1529. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490066301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZGERALD R. J., KEYES P. H. Demonstration of the etiologic role of streptococci in experimental caries in the hamster. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960 Jul;61:9–19. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1960.0138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Berman K. S., Knoettner P., Kapsimalis B. Dental caries and alveolar bone loss in gnotobiotic rats infected with capsule forming streptococci of human origin. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Ooshima T. Inhibitory spectrum of a bacteriocinlike substance (mutacin) produced by some strains of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1975 Jan-Feb;54(1):140–145. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540010801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Gibbons R. J. Bacteriocins from human and rodent streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1969 Mar;14(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(69)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Richmond S., West C., Gibbons R. J. Fingerprinting human oral streptococci by bacteriocin production and sensitivity. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B. Human streptococci and experimental caries in hamsters. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Apr;11(4):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasse B., Jordan H. V., Edwardsson S., Svensson I., Trell L. The occurrence of certain "caries-inducing" streptococci in human dental plaque material with special reference to frequency and activity of caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Aug;13(8):911–918. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. H. Effect of the medium on bacteriocin production among strains of Streptococcus mutans. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Aug;24(2):294–295. doi: 10.1128/am.24.2.294-295.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., ARAN A. P., SASLAW M. S. EXPERIMENTAL CARIES INDUCED IN ANIMALS BY STREPTOCOCCI OF HUMAN ORIGIN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:766–770. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINNER D. D., JABLON J. M., HADDOX C. H., Jr, ARAN A., SASLAW M. S. USE OF FLUORESCENT-ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE TO IDENTIFY EXPERIMENTAL HAMSTER AND RAT STRAINS OF CARIOGENIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Dent Res. 1965 May-Jun;44:471–475. doi: 10.1177/00220345650440030501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Spanjaerdt Speckman E. A., Stouthamer A. H. Mode of action of a bacteriocin produced by Enterobacter cloacae DF13. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):287–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02219150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]